Abstract
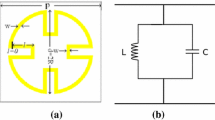
In this paper, an azimuthally periodic wedge-shaped circular aperture frequency selective surface (FSS) is discussed, which provides the dual polarized and angular stable frequency response with significantly more fractional bandwidth (FBW) up to 50° angle-of-incidence (AOI) at S-band, Ku-band and Ka-band. In addition to this, the equivalent circuit (EC) parameters of proposed bandpass FSS structure are obtained using the transmission-line approach, which are further utilized to compute the geometrical parameters of the proposed bandpass FSS structure at 3, 15 and 25 GHz. The numerical results computed by transmission-line approach are supported with the simulation results, which have been obtained using commercially available simulators such as CST Microwave Studio (finite integral technique) and Ansoft HFSS (finite element method) at each frequency of interest.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munk, B. A. (2000). Frequency selective surface: Theory and design (1st ed.). New York: Wiley.
Zhang, L., Yang, G., Wu, Q., & Hua, J. (2012). A novel active frequency selective surface with wideband tuning range for EMC purpose. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 48(11), 4534–4537.
Te-Kao, W. (1994). Four-band frequency selective surface with double-square-loop patch elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 42(12), 1659–1663.
Bharti, G., Jha, K. R., Singh, G., & Jyoti, R. (2015). Design of angular and polarization stable modified circular ring frequency selective surface for satellite communication. International Journal of Microwave and Microwave Technologies. doi: 10.1017/S1759078715000331.
Gustafsson, M., Karlsson, A., Rebelo, A. P., & Widenberg, B. (2006). Design of frequency selective windows for improved indoor outdoor communication. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54(6), 1897–1900.
Mias, C. Tsokonas, C. & Oswald, C. (2002). An investigation into the feasibility of designing frequency selective windows employing periodic structures. Technical report AY3922, The Nottingham Trent University, Burton Street, Nottingham, NG1 4BU, U.K.
Costa, F., Amabile, C., Monorchio, A., & Prati, E. (2011). Waveguide dielectric permittivity measurement technique based on resonant FSS filters. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 21(5), 273–275.
Genovesi, S., Costa, F., & Monorchio, A. (2012). Low-profile array with reduced radar cross section by using hybrid frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60(5), 2327–2335.
Raspopoulos, M., & Stavrou, S. (2011). Frequency selective buildings through frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 59(8), 2998–3005.
Izquierdo, B. S., Parker, E. A., & Batchelor, J. C. (2011). Switchable frequency selective slot arrays. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 59(7), 2728–2731.
Li, B., & Shen, Z. (2014). Bandpass frequency selective structure with wideband spurious rejection. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 145–148.
Bardi, I., Remski, R., Perry, D., & Cendes, Z. (2002). Plane wave scattering from frequency-selective surfaces by the finite-element method. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 38(2), 641–644.
Mittra, R., Chan, C. H., & Cwik, T. (1988). Techniques for analyzing frequency selective surfaces: A review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 76(12), 1593–1615.
Orta, R., Tascone, R., & Zich, R. (1985). A unified formulation for the analysis of general frequency selective surfaces. Electromagnetics, 5(4), 307–329.
Bozzi, M., & Perregrini, L. (1999). Efficient analysis of thin conductive screens perforated periodically with arbitrarily shaped apertures. IEE Electronics Letters, 35(13), 1085–1087.
Hsieh, L. H., & Chang, K. (2002). “Equivalent lumped elements G, L, C, and unloaded Q’s of closed- and open-loop ring resonators. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 50(2), 453–460.
Langley, R. J., & Parker, E. A. (1983). Double-square frequency-selective surfaces and their equivalent circuit. IEE Electronics Letters, 19(17), 675–677.
Jha, K. R., Singh, G., & Jyoti, R. (2012). A simple synthesis technique of single square loop frequency selective surface. Progress in Electromagnetic Research B, 45, 165–185.
Costa, F., Monorchio, A., & Manara, G. (2012). Efficient analysis of frequency selective surfaces by a simple equivalent-circuit model. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 54(4), 35–48.
Yao, X., Bai, M., & Miao, J. (2011). Equivalent circuit method for analyzing frequency selective surface with ring patch in oblique angles of incidence. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 10, 820–823.
