Abstract
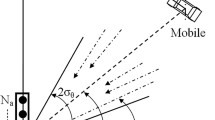
In this paper, we propose a new low-complexity method to jointly estimate the multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channel parameters namely the mean angle of arrival (AoA), the angular spread (AS) and the maximum Doppler spread (DS). We consider Gaussian and Laplacian angular distributions for the incoming AoAs in the case of a Rayleigh channel model. Our estimator is based on the magnitudes and phases of the space–time correlation functions of the received signals. To this end, closed-form expressions of the required functions were derived. Two different approaches are studied using these cross-correlation functions; first at a non zero time lag and second at two different time lags. To evaluate the robustness of the proposed estimator, the two Stage approach and the improved maximum likelihood method based on the Gauss Newton algorithm are taken as benchmarks for the mean AoA and the AS estimation. For the maximum DS, the two Rays and the auto-correlation based algorithms are chosen. Simulation results show that the proposed estimator offers more accurate estimates in almost all considered scenarios. We also compare our work to a recent joint estimator which exploits the Derivatives of the cross-correlation function (DCCF). Our method outperforms the DCCF algorithm at a lower computational cost.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, M., & Cho, D. (2001). A new adaptative power control scheme based on mobile velocity in wireless mobile communication systems. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, 4, 2878–2882.
Vijayan, R., & Holtzman, J. M. (1993). A model for analyzing handoff algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 42, 351–356.
Austin, M. D., & Stuber, G. L. (1994). Velocity adaptative handoff algorithms for microcellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 43, 549–561.
Sun, C., Cheng, J., & Ohira, T. (2008). Handbook on advancements in smart antenna technologies for wireless networks. New York: Information Science Publishing.
Kikuchi, S., Sano, A., Tisuji, H., & Miura, R. (2004). Mobile localization using local scattering model in multipath environments. In Proceedings of IEEE 60th VTC (Vol. 60, pp. 339–343).
Rao, A. M., & Jones, D. L. (2003). Efficient detection with arrays in the presence of angular spreading. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(2), 301–312.
Zhang, H., & Abdi, A. (2009). Nonparametric mobile speed estimation in fading channels: Performance analysis and experimental results. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8, 1683–1692.
Tsai, Y. R., & Yang, K. J. (2009). Approximate ML Doppler spread estimation over flat rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 16(11), 1007–1010.
Baddour, K., & Beaulieu, N. C. (2005). Robust Doppler spread estimation in nonisotropic fading channels. IEEE Transactions Wireless Communication, 4, 2677–2682.
Tepedelenlioglu, C., & Giannakis, G. B. (2001). On velocity estimation and correlation properties of narrow-band mobile communication channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 50(4), 1039–1052.
Souden, M., Affes, S., Benesty, J., & Bahroun, R. (2009). Robust Doppler spread estimation in the presence of a residual carrier frequency offset. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 57, 4148–4153.
Ko, Y. C., & Jeong, G. (2002). Doppler spread estimation in mobile communication systems. Vehicular Technology Conference VTC Spring, 4, 1941–1945.
Ali, G. A., Manzoor, S., & Jeoti, V. (2010). A new Doppler spread estimation algorithm based on zero crossings of the auto-correlation. In International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS).
Yunhe, C. (2010). Joint estimation of angle and Doppler frequency for bistatic MIMO radar. Electronics Letters, 46, 170–172.
Bengtsson, M., & Ottersten, B. (2000). Low-complexity estimators for distributed sources. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 48(8), 2185–2194.
Souden, M., Affes, S., & Benesty, J. (2008). A two-stage approach to estimate the angles of arrival and the angular spreads of locally scattered sources. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(5), 1968–1983.
Kikuchi, S., Sano, A., Tsuji, H., & Miura, R. (2003). A novel approach to mobile-terminal positioning using single array antenna in urban environments. IEEE Conference on Vehicular Technology VTC-Fall, 2, 1010–1014.
Li, J., & Zhang, X. (2011). Improved joint DoD and DoA estimation for MIMO array with velocity receive sensors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 18, 717–720.
Yan, H., Li, J., & Liao, G. (2008). Multitarget identification and localization using bistatic MIMO radar systems. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 48.
Jinli, C., Hong, G., & Weimin, S. (2008). Angle estimation using esprit without pairing in MIMO radar. Electronics Letters, 44, 1422–1423.
Li, J., Conan, J., & Pierre, S. (2006). Using antenna array in multipath environment for wireless sensor positioning. In Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC Fall IEEE (Vol. 64).
Ben Rejeb, N., Bousnina, I., Ben Salah, M. B., & Samet, A. (2014). Joint mean angle of arrival, angular and Doppler spreads estimation in macrocell environments. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2014, 133.
Ben Rejeb, N., Bousnina, I., Ben Salah, M. B., & Samet, A. (2015). Mean angle of arrival, angular and Doppler spreads estimation in MIMO system. IET Signal Processing, 9(5), 395–402.
Abdi, A., & Kaveh, M. (2002). Parametric modeling and estimation of the spatial characteristics of a source with local scattering. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 3, 2821–2824.
Pedersen, K. I., Mogensen, P. E., & Fleury, B. H. (1997). Power azimuth spectrum in outdoor environments. Electronics Letters, 33, 1583–1584.
Tsai, J.-A, Buehrer, R. M., & Woerner, B. D. (2002). The impact of AOA energy distribution on the spatial fading correlation of linear antenna array. IEEE 55th Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC Spring.
Abdi, A., & Kaveh, M. (2002). A space-time correlation model for multielement antenna systems in mobile fading channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 20, 550–560.
Bousnina, I., Stephenne, A., Affes, S., & Samet, A. (2011). A new low-complexity angular spread estimator in the presence of line-of-sight with angular distribution selection. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2011, 88.
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Spatial channel model for multiple input multiple output (MIMO) simulations (3GPP TR 25.996 version 11.0.0 Release 11). September 2012.
Spiegel, M. R., & Liu, J. (1999). Schaum’s mathematical handbook of formulas and tables (2nd ed.). New York: MacGraw Hill.
Kendall, W. B. (1965). Unambiguous accuracy of an interferometer angle-measuring system. IEEE Transactions on Space Electronics and Telemetry, SET–11, 62–70.
Trump, Tonu, & Ottersten, Bjorn. (1996). Estimation of nominal direction of arrival and angular spread using an array of sensors. ELSEVIER Signal Processing Special Issue on Subspace Methods Part I: Array Signal Processing and Subspace Computations, 50, 57–69.
Tepedelenlioglu, Cihan. (2002). Performance analysis of velocity (Doppler) estimators in mobile communications. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 3, 2201–2204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Rejeb, N., Bousnina, I., Ben Salah, M.B. et al. Joint Estimation of MIMO Channel Parameters Using Space–Time Correlation Matrix for Different Angular Distributions. Wireless Pers Commun 102, 163–181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5832-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5832-0