Abstract
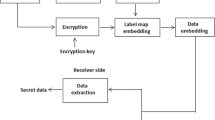
Recently, more importance is given to reversible data hiding (RDH) schemes because it restores original cover image without loss after the secret data is extracted and it is useful in authentication and integrity checking. In this paper, a novel RDH scheme for digital images is proposed that has high capacity with low distortion. The cover image is divided into blocks and all the pixels in the block are converted into odd value or even value by computing the optimal value of the block. The optimal value is mean, median, max histogram or min–max average which is very nearer to the pixels in the block. Secret data is directly embedded into blocks using odd even property. In the receiving end, after extracting secret data cover image can be recovered to its original form by computing the same optimal value. The proposed scheme is tested with several monochrome images and color images. The experimental results reveal that the proposed scheme has high hiding capacity with low distortion.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yongjian, H., Lee, H.-K., & Li, J. (2009). DE-based reversible data hiding with improved overflow location map. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 19, 250–260.
Wu, H.-C., Lee, C.-C., Tsai, C.-S., Chu, Y.-P., & Chen, H.-R. (2009). A high capacity reversible data hiding scheme with edge prediction and difference expansion. Journal of Systems and Software, 82, 1966–1973.
Lee, C.-F., Chen, H.-L., & Tso, H.-K. (2010). Embedding capacity raising in reversible data hiding based on prediction of difference expansion. Journal of Systems and Software, 83, 1864–1872.
Bo, O., Li, X., Zhao, Y., & Ni, R. (2013). Reversible data hiding based on PDE predictor. Journal of Systems and Software, 86, 2700–2709.
Leung, H. Y., Cheng, L. M., Liu, F., & Fu, Q. K. (2013). Adaptive reversible data hiding based on block median preservation and modification of prediction errors. Journal of Systems and Software, 86, 2204–2219.
Bo, O., Li, X., Zhao, Y., & Ni, R. (2014). Reversible data hiding using invariant pixel-value-ordering and prediction-error expansion. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 29, 760–772.
Luo, L., Chen, Z., Chen, M., Zeng, X., & Xiong, Z. (2010). Reversible image watermarking using interpolation technique. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 5, 187–193.
Hong, W., & Chen, T.-S. (2011). Reversible data embedding for high quality images using interpolation and reference pixel distribution mechanism. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 22, 131–140.
Tai, W.-L., Yeh, C.-M., & Chang, C.-C. (2009). Reversible data hiding based on histogram modification of pixel differences. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 19, 906–910.
Kim, K.-S., Lee, M.-J., Lee, H.-Y., & Lee, H.-K. (2009). Reversible data hiding exploiting spatial correlation between sub-sampled images. Pattern Recognition, 42, 3083–3096.
Yang, C.-H., & Tsai, M.-H. (2010). Improving histogram-based reversible data hiding by interleaving predictions. IET Image Processing, 4, 223–234.
Hong, W., & Chen, T.-S. (2010). A local variance-controlled reversible data hiding method using prediction and histogram-shifting. Journal of Systems and Software, 83, 2653–2663.
Zhao, Z., Luo, H., Zhe-Ming, L., & Pan, J.-S. (2011). Reversible data hiding based on multilevel histogram modification and sequential recovery. International Journal of Electronics Communication and Computer Technology, 65, 814–826.
Coatrieux, G., Pan, W., Cuppens-Boulahia, N., Cuppens, F., & Roux, C. (2013). Reversible watermarking based on invariant image classification and dynamic histogram shifting. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 8, 111–120.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Gui, X., & Yang, B. (2015). Efficient reversible data hiding based on multiple histograms modification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10, 2016–2027.
Bouslimi, D., Coatrieux, G., Cozic, M., & Roux, C. (2012). A joint encryption/watermarking system for verifying the reliability of medical images. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 16, 891–899.
Zhang, X. (2012). Separable reversible data hiding in encrypted images. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7, 826–832.
Ma, K., Zhang, W., Zhao, X., Nenghai, Yu., & Li, F. (2013). Reversible data hiding in encrypted images by reserving room before encryption. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 8, 553–562.
Zhang, W., Ma, K., & Yu, N. (2014). Reversibility improved data hiding in encrypted images. Signal Processing, 94, 118–127.
Qian, Z., Zhang, X., & Wang, S. (2014). Reversible data hiding in encrypted JPEG bitstream. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 16, 1486–1491.
Zhou, J., Sun, W., Dong, L., Liu, X., Au, O. C., & Tang, Y. Y. (2016). Secure reversible image data hiding over encrypted domain via key modulation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 26, 441–452.
Liu, T.-Y., & Tsai, W.-H. (2010). Generic lossless visible watermarking: A new approach. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 19, 1224–1235.
Lin, P.-Y., Chen, Y.-H., Chang, C.-C., & Lee, J.-S. (2013). Contrast-adaptive removable visible watermarking (CARVW) mechanism. Image and Vision Computing, 31, 311–321.
Yang, H., & Yin, J. (2015). A secure removable visible watermarking for BTC compressed images. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 74, 1725–1739.
Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Yu, J., & Qian, Z. (2015). Reversible visible watermark embedded in encrypted domain. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference signal and information processing (pp. 826–830).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brabin, D.R.D., Perinbam, J.R.P. & Meganathan, D. A Block Based Reversible Data Hiding Scheme for Digital Images Using Optimal Value Computation. Wireless Pers Commun 94, 2583–2596 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3817-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3817-4