Abstract
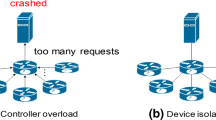
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is a new form for networking that has the potential to have a major impact on Internet technology. Key aspects of SDN include the separation of data plane and the control plane. SDN architecture facilitates the management of complex networks and represents a new solution for future network applications Internet technology. As the size of networks increases, the scalability of the centralized controller becomes increasingly important. This work proposed a load-balancing mechanism for use in a multiple-controller SDN environment by implement a hierarchical control plane with both a meta-control plane and a local control plane. The meta-control plane analyzes the resources and utilization of the local control plane to optimize processing performance. This mechanism supports the load balancing of the local control plane to optimize data plane performance and eliminate the bottleneck of the centralized control in a network. This work analyzes the proposed load-balancing mechanism in a multiple-controller SDN environment. The results indicate that the meta controller based manager mechanism can monitors and effectively deal with the loading of the overloaded local controller. Based on the results thus obtained, the proposed local control plane scheduling balances the loadings of the multiple controllers and increases the network throughput by 12.7 and 9.2 % over those achieved using a centralized controller and multiple controllers without a scheduling mechanism.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., Gong, X., Wang, W., & Que, X. (2012). VNMC for network virtualization in Openflow network. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on cloud computing and intelligent systems (pp. 797–801).
Salvadori, E., Corin, R. D., Broglio, A., & Gerola, M. (2011). Generalizing virtual network topologies in OpenFlow-based networks. In Proceedings of the global telecommunications conference (pp. 1–6).
Corin, R. D., Gerola, M., Riggio, R., Pellegrini, F. D., & Salvadori, E. (2012). VeRTIGO: Network virtualization and beyond. In Proceedings of European workshop on software defined networking, (pp. 24–29).
Shah, S. A., Faiz, J., Farooq, M., Shafi, A., & Mehdi, S. A. (2013). An architectural evaluation of SDN controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications, (pp. 3504–3508).
Gorbunov, S., Ganjali, Y., Casado, M., & Sherwood, R. (2012). On controller performance in software-defined networks. In Proceedings of the USENIX conference on hot topics in management of internet, (pp. 10–15).
Othman, M. M. O., & Okamura, K. (2013). Enhancing control model to ease off centralized control of flow-based SDNs. In Proceedings of the IEEE annual computer software and applications conference, (pp. 467–470).
Phemius, K., & Bouet, M. (2013). OpenFlow: Why latency does matter. In Proceedings of the IFIP/IEEE international symposium on integrated network management (IM), (pp. 680–683).
Azodolmolky, S., Wieder, P., & Yahyapour, R. (2013). Performance evaluation of a scalable software-defined networking deployment. In Proceedings of second European workshop on software defined networks (pp. 68–74).
Guan, X., Choi, B. Y., & Song, S. (2013). Reliability and scalability issues in software defined network frameworks. In Proceedings of second GENI research and educational experiment workshop, (pp. 102–103).
Min, S., Kim, S., Lee, J., Kim, B., Hong, W., & Kong, J. (2012). Implementation of an OpenFlow network virtualization for multi-controller environment. In Proceedings of international conference on advanced communication technology, (pp. 589–592).
Lin, P., Bi, J., & Hu, H. (2012). ASIC: An architecture for scalable intra-domain control in OpenFlow. In Proceedings of the international conference on future internet technologies, (pp. 21–26).
Huang, W. Y., Hu, J. W., Lin, S. C., & Liu, T. L. (2012). Design and implementation of an automatic network topology discovery system for the future internet across different domains. In Proceedings of 26th international conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops, (pp. 903–908).
Shojafar, M., Cordeschi, N., & Baccarelli, E. (2016). Energy-efficient adaptive resource management for real-time vehicular cloud services. PrePrints: IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing.
Zhou, Y., Ruan, L., Xiao, L., & Liu, R. (2014). A method for load balancing based on software defined network. Advanced Science and Technology Letters, 45, 43–48.
Bradai, A., Benslimane, A., & Singh, K. (2015). Dynamic anchor points selection for mobility management in software defined networks. Journal of Network & Computer Applications, 57, 1–11.
He, J., Huang, Y., & Chang, D. (2015). Simulation-based heuristic method for container supply chain network optimization. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 29(3), 339–354.
Wang, W., Hu, Y., Que, X., & Gong, X. (2012). Autonomicity design in OpenFlow based software defined networking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom workshops, (pp. 818–823).
Fernandez, M. P. (2013). Comparing OpenFlow controller paradigms scalability: Reactive and proactive. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on advanced information networking and applications (pp. 1009–1016).
Oh, H., Lee, J., & Kim, C. (2011). A flow-based hybrid mechanism to improve performance in NOX and wireless OpenFlow switch networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–4).
Yeganeh, S. H., & Ganjali, Y. (2012). Kandoo: A framework for efficient and scalable offloading of control applications. In Proceedings of the first workshop on hot topics in software defined networks (pp. 19–24).
Koponen, T., Casado, M., Gude, N., Stribling, J., Poutievski, L., Zhu, M., Ramanathan, R., Iwata, Y., Inoue, H., Hama, T., & Shenker, S. (2010). Onix: A distributed control platform for large-scale production networks. In Proceedings of the USENIX conference on operating systems design and implementation (pp. 1–6).
Yao, G., Bi, J., & Guo, L. (2013). On the cascading failures of multi-controllers in software defined networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on network protocols (pp. 1–2).
Acknowledgments
Authors thank for financial supports of the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan under contract MOST 103-2221-E-011-069-MY2 and the Institute of Information Industry, Taiwan under project—SDN Test Cases Development and Implementation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, YW., Chen, JL., Tsai, YH. et al. Load-Balancing Multiple Controllers Mechanism for Software-Defined Networking. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 3549–3574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3790-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3790-y