Abstract
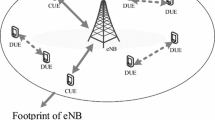
Device-to-device (D2D) communication in cellular networks is considered as an emerging technology in future mobile communication systems (e.g. LTE release 12 and beyond). However, most conventional D2D studies have emphasized one-to-one communications, in which only two D2D users directly communicate with each other. This is because these studies were focused on reducing interference between D2D users and base stations or cellular users via power allocation, interference cancellation, and so on. In this paper, however, we focus on multi-link D2D communication in cellular networks, in which more than two D2D users can exchange their information symbols simultaneously, such as a mesh network. Multi-link D2D communication requires a suitable transmission scheme for its efficiency and reliability; thus, we employ hybrid space-time block coding and spatial multiplexing (hybrid STBC–SM). This not only improves reliability, but also increases network data rates. Compared with other transmission schemes (e.g. STBC and SM), the proposed multi-link D2D communication method using hybrid STBC–SM provides improved performance in terms of bit error rate, frame error rate, symbol rates, and effective throughput.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astely, D., Dahlman, E., Fodor, G., Parkvall, S., & Sachs, J. (2013). LTE release 12 and beyond [accepted from open call]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(7), 154–160.
Doppler, K., Rinne, M., Wijting, C., Ribeiro, C. B., & Hugl, K. (2009). Device-to-device communication as an underlay to LTE-advanced networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(12), 42–49.
Doppler, K., Yu, C. H., Riberio, C. B., & Janis, P. (2010). Mode selection for device-to-device communication underlaying an LTE-advanced network. In Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), 2010 (pp. 1–6).
Min, H., Seo, W., Lee, J., Park, S., & Hong, D. (2011). Reliability improvement using receive mode selection in the device-to-device uplink period underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(2), 413–418.
Yu, C. H., Doppler, K., Ribeiro, C. B., & Tirkkonen, O. (2011). Resource sharing optimization for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(8), 2752–2763.
Kaufman, B., Lilleberg, J., & Aazhang, B. (2013). Spectrum sharing scheme between cellular users and ad-hoc device-to-device users. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(3), 1038–1049.
Yu, C. H., Tirkkonen, O., Doppler, K., & Ribeiro, C. (2009). Power optimization of device-to-device communication underlaying cellular communication. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), 2009 (pp. 1–5).
Lee, D., Kim, S. I., Lee, J., & Heo, J. (2014). Power allocation and transmission period selection for device-to-device communication as an underlay to cellular networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 79(1), 1–20.
Xu, S., Wang, H., Chen, T., Huang, Q., & Peng, T. (2010). Effective interference cancellation scheme for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks. In Proceedings of IEEE vehicular technology conference (VTC) 2010-Fall (pp. 1–5).
Wang, D., & Wang, X. (2014). Effective interference cancellation schemes for device-to-device multicast uplink period underlaying cellular networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 75(4), 2201–2216.
Alamouti, S. (1998). A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 16(8), 1451–1458.
Wolniansky, P. W., Foschini, G. J., Golden, G. D., & Valenzuela, R. A. (1998). V-BLAST: An architecture for realizing very high data rates over the rich-scattering wireless channel. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on signal, systems, and electronics (ISSSE) (pp. 295–300).
Zheng, L., & Tse, D. N. C. (2003). Diversity and multiplexing: A fundamental tradeoff in multiple-antenna channels. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 49(5), 1073–1096.
Zhao, L., & Dubey, V. K. (2005). Detection schemes for space-time block code and spatial multiplexing combined system. IEEE Communications Letters, 9(1), 49–51.
Zhuang, X., Vook, F. W. , R-Leveil, S., & Gosse. K. (2003). Transmit diversity and spatial multiplexing in four-transmit-antenna OFDM. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 2316–2320).
You, D., & Kim, D. H. (2014). Multi-device-to-multi-device communication in cellular network for efficient contents distribution. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on consumer electronics (ICCE), 2014 (pp. 244–247).
Qualcomm. (2013). Way forward D2D deployments. 3GPP TSG RAN WG1 Meeting #72bis, R1–131689.
Dohler, M., Lefranc, E., & Aghvami, H. (2002). Space-time block codes for virtual antenna arrays. In Proceedings of IEEE personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), 2002 (pp. 414–417).
Cho, Y. S., Kim, J., Yang, W. Y., & Kang, C. G. (2010). MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communications with MATLAB. Hoboken: Wiley.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. NRF-2015R1A2A2A03008129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, D., Kim, D.H. Hybrid STBC–SM Suitable for Multi-link Device-to-Device Communication in Cellular Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 1507–1518 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4253-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4253-9