Abstract
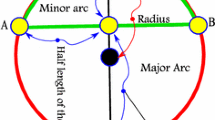
The current restricted area based range free localization schemes use various geometric shapes such as triangle, rectangle, and circle to determine the residence area of the sensor node. Then this residence area is used to localize the sensor node. However, the existing work requires higher density of anchor deployment to gain the acceptable accuracy of position estimation. In this paper, we overcome the density dependent accuracy of localization by proposing a new localization scheme called geometric anchor beacon (GAB). The proposed scheme is based on analytical geometry of an arc. In the proposed scheme, the \(Cramers \ rule\) is used, where the intersecting point of two perpendicular bisectors of the chords is taken as the estimated position of the sensor node. Simulation results show that, GAB shows less estimation error than any other range-free localization schemes such as CAB, Centroid, Convex, and APIT.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., et al. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 38(4), 393–422.
Girod, L., & Estrin, D. (2001). Robust range estimation using acoustic and multi-modal sensing. In IEEE IROS01 (pp. 1312–1320), Hawaii, USA.
Niculescu, D., & Nath, B. (2003). Ad hoc positioning system (APS) using AOA. In: IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1734–1743), San Francisco, USA.
Priyantha, N., Chakraborthy, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). The cricket location- support system. In ACM Mobicom (pp. 32-43).
Bulusu, N., Heidemann, J., & Estrin, D. (2000). Gps-less low cost outdoor localization for very small devices. IEEE Personal Communication, 7(5), 28–34.
He, T., Huang, C., Blum, B., et al. (2005). Range-free localization schemes for large scale sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing System, 4(4), 877–906.
Niculescu, D., & Nath, B. (2001). Ad hoc positioning system (APS). In IEEE GLOBE-COM 01 (pp. 2926–2931). San Antonio, TX.
Lance, D., Kristofer, S. P., & El Ghaoui, L. (2001). Convex position estimation in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1655–1663), Alaska, USA.
Vivekanandan, V., & Vincent, W. W. (2007). Concentric anchor beacon localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 56(5), 2733–2744.
Jacobs, H. R. (1987). Geometry. San Francisco, CA: Freeman.
Singh, M., & Khilar, P. M. (2016). Mobile beacon based range free localization method for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks. doi:10.1007/s11276-016-1227-x.
Singh, M., & Khilar, P. M. (2015). An analytical geometric range free localization scheme based on mobile beacon points in wireless sensor network. Wireless Networks. doi:10.1007/s11276-015-1116-8.
Lee, S., Kim, E., Kim, C., & Kim, K. (2009). Localization with a mobile beacon based on geometric constraints in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(12), 5801–5805.
Xiao, B., Chen, H., & Zhou, S. (2008). Distributed localization using a moving beacon in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 19(5), 587–600.
Guerrero, E., Xiong, H. G., Gao, Q., Cova, G., Ricardo, R., & Estvez, J. (2009). ADAL: A distributed range-free localization algorithm based on a mobile beacon for wireless sensor networks. In International Conference on ultra modern telecommunications and workshops, 2009. ICUMT’09 (pp. 1–7). IEEE
Chen, Y. S., Ting, Y. J., Ke, C. H., Chilamkruti, N., & Park, J. H. (2013). Efficient localization scheme with ring overlapping by utilizing mobile anchors in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS), 12(2), 20.
Liu, C., Scott, T., Wu, K., & Hoffman, D. (2007). Range-free sensor localization with ring overlapping based on comparison of received signal strength indicator. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 2(5/6), 399–413.
Ssu, K. F., Ou, C. H., & Jiau, H. C. (2005). Localization with mobile anchor points in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 54(3), 1187–1197.
Sichitiu, M., Ramadurai, V., & Peddabachagari, P. (2003). Simple algorithm for out- door localization of wireless sensor networks with inaccurate range mea- surements. Las Vegas, NV: ICWN.
Liu, C., Wu, K., & He, T. (2004). Sensor localization with ring overlapping based on comparison of received signal strength indicator. In IEEE MASS (pp. 516–518), Fort Lauderdale, FL.
Liu, C., & Wu, K. (2005). Performance evaluation of range-free localization methods for wireless sensor networks. In IEEE IPCCC (pp. 59–66), Phoenix, AZ.
Sheu, J.-P., Chen, P.-C., & Hsu, C.-S. (2008). A distributed localization scheme for wireless sensor networks with improved grid-scan and vector-based refinement. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(9), 1110–1123.
Sheu, J.-P., Li, J.-M., & Hsu, C.-S. (2006). A distributed location estimating algorithm for wireless sensor networks (pp. 218–225). IEEE Computer Society.
Yan, Z., Chang, Y., Shen, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2009). A grid-scan localization algorithm for wireless sensor network (pp. 142–146). IEEE Computer Society.
Kim, T., Son, M., Choi, W., Song, M., Choo, H. (2010). Low-cost two-hop anchor node-based distributed range-free localization in wireless sensor networks. In ICCSA (pp. 129–141).
Xing, G., Lu, C., Zhang, Y., Huang, Q., & Pless, R. (2005). Minimum power configuration in wireless sensor networks. New York: ACM MobiHoc.
Crossbow Technology [Online]. http://www.xbow.com/.
Ni, S.-Y., Tseng, Y.-C., Chen, Y.-S., & Sheu, J.-P. (1999). The broadcast storm problem in a mobile ad hoc network. In ACM international conference on mobile computing networking (MOBICOM) (pp. 151–162), Seattle, WA.
Williams, B., & Camp, T. (2002). Comparison of broadcasting techniques for mobile ad hoc networks. In ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking computing (MOBIHOC) (pp. 194–205), Lausanne, Switzerland.
Osipov, E., & Tschudin, C. (2004). Improving the path optimality of reactive ad hoc routing protocols through de-coherent rreq waves. Technical report, University of Basel, Technical Report CS-2004-002
Bo, C., Ren, D., Tang, S., Li, X.-Y., Mao, X., Huang, Q., et al. (2002). Locating sensors in the forest: A case study in greenorbs. In INFOCOM.
Zhong, Z., & He, T. (2011). Rsd: A metric for achieving range-free localization beyond connectivity. EEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(11), 1943–1951.
He, T., Huang, C., Lum, B., Stankovic, J., & Adelzaher, T. (2003). Range-free localization schemes for large scale sensor networks. San Diego, CA: ACM MobiCom.
Mistry, H. P., & Mistry, N. H. (2015). RSSI based localization scheme in wireless sensor networks: A survey. In 2015 fifth international conference on advanced computing and communication technologies (pp. 647–652), IEEE.
Tomic, S., Beko, M., Dinis, R., Dimic, G., & Tuba, M. (2015). Distributed RSS-based localization in wireless sensor networks with node selection mechanism. In Doctoral conference on computing, electrical and industrial systems (pp. 204–214). Springer.
Luo, Q., Peng, Y., Li, J., & Peng, X. (2016). RSSI-based localization through uncertain data mapping for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(9), 3155–3162.
Santana, J. A., Macías, E., Suárez, Á., Marrero, D., & Mena, V. (2016). Adaptive estimation of WiFi RSSI and its impact over advanced wireless services. Mobile Networks and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11036-016-0729-1.
Woodward, E. (1978). Geometry-plane, solid and analytic problem solver, research and education association (p. 359). ISBN 9780878915101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Khilar, P.M. A Range Free Geometric Technique for Localization of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Based on Controlled Communication Range. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 1359–1385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3686-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3686-x