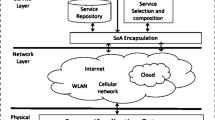
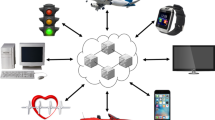
Abstract
Blockchain (BC) represents a distributed ledger technology that has been utilized for providing security and privacy in distributed networks. This makes it applicable to the distributed nature of IoT, which still suffers from privacy and security vulnerabilities. However, the core BC technology is computationally expensive and commonly involves high bandwidth overhead and delays not suitable for IoT related scenarios. In order to foster the synergy between BC and IoT, recent research advancements have specifically focused on developing novel BC approaches that are tailored to the requirements and needs of the specific IoT use cases. The paper elaborates the BC–IoT related issues and provides a comprehensive survey of the current literature and relevant initiated deployments. The paper also identifies the key research and development challenges and discusses the possible aspects for future research.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stellios, I., Kotzanikolaou, P., Psarakis, M., Alcaraz, C., & Lopez, J. (2018). A survey of iot-enabled cyberattacks: Assessing attack paths to critical infrastructures and services. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 20, 3453–3495.
Liang, G., Weller, S. R., Luo, F., Zhao, J., & Dong, Z. Y. (2018). Distributed blockchain-based data protection framework for modern power systems against cyber attacks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2018.2819663.
Karamachoski, J., Gavrilovska, L., & Sefidanoski, A. (2018). The fusion between blockchain and iot for healthcare systems. In ETAI Conference, ETAI ’18 (pp. 1–6).
Mishra, A. K., Tripathy, A. K., Puthal, D., & Yang, L. T. (2018). Analytical model for sybil attack phases in internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6, 379–387.
Singh, A., Ngan, T., Druschel, P., & Wallach, D. S. (2006). Eclipse attacks on overlay networks: Threats and defenses. In Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2006. 25th IEEE international conference on computer communications (pp. 1–12). https://doi.org/10.1109/INFOCOM.2006.231.
Natoli, C., & Gramoli, V. (2016). The balance attack against proof-of-work blockchains: The R3 testbed as an example. arXiv:abs/1612.09426.
Conti, M., Kumar, E. S., Lal, C., & Ruj, S. (2018). A survey on security and privacy issues of bitcoin. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 20, 3416–3452. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2842460.
Gervais, A., Karame, G. O., Wüst, K., Glykantzis, V., Ritzdorf, H., & Capkun, S. (2016). On the security and performance of proof of work blockchains. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security, CCS ’16 (pp. 3–16). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/2976749.2978341.
Duong, T., Chepurnoy, A., Fan, L., & Zhou, H. S. (2018). Twinscoin: A cryptocurrency via proof-of-work and proof-of-stake. In Proceedings of the 2Nd ACM workshop on blockchains, cryptocurrencies, and contracts, BCC ’18 (pp. 1–13). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3205230.3205233.
Christidis, K., & Devetsikiotis, M. (2016). Blockchains and smart contracts for the internet of things. IEEE Access, 4, 2292–2303. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2566339.
Kang, J., Xiong, Z., Niyato, D., Wang, P., Ye, D., & Kim, D. I. (2018). Incentivizing consensus propagation in proof-of-stake based consortium blockchain networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 8, 157–160. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2018.2864758.
Tschorsch, F., & Scheuermann, B. (2016). Bitcoin and beyond: A technical survey on decentralized digital currencies. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 18(3), 2084–2123. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2016.2535718.
Sousa, J., Bessani, A., & Vukolic, M. (2018). A byzantine fault-tolerant ordering service for the hyperledger fabric blockchain platform. In 2018 48th annual IEEE/IFIP international conference on dependable systems and networks (DSN) (pp. 51–58). https://doi.org/10.1109/DSN.2018.00018.
Cachin, C., & Vukolic, M. (2017). Blockchain consensus protocols in the wild. arXiv:abs/1707.01873.
Zheng, Z., Xie, S., Dai, H., Chen, X., & Wang, H. (2017). An overview of blockchain technology: Architecture, consensus, and future trends. In 2017 IEEE international congress on big data (bigdata congress) (pp. 557–564). https://doi.org/10.1109/BigDataCongress.2017.85.
Armknecht, F., Karame, G. O., Mandal, A., Youssef, F., & Zenner, E. (2015). Ripple: Overview and outlook. In M. Conti, M. Schunter, & I. Askoxylakis (Eds.), Trust and Trustworthy Computing (pp. 163–180). Cham: Springer.
Sedgewick, P. E., & de Lemos, R. (2018). Self-adaptation made easy with blockchains. In: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on software engineering for adaptive and self-managing systems, SEAMS ’18 (pp. 192–193). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3194133.3194150.
Mohanty, S., & Vyas, S. (2018). Decentralized autonomous organizations = Blockchain + AI + IoT (pp. 189–206). Berkeley, CA: Apress. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-3808-0_9.
