Abstract
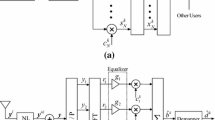
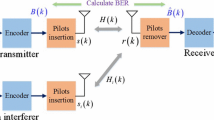
In this paper, channel estimation based on Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN) is proposed to estimate channel frequency responses in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing–interleave division multiple access (OFDM–IDMA) systems. Several channel estimation techniques including least squares (LS) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) known as conventional pilot based channel estimation algorithms and multilayered perceptron (MLP) with two different training algorithms like Levenberg–Marquardt (LM) and resilient backpropagation (RBP) are also utilized to be able to make comparisons with our proposed method with the help of bit error rate and mean square errror (MSE) graphs. It is demonstrated with computer simulations that the method in which RBFNN is used for channel estimation shows better performance than LS, multilayered perceptron–Resilient backpropagation (MLP–RBP) and multilayered perceptron–Levenberg–Marquardt (MLP–LM) without the requirement of channel statistics and noise information that are essential for MMSE algorithm to estimate the channel coefficients. Even though MMSE algorithm still shows the best performance, our proposed channel estimator has the advantage of being less complex and easy to apply which makes it a serious candidate for channel estimation in OFDM–IDMA system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cimini, L. J. (1985). Analysis and simulation of digital mobile channel using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 33(7), 665–675.
Marchetti, N., Rahman, I. M., Kumar, S., & Parasad, R. (2009). OFDM: Principles and challenges. In V. Tarokh (Ed.), New directions in wireless communications research (pp. 29–62). New york: Springer.
Guan, Y., Xu, T., Leuken, V. R., & Qian, M. (2014). Parallel channel estimator and equalizer for mobile OFDM system. Wireless Personel Communications, 33(3), 839–861.
Subotic, V., & Primak, S. (2006). BER analysis of equalized OFDM systems in Nagakami, m < 1 fading. Wireless Personal Communications, 40(3), 281–290.
Ping, L., & Liu, L. (2004). Analysis and design of IDMA systems based on SNR evolution and power allocation. In Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC’04-Fall) (pp. 1068–1072).
Mahafeno, I., Langlais, C., & Jego, C. (2006). OFDM-IDMA versus IDMA with ISI cancellation for quasi-static Rayleigh fading multipath channels. In 4th International Symposium on Turbo Codes and Related Topics (pp. 3–7).
Xiao, Y., He, X., Hu, S., & Li, S. (2012). Variable interleaver allocation for downlink OFDM–IDMA. Wireless Personal Communications, 67(2), 359–366.
Wang, P., Xiao, J., & Ping, L. (2006). Comparison of orthogonal and nonorthogonal approaches to future wireless cellular systems. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 1(3), 4–11.
Schoeneich, H., & Hoeher, P. A. (2004). Adaptive interleave division multiple access: A potential air interference for 4G bearer services and wireless LANs. In International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks (WOCN 2004) (pp. 179–182).
Coleri, S., Ergen, M., Puri, A., & Bahai, A. (2002). Channel estimation techniques based on pilot arrangement in OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 48(3), 223–229.
de Beek, J.J.V., Edfors, O.S., Sandell, M., Wilson, S.K., & Börjesson, O.P. (1995). On channel estimation in OFDM systems. In 45th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (pp. 815–819).
Hsieh, M. H., & Wei, C. H. (2005). Channel estimation for OFDM system based on comb-type pilot arrangement in frequency selective fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 44(1), 217–225.
Schoeneich, H., & Hoeher, P. A. (2006). Iterative pilot-layer aided channel estimation with emphasis on interleave division multiple access systems. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing,. doi:10.1155/ASP/2006/81729.
Xie, Y., & Georghiades, C. (2003). Two EM-type channel estimation algorithms for OFDM with transmitter diversity. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(1), 106–116.
Münster, M., & Hanzo, L. (2005). Parallel-interference cancellation-assisted decision-directed channel estimation for OFDM systems using multiple transmit antennas. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(5), 2148–2162.
Cheng, C.H., Cheng, Y.P., Huang, Y.H., & Li, W.C. (2013). Using back propagation neural network for channel estimation and compensation in OFDM systems. In 7th International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS) (pp. 340–345).
Seyman, M. N., & Taspinar, N. (2013). Channel estimation based on neural network in space time block coded MIMO–OFDM system. Digital Signal Processing, 23(1), 275–280.
Seyman, M. N., & Taspinar, N. (2012). MIMO–OFDM channel estimation using ANFIS. Elektronika ir Electrotechnica, 120(4), 75–78.
Seyman, M. N., & Taspinar, N. (2013). Radial basis function neural networks for channel estimation in MIMO–OFDM systems. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 38(8), 2173–2178.
Seyman, M. N., & Taspinar, N. (2008). Channel estimation based on adaptive neuro- fuzzy inference system in OFDM. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 91(7), 2426–2430.
Ping, L., Liu, L., Wu, K. Y., & Leung, W. K. (2006). Interleave-division multiple-access. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(4), 938–947.
Ping, L., Guo, Q., & Tong, J. (2007). The OFDM–IDMA approach to wireless communication system. IEEE Wireless Communications, 14(3), 18–24.
Hagan, M. T., Demuth, B., & Beale, M. (1996). Neural network design. Boston: PWS Publishing Company.
Karayiannis, N. B. (1999). Reformulated radial basis neural networks trained by gradient descent. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 657–671.
Musavi, M. T., Ahmed, W., Chan, K. H., Faris, K. B., & Hummels, D. M. (1992). On the training of radial basis function classifiers. Neural Networks, 5(4), 595–603.
Buhmann, G., & Martin, D. (2003). Radial basis functions: Theory and implementations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a Grant (No. FYL-2013-4799) from Erciyes University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şimşir, Ş., Taşpınar, N. Channel Estimation Using Radial Basis Function Neural Network in OFDM–IDMA System. Wireless Pers Commun 85, 1883–1893 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2877-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2877-1