Abstract
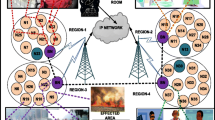
A wireless sensor network (WSN) is a resource-constrained network with limited battery, communication range, processing power, bandwidth, etc. and with requirements changing according to the environment and application. The increased number of WSN applications requires efficient utilization of resources in a changing environment to improve the quality of service of the communication. The medium access control (MAC) layer plays a pivotal role in efficient resource utilization for improving channel capacity, delay, energy consumption, and scalability. The contribution of this paper is the improvement of resource utilization by enhancing the MAC in terms of energy efficiency and scalability across different environments including static and mobile scenarios. This is achieved by designing a cluster-based hybrid MAC mechanism, Green Hybrid MAC, which combines the features of both contention- and schedule-based MAC. It uses schedule-based MAC for inter-cluster communication and a mix of schedule- and contention-based MAC for intra-cluster communication according to the level of collisions in the network. The proposed hybrid MAC mechanism uses a three-hop conflict free scheduling algorithm, Green Conflict Free, for finding schedules and uses hybrid synchronization for managing synchronization among the nodes. The proposed hybrid MAC protocol shows significant improvements in energy efficiency, throughput, scalability, and delay in different static, mobile, and security scenarios compared with state-of-art hybrid MAC protocols.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi, G., Conti, M., Di Francesco, M., & Passarella, A. (2009). Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Elsevier Ad hoc Network, 7(3), 537–568.
Yick, J., Mukherjee, B., & Ghosal, D. (2008). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 52(12), 2292–2330.
Bachir, A., Dohler, M., Watteyne, T., & Leung, K. K. (2010). MAC essentials for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 12(2), 222–248. (Second Quarter).
Amundson, I., & Koutsoukos, X. D. (2009). A Survey on localization for mobile wireless sensor networks. In 2nd International conference on mobile entity localization and tracking in GPS-less environments (MELT’09) (pp. 235–254). Orlando, FL: Springer.
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., Ohmori, S., & Prasad, R. (2011). Hybrid mechanisms: Towards an efficient wireless sensor network medium access control. In 14th international symposium on wireless personal multimedia communications (WPMC’11), Brest, France (pp. 1–5).
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., Ohmori, S., & Prasad, R. (2012). GCF: Green conflict free TDMA scheduling algorithm for wireless sensor network. In IEEE international conference on communication-3rd workshop on energy efficiency in wireless networks & wireless networks for energy efficiency (ICC-E2Nets’12), Ottawa, Canada (pp. 5795–5799).
Ammeer Ahmed Abbasi. (2007). Mohamed Younis. A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor network, elsevier computer communication, 30(14–15), 2826–2841.
Ganeriwal, S., Kumar, R., & Srivastava, M. B. (2003). Timing-sync protocol for sensor networks. In ACM SenSys, New York, NY, USA (pp. 138–149).
Weilian, S., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2005). Time-diffusion synchronization protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 13(2), 384–397.
Rhee, I., Warrier, A., Aia, M., Min, J., & Sichitiu, M. L. (2008). ZMAC: A hybrid MAC for wireless sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 16(3), 511–524.
Brownfield, M. I., Mehrjoo, K., Fayez, A. S., & Davis, N. J. (2006). Wireless sensor network energy-adaptive MAC protocol. In IEEE CCNC, Las Vegas, NV (pp. 778–782).
Ahn, G.-S., Miluzzo, E., Campbell, A. T., Hong, S. G., & Cuomo, F. (2006). Funneling-MAC: A localized, sink-oriented MAC for boosting fidelity in sensor networks. In ACM SenSys. Boulder, Colorado (pp. 293–306), November 1–3, 2006.
Cho, H.-W., Cho, M.-H., Chung, J.-M., & Jeong, W.-C. (2007). A centralized hybrid MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In ISSNIP, Melbourne (pp. 455–460). December 3–6, 2007.
Salajegheh, M., Soroush, H., & Kalis, A. (2007). HyMAC: Hybrid TDMA/FDMA medium access control protocol for wireless sensor networks. In 18th IEEE PIMRC, Athens (pp. 1–5). September 3–7, 2007.
