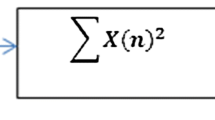Abstract
Cognitive radio is considered as the most intelligent solution to enable flexible use of the frequency spectrum. It allows the secondary user to use the band in which the primary user is idle. Spectrum sensing is a major task in cognitive radio systems. In this task, the secondary user is required to sense the frequency spectrum and vacate the band once the primary user is detected. The actual utilization and the achievable throughput of a cognitive radio system depend on the correctly detected holes and the spectrum sensing time. In this paper, a new adaptive sensing time technique based on the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is proposed to improve the actual spectrum utilization and the achievable throughput.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitola, J., III, & Maguire, G. Q., Jr. (1999). Cognitive radios: making software radio more personal. IEEE Personal Communications, 6(4), 13–18.
Ding, Xu, & Li, Qun. (2015). On the effective capacity region for cognitive radio multiple access channels. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 69(6), 958–961.
Barnes, S. D., & Maharaj, B. T. (2014). Prediction based channel allocation performance for cognitive radio. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 68(4), 336–345.
Tang, L., Chen, Y., Hines, E. L., & Alouini, M. S. (2011). Effect of primary user traffic on sensing-throughput tradeoff for cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(4), 1063–1068.
Zou, Y., Yao, Y.-D., & Zheng, B. (2010). Spectrum sensing and data transmission tradeoff in cognitive radio networks. In IEEE wireless and optical communications conference, Article ID 5510601 (pp. 1–5).
Liang, Y.-C., Zeng, Y, Peh, E., & Hoang, A. T. (2007). Sensing-throughput tradeoff for cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 5330–5335).
Liang, Y.-C., Zeng, Y., Peh, E. C., & Hoang, A. T. (2008). Sensing-throughput tradeoff for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transaction on Wireless Communications, 7(4), 1326–1337.
Stotas, S., & Nallanathan, A. (2012). On the throughput and spectrum sensing enhancement of opportunistic spectrum access cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transaction on Wireless communications, 11(1), 97–107.
Zhang, S., Zhao, H., Wang, S., & Wei, J. (2014). A cross-layer rethink on the sensing -throughput tradeoff for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communication Letters, 18(7), 1226–1229.
Treeumnuk, D., Popescu, D.C. (2012). Energy detector with adaptive sensing widow for improved spectrum utilization in dynamic cognitive radio system. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Old Dominion University, USA (pp. 1528–1532).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkady, M.S., Abd-Elnaby, M., El-Dolil, S.A. et al. An Adaptive Sensing Time Based on SNR for Spectrum Utilization Enhancement in Cognitive Radio. Wireless Pers Commun 106, 307–319 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6071-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6071-0