Abstract
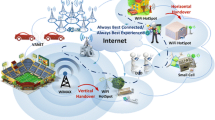
Modern smartphones and wireless-enabled devices are equipped with a number of interfaces to access multiple networks in heterogeneous wireless networks. Seamless mobility between these networks can be achieved by optimizing parameters related with vertical handover management . This paper presents a detailed review of the recent schemes used for context-aware vertical handover management in heterogeneous wireless networks. In particular, we reviewed user-centric, network centric, and hybrid schemes, and compare them in context of throughput, packet loss ratio, and other advantages such as handover delay, cost, energy, and bandwidth optimization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buddhikot, M. M., et al. (2003). Design and implementation of a WLAN/CDMA 2000 interworking architecture. IEEE Communication Magazine, 41(11), 90–100.
McNair, J., & Zhu, F. (2004). Vertical handoffs in fourth-generation. IEEE Wireless Communication, 11(3), 8–15.
Sydir, J., & Taori, R. (2009). An evolved cellular system architecture incorporating relay stations—[WiMAX update]. IEEE Communication Magazine, 47(6), 115–121.
Chandrasekhar, V., Andrews, J., & Gatherer, A. (2008). Femtocell networks: a survey. IEEE Communication Magazine, 46(9), 59–67.
Yeh, S.-P., Talwar, S., Lee, S.-C., & Kim, H. (2008). WiMAX femtocells: A perspective on network architecture, capacity, and coverage. IEEE Communication Magazine, 46(10), 58–65.
IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks—Part 21: Media independent handover. IEEE Standard (2008).
D. S. X. 16. [Online]. http://www.dell.com/us/en/home/notebooks/laptop-studio-xps-16/pd.aspx?refid=laptop-studio-xps-16\&cs=19\&s=dhs
F. L. P8020. [Online]. http://www.fmworld.net/globalpc/products/index.html
T. S. series. [Online]. www.lenovo.com
T. P. R600-ST520 W. [Online]. http://laptops.toshiba.com/laptops/portege/R600
N. Corporation. (2009). Nokia Booklet 3G brings all day mobility to the PC world: Press release. [Online]. http://www.nokia.com/press/press-releases/showpressrelease?newsid=1336683
I. Inc. Enabling small form factors and energy-efficient performance: White paper. [Online]. http://download.intel.com/technology/wimax/deliver-wimax-faster.pdf
I. Inc. (2007). Welcome to your internet future—Mobile broadband brought to you by WiMAX: White Paper. [Online]. http://download.intel.com/network/connectivity/products/wireless/318987.pdf
I. Inc. (2009). Intel WiMAX/WiFi link 5150, product brief. [Online]. http://download.intel.com/network/connectivity/products/wireless/320663/5150.pdf
I. Inc. (2008). Intel WiMAX/WiFi link 5350, product brief. [Online]. http://download.intel.com/network/connectivity/products/wireless/320663.pdf
Chan, P. M. L., Sheriff, R. E., Hu, Y. F., & Conforto, P. (2001). Mobility management incorporating fuzzy logic for heterogeneous a IP environment. IEEE Communications Magazine, 39(12), 42–51.
Stevens-Navarro, E., & Wong, V. W. S. (2006). Comparison between vertical handoff decision algorithms for heterogeneous wireless networks. In IEEE 63rd vehicular technology conference (pp. 947–951). Melbourne, Vic.
Huang, H., & Hu, W. (2011). A fast handover scheme based on GPS information for IEEE 802.16e on high-speed railway. In International conference on electronics, communications and control (ICECC) (pp. 2408–2412). Ningbo.
Leu, F.-Y., & Liang, K.-C. (2011). A location-based handoff scheme based on IEEE 802.21 in heterogeneous wireless networks. In Fifth international conference on innovative mobile and internet services in ubiquitous computing (IMIS) (pp. 571–576). Seoul.
Pahlavan, K., Krishnamurthy, P., Hatami, A., & Ylianttila, M. (2000). Handoff in hybrid mobile data networks. IEEE Personal Communications, 7(2), 34–47.
Zdarsky, F. A., Schmitt, J. B. (2004). Handover in mobile communication networks: Who is in control anyway?. In Proceedings of the 30th euromicro conference (pp. 205–212).
