Abstract
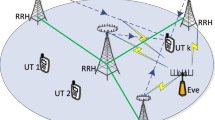
In this paper we address physical layer security of multiple input multiple output (MIMO) communication system in presence of multiple destinations and passive eavesdroppers. Since the eavesdroppers are passive, it is assumed that channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdroppers are not available at the source. Spatial beamforming and artificial noise broadcasting are chosen as the strategy for securing the transmission. Secrecy capacity for optimum power allocation and uniform power allocation with power constraints are analyzed. Optimum power allocation technique is applied when all the authorized users have different data rates. Uniform power allocation is done when all the authorized users have the same data rate. The analytical results are derived and validated through simulation results and finally it is compared with existing methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forouzan, B. A. (2004). Cryptography and network security. New York: McGraw Hill.
Wyner, A. (1975). Wire-tap channel. Bell System Techinical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Csiszar, I., & Korner, J. (1978). Broadcast channels with confidential messages. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(3), 339–348.
Leung Yan Cheong, S., & Hellman, M. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Swindlehurst, A.(2009) Fixed SINR solutions for the MIMO wiretap channel. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009. (pp. 2437–2440).
Liao, W. C., Chang, T. H., Ma, W. K., & Chi, C. Y. (2011). QoS-based transmit beamforming in the presence of eavesdroppers: An optimized artificial-noise-aided approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(3), 1202–1216.
Romero-Zurita, N., Ghogho, M., McLernon, D.(2011) Physical layer security of MIMO frequency selective channels by beamforming and noise generation. In 19th European signal processing conference, 2011, Aug 2011 (pp. 829–833).
Ghogho, M., & Swami, A.(2011) Physical-layer secrecy of MIMO communications in the presence of a poisson random field of eavesdroppers. In IEEE international conference on communications workshops (ICC), 2011, Jun 2011 (pp. 1–5).
Shafiee, S., & Ulukus, S.(2007) Achievable rates in Gaussian MISO channels with secrecy constraints. In IEEE international symposium on information theory, ISIT 2007, June (pp. 2466–2470).
Romero-Zurita, N., Ghogho, M., & McLernon, D. (2012). Outage probability based power distribution between data and artificial noise for physical layer security. IEEE Signal Processing Letter, 19(2), 71–74.
Majhi, S., Qian, H., Xiang, W., Addepalli, S., & Gao, Z.(2011) Analysis of outage probability for opportunistic decode-and-forward relaying network over asymmetric fading channels. In 2011 third international conference on ubiquitous and future networks (ICUFN) (pp. 135–139).
Pei, Y., Liang, Y. C., Zhang, L., Teh, K. C., & Li, K. H. (2010). Secure communication over MISO cognitive radio channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(4), 1494–1502.
Goel, S., & Negi, R. (2008). Guaranteeing secrecy using artificial noise. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(6), 2180–2189.
Zappone, A., Lin, P. H., & Jorswieck, E. (2016). Energy efficiency of confidential multi-antenna systems with artificial noise and statistical CSI. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 10(8), 1462–1477.
Kandukuri, S., & Boyd, S. (2002). Optimal power control in interference-limited fading wireless channels with outage-probability specifications. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(1), 46–55.
Mukherjee, A., Swindlehurst, A. L.(2009) Fixed-rate power allocation strategies for enhanced secrecy in MIMO wiretap channels. In IEEE 10th Workshop on Signal Processing Advances. Wireless Communications, 2009 (pp. 344–348).
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S., & Hellman, M. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Liang, Y., Poor, H. V., & Shamai, S. (2008). Secure communication over fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(6), 2470–2492.
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by Visvesvaraya PhD scheme for Electronics and IT, Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) Government of India, being implemented by Digital India Corporation (formerly Media Lab Asia). Nibedita Nandan is a PhD scholar under Visvesvaraya PhD scheme and S. Majhi is recipient of Sir Visvesvaraya Young Faculty Research Fellow award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majhi, S., Nandan, N. Secrecy Capacity Analysis of MIMO System over Multiple Destinations and Multiple Eavesdroppers. Wireless Pers Commun 100, 1009–1022 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5363-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5363-8