Abstract
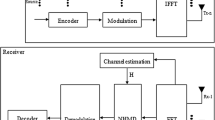
In this work, we investigate the use of domain decomposition techniques in developing novel block-wise PIC detectors for communication systems. Specifically, we consider the cancellation of inter-antenna-interference in the uplink of massive MIMO systems and develop a new block-wise PIC detector based on additive Schwarz method. Up to our knowledge, this is the first time domain decomposition techniques are applied within the wireless communication field. Careful inspection of the channel cross-correlation matrix reveals the fact that the latter has a special structure which supports the use of block iterative methods. We exploit this fact and develop a block-wise PIC detector that is suitable for implementation on parallel processors. Convergence analysis and the impact of various parameters such as the level of overlap and the number of blocks on the convergence behavior of the novel PIC detector are considered. Simulation results show important improvement in convergence speed compared to the conventional linear PIC detector.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hossain, E., Rasti, M., Tabassum, H., & Abdelnasser, A. (2014). Evolution towards 5G multi-tier cellular wireless networks: An interference management perspective. IEEE Wireless Communications, 21(3), 18–127.
Honig, M. L. (2009). Advances in multiuser detection. In Wiley Series in telecommunications and signal processing. Wiley.
Yang, S., & Hanzo, L. (2015). Fifty years of MIMO detection: The road to large-scale MIMOs. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 17(4), 1941–1988.
Lu, L., Li, G. Y., Swindlehurst, A. L., Ashikhmin, A., & Zhang, R. (2014). An overview of massive MIMO: Benefits and challenges. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 8(5), 742–758.
Bentrcia, A., & Zerguine, A. (2009). A new linear group-wise parallel interference cancellation detector. Wireless Personal Communications, 49(1), 23–34.
Pllana, S., & Xhafa, F. (2017). Programming multi-core and many-core computing systems. Hoboken: Wiley.
Okrouhlík, M. (2008). Numerical methods in computational mechanics. Technical report, Institute of Thermomechanics, Prague.
Gander, M. J. (2008). Schwarz methods over the course of time. Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis, 31, 228–255.
Griebel, M., & Oswald, P. (1995). On the abstract theory of additive and multiplicative Schwarz algorithms. Numerische Mathematik, 70(2), 163–180.
Nabben, R. (2003). Comparisons between multiplicative and additive Schwarz iterations in domain decomposition methods. Numerische Mathematik, 95(1), 145–162.
Bai, Z. Z. (2003). On the convergence of additive and multiplicative splitting iterations for systems of linear equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 154(1), 195–214.
Holst, M. (1994). An algebraic Schwarz theory. Technical report CRPC-94-12, Applied mathematics and CRPC, California Institute of Technology.
van Zelst, A & Hammerschmidt, J. S. (2002). A single coefficient spatial correlation model for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radio channels. In Proceedings of URSI XXVIIth general assembly (pp. 1–4). Maastricht, The Netherlands.
Saad, Y. (2003). Iterative methods for sparse linear systems. Philadelphia: SIAM.
Smith, B. (2004). Domain decomposition: Parallel multilevel methods for elliptic partial differential equations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Yanai, H., Takeuchi, K., & Takane, Y. (2011). Projection matrices generalized inverse matrices and singular value decomposition. New York: Springer.
Yu, T., Xiao, Z. & Wong, M. D. (2012). Efficient parallel power grid analysis via additive Schwarz method. ICCAD (pp. 399–406).
Cai, X.-C., & Sarkis, M. (1999). A restricted additive Schwarz preconditioner for general sparse linear systems. SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing, 21, 792–797.
Loisel, S., Nabben, R., & Szyld, D. B. (2008). On hybrid multigrid-Schwarz algorithms. Journal of Scientific Computing, 36(2), 165–175.
Frommer, A., Nabben, R., & Szyld, D. B. (2008). Convergence of stationary iterative methods for hermitian semidefinite linear systems and applications to Schwarz methods. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 30(2), 925–938.
Frommer, A., Nabben, R. & Szyld, D. B. (2001). An algebraic convergence theory for restricted additive and multiplicative Schwarz methods. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on domain decomposition methods in Lyon, France, (pp. 369–375).
Nabben, R., & Szyld, D. B. (2006). Schwarz iterations for symmetric positive semidefinite problems. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 29(1), 98–116.
Quarteroni, A., Sacco, R., & Saleri, F. (2000). Numerical mathematics. New York: Springer.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the support of King Saud University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bentrcia, A. Domain Decomposition Based PIC Detectors for Massive MIMO. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 2141–2160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4290-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4290-4