Abstract
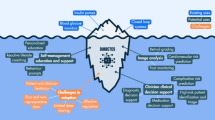
The KNOWLEDGE-CARE vision is to enable new e-health services that are personalized, preventive, predictive, pre-emptive, participatory, pervasive and precise. This vision aims to make a move from reactive medicine to predictive medicine, developing dynamic and responsive models through knowledge extraction and using such models for personalized clinical healthcare. The proposed healthcare ecosystem can learn over time and can adapt to the variation seen in the actual real-world population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, P., Ash, J., Bates, D., Overhage, J., & Sands, D. (2006). Personal health records: Definitions, benefits, and strategies for overcoming barriers to adoption. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 13(2), 121–126.
Detmer, D., Bloomrosen, M., Raymond, B., & Tang, P. (2008). Integrated personal health records: Transformative tools for consumer-centric care. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 8(1), 1–14.
Anual Report on “The Adoption of Health Information Technology and Related Efforts to Facilitate the Electronic Use and Exchange of Health Information”, The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), October 2014.
Aragüés, A., Escayola, J., Martínez, I., del Valle, P., Muñoz, P., Trigo, J. D., et al. (2011). Trends and challenges of the emerging technologies toward interoperability and standardization in e-health communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(11), 182–188.
Bousquet, J., et al. (2011). Systems medicine and integrated care to combat chronic noncommunicable diseases. Genome Medicine, 3, 43.
Jimenez-Fernandez, S., de Toledo, P., & del Pozo, F. (2013). Usability and interoperability in wireless sensor networks for patient telemonitoring in chronic disease management. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 60(12), 3331–3339.
De Sanctis, M., Cianca, E., Di Domenico, S., Provenziani, D., Bianchi, G., & Ruggieri, M. (2015). WIBECAM: Device free human activity recognition through WiFi beacon-enabled camera. In 2nd Workshop on Physical Analytics (WPA’15) in the 13th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys 2015), Florence, Italy, May 22, 2015.
Bisio, I., Lavagetto, F., Marchese, M., & Sciarrone, A. (2015). A smartphone-centric platform for remote health monitoring of heart failure. International Journal of Communication Systems, 28(11), 25.
De Sanctis, M., Stallo, C., Parracino, S., Ruggieri, M., & Prasad, R. (2012). Interoperability solutions between smartphones and wireless sensor networks. In 2012 IEEE First AESS European Conference on Satellite Telecommunications (ESTEL Conference 2012), Roma (Italy), October 2–5, 2012.
Militano, L., Condoluci, M., Araniti, G., Iera, A. (2013). Multicast service delivery solutions in LTE-Advanced systems. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 5954–5958, June 9–13, 2013.
Condoluci, M., Dohler, M., Araniti, G., Molinaro, A., & Zheng, K. (2015). Toward 5G densenets: Architectural advances for effective machine-type communications over femtocells. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(1), 134–141.
Bisio, I., & Marchese, M. (2007). Satellite earth station (SeS) selection method for satellite-based sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 11(12), 970–972.
Bisio, I., & Marchese, M. (2008). Performance evaluation of bandwidth allocation methods in a geostationary satellite channel in the presence of internet traffic. Elsevier Computer Networks, 52(1), 275–291.
Amadeo, M., Araniti, G., Iera, A., Molinaro, A. (2011). A satellite-LTE network with delay-tolerant capabilities: Design and performance evaluation. In Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), 2011 IEEE, September 5–8, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Sanctis, M. Personalized Ubiquitous Health and Wellness Care: The KNOWLEDGE-CARE Vision. Wireless Pers Commun 88, 53–62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3241-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3241-9