Perkins, C. E. (2002). Mobile IP. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(5), 66–82.
Pyun, J.-Y. (2008). Context-aware streaming video system for vertical handover over wireless overlay network. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 54(1), 71–79.
Indulska, J., & Balasubramaniam, S. (2004). Context-aware vertical handovers between WLAN and 3G networks. In IEEE 59th vehicular technology conference (pp. 3019–302).
Prehofer, C., Nafisi, N., & Wei, Q. (2005). A framework for context-aware handover decisions. In 14th IEEE proceedings on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 2794–2798).
Fiterau, M., Ormond, O., & Muntean, G. (2009). Performance of handover for multiple users in heterogeneous wireless networks. In IEEE 34th conference on local computer networks (pp. 257–260). Zurich.
Pawar, P., van Beijnum, B.-J., Hermens, H., Wac, K., & Konstantas, D. (2009). Context-aware computing support for network-assisted seamless vertical handover in remote patient monitoring. In International conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops (pp. 351–358). Bradford.
Pervaiz, H., & Bigham, J. (2009). Game theoretical formulation of network selection in competing wireless networks: An analytic hierarchy process model. In Third international conference on next generation mobile applications, services and technologies (pp. 292–297). Cardiff, Wales.
Hong, C. P., Kang, T. H., & Kim, S. D. (2006). A profile based vertical handoff scheme for ubiquitous computing environment. In 9th Asia-Pacific network operations and management symposium (pp. 102–111). Busan.
Gavrilescu, M., et al. (2011). Context-aware reconfigurable interoperability for vertical handover in wireless communications. In 2nd International conference on wireless communication, vehicular technology, information theory and aerospace and electronic systems technology (pp. 1–5). Chennai.
Andrei, V., Popovici, E. C., Fratu, O., & Halunga, S. (2009) The architecture of a software module, supporting vertical handover in heterogenous networks. In Proceedings of international conference ETAI.
Popovici, E. C., Andrei, V., Fratu, O., & Halunga, S. V. (2009). Real-time monitoring design of a wireless network device for vertical handover on multimod terminals. In 2nd International symposium on applied sciences in biomedical and communication technologies (pp. 1–6). Bratislava.
Andrei, V., Popovici, E. C., Fratu, O., & Halunga, S. V. (2010). Solution for implementing IEEE 802.21 media independent information service. In 8th International conference on communications (COMM) (pp. 519–522). Bucharest.
Andrei, V., Poovici, E. C., Fratu, O., & Halunga, S. V. (2010). Development of an IEEE 802.21 media independent information service. In IEEE international conference on automation quality and testing robotics Cluj-Napoca, Romania.
Nam, M., Choi, N., Seok, Y., & Choi, Y. (2004). WISE: Energy-efficient interface selection on vertical handoff between 3G networks and WLANs. In IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 692–698).
Seo, S. H., & Song, J. S. (2009). An energy-efficient interface selection for multi-mode terminals by utilizing out-of-band paging channels. Telecommunication Systems Springer, 42(1–2), 151–161.
Salawu, N., & Onwuka, E. N. (2009). Energy optimisation mechanism for for mobile terminals using vertical handoff between WLAN and CDMA2000 networks. Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies, 15, 51–58.
Shih, E., Bahl, P., & Sinclair, M. J. (2002). Wake on wireless: An event driven energy saving strategy for battery operated devices. In Proceedings of the 8th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking MobiCom ‘02 (pp. 160–171). Atlanta, Georgia.
Perrucci, G. P., Fitzek, F. H. P., Sasso, G., Kellerer, W., & Widmer, J. (2009). On the impact of 2G and 3G network usage for mobile phones’ battery life. In European wireless conference (pp. 255–259). Aalborg.
Fitzek, F., Pedersen, M., Perrucci, G. P., & Larsen, T. (2008). Energy and link measurements for mobile phones using IEEE802.11b/g, In 6th International symposium on modeling and optimization in mobile, ad hoc, and wireless networks and workshops (pp. 36–36). Berlin.
Harris, A. F., Stojanovic, M., & Zorzi, M. (2009). Idle-time energy savings through wake-up modes in underwater acoustic networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 7(4), 770–777.
