Abstract
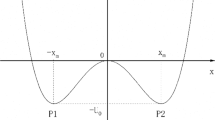
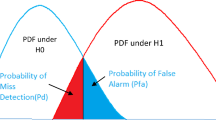
As a core technology of cognitive radio, the spectrum sensing method requires accurate perform and fast sensing in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) environment. In this paper, an energy-based spectrum sensing method based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO) and tri-stable stochastic resonance (TSR) is proposed. In this method, TSR was adopted to achieve greater SNR output than bi-stable stochastic resonance (BSR). To overcome the shortage that TSR can only set fixed parameters by experience, QPSO was adopted to adjust parameters of TSR adaptively when the noise power was fixed. Simulation results of SNR and spectrum show that the convergence, the output SNR in convergence status of QPSO–TSR performs better than QPSO–BSR under low input SNR, while QPSO–TSR has a slight delay due to its optimization searching process. The simulation result of receiver operating characteristic curves show that the proposed scheme has an excellent convergence performance and can improve the detection probability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(2), 201–220. doi:10.1109/Jsac.2004.839380.
Urkowitz, H. (1967). Energy detection of unknown deterministic signals. Proceedings of the IEEE, 55(4), 523–531.
Sutton, P. D., Nolan, K. E., & Doyle, L. E. (2008). Cyclostationary signatures in practical cognitive radio applications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 26(1), 13–24. doi:10.1109/Jsac.2008.080103.
Zeng, Y., & Liang, Y. C. (2009). Spectrum-sensing algorithms for cognitive radio based on statistical covariances. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(4), 1804–1815.
Font-Segura, J., & Wang, X. D. (2010). GLRT-based spectrum sensing for cognitive radio with prior information. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(7), 2137–2146. doi:10.1109/Tcomm.2010.07.090556.
Emara, M., Ali, H. S., Khamis, S. E. A., & Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2016). Spectrum sensing optimization and performance enhancement of cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(2), 925–941. doi:10.1007/s11277-015-2962-5.
Bera, D., Chakrabarti, I., & Pathak, S. S. (2016). Modelling of cooperative spectrum sensing over rayleigh fading without CSI in cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(3), 1281–1297. doi:10.1007/s11277-015-2988-8.
He, D., Lin, Y., He, C., & Jiang, L. (2010). A novel spectrum-sensing technique in cognitive radio based on stochastic resonance. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(4), 1680–1688. doi:10.1109/tvt.2010.2042311.
Benzi, R., Sutera, A., & Vulpiani, A. (1981). The mechanism of stochastic resonance. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 14(11), L453–L457.
Chapeau, F. (1997). Input–output gains for signal in noise in stochastic resonance. Physics Letters A, 232(1–2), 41–48.
He, D. (2013). Chaotic stochastic resonance energy detection fusion used in cooperative spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(2), 620–627. doi:10.1109/tvt.2012.2224680.
Li, Q., & Li, Z. (2014). A novel sequential spectrum sensing method in cognitive radio using suprathreshold stochastic resonance. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(4), 1717–1725. doi:10.1109/tvt.2013.2287616.
Lai, Z. H., & Leng, Y. G. (2015). Dynamic response and stochastic resonance of a tri-stable system. Acta Physica Sinica, 64(20), 77–88. doi:10.7498/aps.64.200503.
Leng, Y. G., & Lai, Z. H. (2014). Generalized parameter-adjusted stochastic resonance of Duffng oscillator based on Kramers rate. Acta Physica Sinica, 63(2), 34–42.
Li, Q. (2007). Research of adaptive stochastic resonance based on approximate entropy. Acta Physica Sinica, 56(12), 6803–6808. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.12.005.
Couceiro, M., & Ghamisi, P. (2016). Particle swarm optimization. Springer International Publishing.
Omkar, S. N., Khandelwal, R., Ananth, T. V. S., Naik, G. N., & Gopalakrishnan, S. (2009). Quantum behaved Particle Swarm Optimization (QPSO) for multi-objective design optimization of composite structures. Expert Systems with Applications An International Journal, 36(8), 11312–11322.
Li, Y. B., Zhang, B. L., Liu, Z. X., & Zhang, Z. Y. (2014). Adaptive stochastic resonance method based on quantum particle swarm optimization. Acta Physica Sinica, 63(16), 36–43. doi:10.7498/aps.63.160504.
Mcnamara, B., & Wiesenfeld, K. (1989). Theory of stochastic resonance. Physical Review A, 39(9), 4854–4869.
Kolman, D. (2000). Numerical mathematics. Berlin: Springer.
Wang, J., Ren, X., Zhang, S., Zhang, D., Li, H., & Li, S. (2014). Adaptive bistable stochastic resonance aided spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(7), 4014–4024. doi:10.1109/twc.2014.2317779.
Acknowledgements
Our work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61261002, 61461052, 11564044), the Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2015Y020), the Spectrum Sensing and borderlands Security Key Laboratory of Universities in Yunnan (Grant No. C6165903), and the Key Program of Natural Science of Yunnan Province (Grant Nos. 2013FA006, 2015FA015). The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Huang, M. & Yang, JJ. A Novel Spectrum Sensing Method Based on Tri-Stable Stochastic Resonance and Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 2635–2647 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-3945-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-3945-5