Nair, R. U., & Jha, R. M. (2014). Electromagnetic design and performance analysis of airborne radomes: Trends and perspectives [Antenna Applications Corner]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, IEEE, 56(4), 276–298.
Lee, C. K., & Langley, R. J. (1985). Equivalent-circuit models for frequency selective surfaces at oblique angles of incidence. IEE Proceedings H on Microwaves Antennas and Propagation, 132(6), 395–399.
Reed, J. A. (1997). Frequency selective surfaces with multiple periodic elements. Ph.D. thesis, The University of Texas, Dallas, 1997.
Sung, G. H. H., Sowerby, K. W., & Williamson, A. G. (2005). Equivalent circuit modelling of a frequency selective plasterboard wall. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on antennas and propagation, Washington DC, USA, July 3–8 (pp. 400–403).
Hosseinipanah, M., Wu, Q., Zhang, C., Minji, F. A., & Yang, G. Y. (2008). Design of square-loop frequency selective surfaces utilize C-band radar stations. In Proc. int. conf. on microwave and millimeter wave technology, 2008, Nanjing, China, April 21–24 (pp. 66–68).
Sung, H. H. (2006). Frequency selective wallpaper for mitigating indoor wireless interference. Ph.D. thesis, Aukland University, NZ.
Parker, E. A., & Hamdy, S. M. A. (1981). Rings as elements for frequency selective surfaces. IEE Electronics Letters, 17(17), 612–614.
Huang, J., Wu, T. K., & Lee, S. W. (1994). Tri-band frequency selective surface with circular ring elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 42(2), 166–175.
Izquierdo, B. S., & Parker, E. A. (2014). Dual polarized reconfigurable frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 62(2), 764–771.
Yang, G., Zhang, T., Li, W., & Wu, Q. (2010). A novel stable miniaturized frequency selective surface. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 9, 1018–1021.
Chiu, C. N., & Wang, W. (2013). A dual-frequency miniaturized-element FSS with closely located resonances. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 12, 163–165.
Yan, M., Que, S., Wang, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, A., Xia, S., & Wang, W. (2014). A novel miniaturized frequency selective surface with stable resonance. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 639–641.
Guang-Ming, T., Jun-Gang, M., & Jin-Ming, D. (2012). A novel four-legged loaded element thick-screen frequency selective surface with a stable performance. Chinese Physics B, 21(12), 1–8.
Bharti, Garima, Jha, K. R., Singh, G., & Jyoti, R. (2015). Azimuthally periodic wedge-shaped metallic vane loaded circular ring frequency selective surface. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 7(1), 95–106.
Dubrovka, R., Vazquez, J., Parini, C., & Moore, D. (2006). Equivalent circuit method for analysis and synthesis of frequency selective surfaces. IEE Proceedings Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 153(3), 213–220.
Langley, R. J., & Parker, E. A. (1982). Equivalent circuit model for arrays of square loops. IEE Electronics Letters, 18(7), 294–296.
Chang, K. (1996). Microwave ring circuits and antennas. New York: Wiley.
Bahl, I. (2003). Lumped elements for rf and microwave circuits (1st ed.). London: Artech House.
Planar EM Technical notes, CST Microwave Studio: Floquet Port help. http://www.slideshare.net/bundahamka/cst-training-core-module-antenna-2.
Planar EM Technical notes, Getting started with HFSS: Floquet Port help. http://www.scribd.com/doc/27207025/Getting-Started-With-HFSS#scribd.
Yang, Y., Wang, X. H., & Zhou, H. (2012). Dual-band frequency selective surface with miniaturized element in low frequencies. Progress in Electromagnetic Research Letter, 33, 167–175.
Acknowledgments
The authors are sincerely thankful to the anonymous reviewer for critical comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript and also to the Indian Space Research Organization vide Project No. ISRO/RES/4/579/10-11 for the financial aid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharti, G., Jha, K.R., Singh, G. et al. Design of Azimuthally Periodic Wedge-Shaped Circular Ring Bandpass Frequency Selective Surface Using Transmission-Line Method. Wireless Pers Commun 85, 1411–1428 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2848-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2848-6