A. Communications. (2003) Power consumption and energy efficiency. [Online]. http://www.atheros.com/pt/papers.html
Xenakis, D., Passas, N., Di Gregorio, L., & Verikoukis, C. (2011). A context-aware vertical handover framework towards energy-efficiency. In IEEE 73rd vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5). Yokohama.
Inoue, M., Hasegawa, M., & Morikawa, H. (2055). Decentralized ubiquitous networking server for context-aware seamless services. In IEEE 61st vehicular technology conference (pp. 1550–2252).
Wu, G., Mizuno, M., & Havinga, P. J. M. (2002). MIRAI architecture for heterogeneous network. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(2), 126–134.
Hasegawa, M., et al. (2003). Cross-device handover using the service mobility proxy. In WPMC’03 (Vol. 2, pp. 1033–1037).
Liao, Q., Penna, F., Stanczak, S., Ren, Z., & Fertl, P. (2013). Context-aware handover optimization for relay-aided vehicular terminals. In IEEE 14th workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (pp. 555–559). Darmstadt.
Einhaus, M., Klein, O., & Lott, M. (2005). Interference averaging and avoidance in the downlink of an OFDMA system. In 16th International symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 905–910). Berlin.
GPP. (2012). TS 36.331, radio resource control (RRC); protocol specification. [Online]. http://www.3gpp.org
Flanagan, J. A., & Novosad, T. (2002). WCDMA network cost function minimization for soft handover optimization with variable user load. In IEEE 56th vehicular technology conference, (pp. 2224–2228).
Chen, S., Hwang, C., Beckmann, M., & Krelle, W. (1992). Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: Methods and applications. Secaucus, NJ: Springer.
Mateo, J. R. S. C. (2012). TOPSIS. In Multi criteria analysis in the renewable energy industry. (pp. 43–48). London: Springer.
TalebiFard, P., & Leung, V. C. M. (2011). A dynamic context-aware access network selection for handover in heterogeneous network environments. In IEEE conference on computer communications workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS) (pp. 385–390). Shanghai.
Erl, T. (2007). Principles of service design. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Padovitz, A., Loke, S. W., & Zaslavsky, A. (2004). Towards a theory of context spaces. In Proceedings of the second IEEE annual conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops (pp. 38–42).
Padovitz, A., Loke, S., Zaslavsky, A., Burg, B., & Bartolini, C. (2005). An Approach to Data Fusion for Context Awareness. In 5th International and interdisciplinary conference (pp. 353–367). Paris.
Schilit, B. (1995). A context-aware system architecture for mobile distributed. In Unpublished PhD, Columbia University.
Kim, Y., & Lee, K. (2006). A quality measurement method of context information in ubiquitous environments. In International conference on hybrid information technology (pp. 576–581). Cheju Island.
Manzoor, A., Truong, H., & Dustdar, S. (2008). On the evaluation of quality of context. In EuroSSC ‘08 proceedings of the 3rd european conference on smart sensing and context (pp. 140–153).
Buchholz, T., Kupper, A., & Schiffers, M. (2003). Quality of context: What it is and why we need it. In Proceedings of the workshop of the HP OpenView University Association.
Al Mosawi, T., Shuaib, H., & Aghvami, A. H. (2009). A fast handover scheme based on smart triggers and SIP. In IEEE 70th vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5). Anchorage, AK.
Chien, S. F., Liu, H., Low, A. L. Y., Maciocco, C., & Ho, Y. L. (2008). Smart predictive trigger for effective handover in wireless networks. In IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 2175–2181). Beijing.
Melia, T., Boscolo, L., Vidal, A., & de la Oliva, A. (2007). IEEE 802.21 reliable event service support for network controlled handover scenarios. In IEEE global telecommunications conference (pp. 5000–5005). Washington, DC.
Yoo, S.-J., Cypher, D., & Golmie, N. (2007). LMS predictive link triggering for seamless handovers in heterogeneous wireless networks. In IEEE military communications conference (pp. 1–7). Orlando, FL, USA.
Pontes, A., dos Passos Silva, D., Jailton, J., Rodrigues, O., & Dias, K. L. (2008). Handover management in integrated WLAN and mobile WiMAX networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 15(5), 86–95.