Ma, G., & Qiu, D. (2008). An efficient MAC protocol based on hybrid super-frame for wireless sensor networks. In WiCOM, Dalian (pp. 1–4). October 12–14, 2008.
Yahya, B., & Ben-Othman, J. (2008). An energy efficient hybrid medium access control scheme for wireless sensor networks with quality of service guarantees. In IEEE GLOBECOM, New Orleans, LA (pp. 1–5). November 30–December 4, 2008.
Ben-Othman, J., Mokdad, L., & Yahya, B. (2001). An energy efficient priority-based QoS MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In IEEE ICC, Kyoto (pp. 1–6). June 5–9, 2011.
Sitanayah, L., Sreenan, C. J., & Brown, K. N. (2010). ER-MAC: A Hybrid MAC protocol for emergency response wireless sensor networks. In SENSORCOMM, Venice/Mestre (pp. 244–249). July 18–25, 2010.
Maróti, M., Kusy, B., Simon, G., & Lédeczi, Á. (2004). The flooding time synchronization protocol. In ACM SenSys ‘04, New York, NY (pp. 39–49).
Walker, T. O., Monterey Tummala, M., & McEachen, J. (2008). Distributed medium access control with flow-based priority for cooperative multi-hop wireless sensor networks. In HICSS, Waikoloa, HI (pp. 493–497). January 7–10, 2008.
Bernardo, L., Oliveira, R., Pereira, M., Macedo, M., & Pinto, P. (2007). A wireless sensor MAC protocol for bursty data traffic. In PIMRC, Athens (pp. 1–5). September 3–7, 2007.
Salmani, V., & Chou, P. H. (2012). Bin-MAC: A hybrid MAC for ultra-compact wireless sensor nodes. In 8th IEEE international conference on distributed computing in sensor systems, Hangzhou (pp. 158–165). May 16–18, 2012.
Zhuo, S., Song, Y.-Q., Wang, Z., & Wang, Z. (2012). Queue-MAC: A queue-length aware hybrid CSMA/TDMA MAC protocol for providing dynamic adaptation to traffic and duty-cycle variation. In Wireless Sensor Networks, WFCS, Lemgo/Detmold (pp. 105–114), May 21–24, 2012.
Arifuzzaman, M., Matsumoto, M., & Sato, T. (2013). An intelligent hybrid MAC with traffic-differentiation-based QoS for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(6), 2391–2399.
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., Ohmori, S., & Prasad, R. (2013). H-GCF: A hybrid green conflict free scheduling algorithm for mobile wireless sensor networks. In 14th international symposium on wireless personal multimedia communications (WPMC’ 13), Atlanta City, NJ (pp. 1–5).
Qian, Y., Zhou, J., Qian, L., & Chen, K. (2006). Highly scalable multihop clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In ICCCAS’ 06, Guilin, Guangzi (pp. 1527–1531).
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., & Prasad, R. (2014). A hybrid algorithm for efficient wireless sensor network time synchronization. In IEEE Wireless VITAE, Aalborg (pp. 1–5). May 11–14, 2014.
Bettstetter, C., Resta, G., & Santi, P. (2003). The node distribution of the random waypoint mobility model for wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE Transaction on Mobile Computing, 2(3), 257–269.
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., Ohmori, S., & Prasad, R. (2012). Behavioral modelling of WSN MAC layer security attacks: A sequential UML approach. River Publisher’s Journal of Cyber Security and Mobility, 1(1), 65–82.
Perkins, C. E., & Royer E. M. (1999). Ad-hoc on-demand distance vector routing. In IEEE WMCSA, New Orleans, LA (pp. 99–100).
Eisler, M., Labiaga, R., & Stern, H. (2001). Chapter 17: Network performance analysis. In Managing NFS and NIS, O’Reilly (pp. 168–216).
Pawar, P. M., Nielsen, R. H., Prasad, N. R., Ohmori, S., & Prasad, R. (2012). Activity modelling and comparative evaluation of WSN-MAC security attacks. Journal of Cyber Security and Mobility, River Publisher’s, 1(3), 205–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawar, P.M., Nielsen, R.H., Prasad, N.R. et al. GHMAC: Green and Hybrid Medium Access Control for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 1839–1868 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3714-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3714-x