Abstract
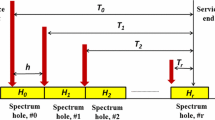
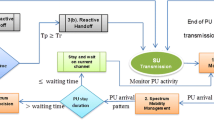
The static frequency allocation in wireless communication became a major concern for efficient spectrum utilization. Also due to spatio-temporal variation, some of the frequency channels are not utilized efficiently. The prologue of open spectrum and dynamic spectrum access (DSA) methodology provides the secondary (unlicensed) users, supported by cognitive radios (CRs) to opportunistically utilize the unused spectrum bands. When a primary user returns to the engaged spectrum band, secondary users should release it immediately through proper handing off to another spectrum band available to the network satisfying the quality of service (QoS) of both the network. Hence the focus of the new spectrum management policies is DSA technology based on CR. Spectrum mobility is considered to be the subsequent big challenge in CR technology. Spectrum mobility is associated with spectrum handoff which is directly associated with link maintenance and QoS. In this paper, we scrupulously investigate and analyze the probability of spectrum handoff under diverse realistic primary and secondary user traffic models. We have established a state of the art standard generalized form of probability of spectrum handoff without switching delay considering secondary user call duration and residual time of availability of spectrum holes as measurement metrics for diverse distribution functions designed for tele-traffic analysis. We thoroughly investigate different distribution models for the residual time under both zero switching delay and finite switching delay conditions. The switching delay (t r ) between spectrum holes comprises of spectrum sensing time and transition delay for realizing all the related parameters. A comprehensive simulation results are presented to validate the generalized theory established in this paper.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Communications Commission (FCC). (2003). Notice for proposed rulemaking (NPRM 03 322): Facilitating opportunities for flexible, efficient, and reliable spectrum use employing spectrum agile radio technologies. ET Docket No. 03 108, December 2003.
Shared Spectrum Company. http://www.sharedspectrum.com/.
Mitola, J., III, & Maguire, G. Q., Jr. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Communication Magazines, 6(4), 13–18.
Akyildiz, F., Lee, W.-Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2006). Next generation/dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks—A survey. Computer Networks, 50(13), 2127–2159.
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23, 201–220.
Jondral, F. K. (2005). Software-defined radio-basics and evolution to cognitive radio. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 3, 275–283.
Tandra, R., & Sahai, A. (2008). SNR walls for signal detection. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2(1), 4–17.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lo, B. F., & Balakrishnan, R. (2011). Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: A survey. Physical Communications, 4(1), 40–62.
Christian, I., Moh, Sn., Chung, I., & Lee, J. (2012). Spectrum mobility in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(6), 114–121.
Del Re, E., Fantacci, R., & Giambene, G. (1995). Handover and dynamic channel allocation techniques in mobile cellular networks. IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology, 44(2), 229–237.
Del Re, E., Fantacci, R., & Giambene, G. (1995). Efficient dynamic channel allocation techniques with handover queuing for mobile satellite networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas Communications, 13(2), 397–405.
Hong, D., & Rappaport, S. S. (1986). Traffic model and performance analysis for cellular mobile radio telephone systems with prioritized and non-prioritized handoff procedures. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 35(3), 77–92.
Lin, Y. B., Mohan, S., & Noerpel, A. (1994). Queuing priority channel assignment strategies for handoff and initial access for a PCS network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 43(3), 704–712.
Yum, T. S., & Yeung, K. L. (1995). Blocking and handoff performance analysis of directed retry in cellular mobile systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 44(3), 645–650.
Bolotin, V. A. (1994). Modeling call holding time distributions for CCS network design and performance analysis. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 12(3), 433–438.
Liu, H, Wang, Z., Li, S., & Yi, M. (2008). Study on the performance of spectrum mobility in cognitive wireless network. In Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (pp. 1010–1014).
Barcelò, F., & Jordan, J. (1999). Channel holding time distribution in public telephony system. In Proceedings of 16th international tele-traffic congress (pp. 107–116). Elsevier Science.
Barcelò, F., & Jordan, J. (2000). Channel holding time distribution in public telephony system (PAMR and PCS). IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 49(5), 1615–1625.
Pattavina, A., & Parini, A. (2005). Modelling voice call interarrival and holding time distributions in mobile networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Teletraffic Congress (ITC’05) (pp. 729–738).
Zhang, Y. (2009). Spectrum handoff in cognitive radio networks: Opportunistic and negotiated situations. In Proceedings of IEEE ICC 2009 (vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 14–18). doi:10.1109/ICC.2009.5199479.
Shoja-Sefat, A., Beheshti, M. T. H., & Moradi, H. (2007). A new statistical model for call holding time simulation in the telephony networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (vol. 1359, no. 1362, pp. 24–27).
Lin, Y. B., & Chlamtac, I. (1999). Effects of Erlang call holding times on PCS call completion. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 48(3), 815–823.
Sánchez, J. I., Barceló, F., & Jordán, J. (1998). Inter arrival time distribution for channel arrivals in cellular telephony. In Proceedings of 5th international workshop on mobile multimedia communication, MoMuc’98 (pp. 245–254). Berlin.
Jedrzycky, C., & Leung, V. C. M. (1996). Probability distribution of channel holding time in cellular telephony system. In Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference (pp. 247–251). Atlanta, GA.
Asmussen, S., Jensen, J. L., & Rojas-Nandayapa, L. (2014). On the Laplace transform of the lognormal distribution. Journal of Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability, 2014. ISSN: 1387-5841, Springer, US. doi:10.1007/s11009-014-9430-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Derivation of Probability of ‘r’ Times Spectrum Handoff for Lognormal Distribution
Appendix: Derivation of Probability of ‘r’ Times Spectrum Handoff for Lognormal Distribution
The probability of zero spectrum handoff for lognormal distribution of residual time is calculated as:
Now
indicates the Laplace transform of lognormal distribution and which is approximated as [25],
where W(.) is the Lambert W function which is defined as the solution of the equation W(x) · exp(W(x)) = x, where exp(W(x)) is an exponential function and W(x) is any complex number.
Hence
Similarly,
Also we can express,
Therefore from Eq. (3), the generalized expression for probability of r handoff (r = 0, 1, 2,….) P r is obtained as P r = (1 − 1 + L) (L)r−1 (1 − L) = L r(1 − L) (Eq. 25).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arif, W., Hoque, S., Sen, D. et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of Spectrum Handoff Under Different Distribution Models for Cognitive Radio Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 85, 2519–2548 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2918-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2918-9