Ferrus, R., Sallent, O., & Agustí, R. (2010). Interworking in heterogeneous wireless networks: Comprehensive framework and future trends. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(2), 22–31.
Lampropoulos, G., Skianis, C., & Neves, P. (2010). Optimized fusion of heterogeneous wireless networks based on media-independent handover operations. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(4), 78–87.
Huang, C.-M., Lee, C.-H., & Tseng, P.-H. (2009). Multihomed SIP-based network mobility using IEEE 802.21 media independent handover. In IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 1–5). Dresden.
Rodriguez, J., Tsagaropoulos, M., Politis, I., Kotsopoulos, S., & Dagiuklas, T. (2009). A middleware architecture supporting seamless and secure multimedia services across an intertechnology radio access network. IEEE Wireless Communications, 16(5), 24–31.
Xiong, M., Cao, J., & Zhang, J. (2011). Context-aware mechanism for IEEE 802.21 media independent handover. In Proceedings of 20th international conference on computer communications and networks (pp. 1–6). Maui, HI.
Yoo, S.-J., Cypher, D., & Golmie, N. (2009). Predictive link trigger mechanism for seamless handovers in heterogeneous wireless networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 9(5), 685–703.
Balasubramaniam, S., Pfeifer, T., & Indulska, J. (2006). Active node supporting context-aware vertical handover in pervasive computing environment with redundant positioning. In 1st International symposium on wireless pervasive computing (pp. 1–6).
Perkins, C. E. (1998). Mobile networking through Mobile IP. IEEE Internet Computing, 2(1), 58–69.
Floroiu, J. W., Ruppelt, R., Sisalem, D., & Voglimacci, J. (2003). Seamless handover in terrestrial radio access networks: A case study. IEEE Communications Magazine, 41(11), 110–116.
Stemm, M., & Katz, R. H. (1998). Vertical handoffs in wireless overlay networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 3(4), 335–350.
Helal, S., Lee, C., Zhang, Y., & Richard, G. G. (2000). An architecture for wireless LAN/WAN integration. In IEEE wireless communications and networking confernce (pp. 1035–1041). Chicago, IL.
Pfeifer, T. (2004). Redundancy vs. Imperfect positioning for context-dependent. In Proceeding of 1st international workshop on advanced context modeling, reasoning, and management (pp. 1079–1085). Nottingham.
Balasubramaniam, S., & Indulska, J. (2004). Vertical handover supporting pervasive computing in future wireless networks. Computer Communications, 27(8), 708–719.
Ahmed, T., Kyamakya, K., & Ludwig, M. (2006). Architecture of a context-aware vertical handover decision model and its performance analysis for GPRS–WiFi handover. In 11th IEEE symposium on computers and communications (pp. 795–801).
Kuhn, G., Eisl, J., & Becker, H. (2007). Co-operative handover in 3G system architecture evolution. In 32nd IEEE conference on local computer networks (pp. 643–650). Dublin.
Zekri, M., Jouaber, B., & Zeghlache, D. (2010). Context aware vertical handover decision making in heterogeneous wireless networks. in IEEE 35th conference on local computer networks (pp. 764–768). Denver, CO.
Taylor, M. S., Waung, W., & Banan, M. (1997). Internetwork mobility: The CDPD approach. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Chan, P. M. L., Hu, Y. F., & Sheriff, R. E. (2002). Implementation of fuzzy multiple objective decision making algorithm in a heterogeneous mobile environment. In IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 332–336).
Kassar, M., Kervella, B., & Pujolle, G. (2007). Architecture of an intelligent inter-system handover management scheme. In Future generation communication and networking (FGCN) (pp. 332–337). Jeju Island.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science Technology (MEST) and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Creative Human Resource Training Project for Regional Innovation (2014). This work was supported by the IT R&D program of MSIP/IITP. [10041145, Self-Organized Software platform (SoSp) for Welfare Devices]. This study was supported by the BK21 Plus project (SW Human Resource Development Program for Supporting Smart Life) funded by the Ministry of Education, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Korea (21A20131600005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Han, K. A Survey of Context Aware Vertical Handover Management Schemes in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 85, 2273–2293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2904-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2904-2