Pahl, C., El Ioini, N., & Helmer, S. (2018). A decision framework for blockchain platforms for IoT and edge computing. In IoTBDS (pp. 105–113).
Yeow, K., Gani, A., Ahmad, R. W., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., & Ko, K. (2018). Decentralized consensus for edge-centric internet of things: A review, taxonomy, and research issues. IEEE Access, 6, 1513–1524. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779263.
Liao, C., Bao, S., Cheng, C., & Chen, K. (2017). On design issues and architectural styles for blockchain-driven iot services. In 2017 IEEE international conference on consumer electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW) (pp. 351–352). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE-China.2017.7991140.
Sharma, P. (2018). Blockchain based hybrid network architecture for the smart city. Future Generation Computer Systems, 86, 650–655.
Vo, H. T., Kundu, A., & Mohania, M. K. (2018). Research directions in blockchain data management and analytics. In EDBT (pp. 445–448).
Yu, X. L., Xu, X., & Liu, B. (2017). EthDrive: A peer-to-peer data storage with provenance. In CAiSE-Forum-DC (pp. 25–32).
Xu, Q., Aung, K. M. M., Zhu, Y., & Yong, K. L. (2018). A blockchain-based storage system for data analytics in the internet of things (pp. 119–138). Cham: Springer.
Steger, M., Dorri, A., Kanhere, S. S., Römer, K., Jurdak, R., & Karner, M. (2018). Secure wireless automotive software updates using blockchains: A proof of concept. In C. Zachäus, B. Müller, & G. Meyer (Eds.), Advanced Microsystems for Automotive Applications 2017 (pp. 137–149). Cham: Springer.
Alvarenga, I. D., Rebello, G. A. F., & Duarte, O. C. M. B. (2018). Securing configuration management and migration of virtual network functions using blockchain. In NOMS 2018–2018 IEEE/IFIP network operations and management symposium (pp. 1–9). https://doi.org/10.1109/NOMS.2018.8406249.
Lee, J. (2018). Patch transporter: Incentivized, decentralized software patch system for WSN and IoT environments. Sensors, 18(2), 574.
Leiba, O., Yitzchak, Y., Bitton, R., Nadler, A., & Shabtai, A. (2018). Incentivized delivery network of iot software updates based on trustless proof-of-distribution. In 2018 IEEE European symposium on security and privacy workshops (EuroSPW) (pp. 29–39).
Azzar, A., & Mottola, L. (2015). Virtual resources for the internet of things. In 2015 IEEE 2nd world forum on internet of things (WF-IoT) (pp. 245–250). https://doi.org/10.1109/WF-IoT.2015.7389060.
Xiong, Z., Zhang, Y., Niyato, D., Wang, P., & Han, Z. (2018). When mobile blockchain meets edge computing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(8), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701095.
Samaniego, M., & Deters, R. (2017). Internet of smart things-iost: Using blockchain and clips to make things autonomous. In 2017 IEEE international conference on cognitive computing (ICCC) (pp. 9–16). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEE.ICCC.2017.9.
Vermesan, O., Bröring, A., Tragos, E., Serrano, M., Bacciu, D., Chessa, S., et al. (2017). Internet of robotic things: Converging sensing/actuating, hypoconnectivity, artificial intelligence and iot platforms. Cognitive Hyperconnected Digital Transformation: Internet of Things Intelligence Evolution, 1, 1–35.
Ferrer, E. C. (2016). The blockchain: A new framework for robotic swarm systems. arXiv:abs/1608.00695.
Golomb, T., Mirsky, Y., & Elovici, Y. (2018). Ciota: Collaborative iot anomaly detection via blockchain. arXiv:abs/1803.03807.
Hashemi, S. H., Faghri, F., & Campbell, R. H. (2017). Decentralized user-centric access control using pubsub over blockchain. arXiv:abs/1710.00110.
Novo, O. (2018). Blockchain meets iot: An architecture for scalable access management in iot. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 1184–1195. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2018.2812239.
Zhang, Y., Kasahara, S., Shen, Y., Jiang, X., & Wan, J. (2018). Smart contract-based access control for the internet of things. arXiv:abs/1802.04410.
Xu, R., Chen, Y., Blasch, E., & Chen, G. (2018). Blendcac: A blockchain-enabled decentralized capability-based access control for iots. arXiv:abs/1804.09267.
Dukkipati, C., Zhang, Y., & Cheng, L. C. (2018). Decentralized, blockchain based access control framework for the heterogeneous internet of things. In Proceedings of the third ACM workshop on attribute-based access control, ABAC’18 (pp. 61–69). New York, NY: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3180457.3180458.
Atlam, H. F., Alenezi, A., Walters, R. J., Wills, G. B., & Daniel, J. (2017). Developing an adaptive risk-based access control model for the internet of things. In 2017 IEEE international conference on internet of things (iThings) and IEEE green computing and communications (GreenCom) and IEEE cyber, physical and social computing (CPSCom) and ieee smart data (SmartData) (pp. 655–661). https://doi.org/10.1109/iThings-GreenCom-CPSCom-SmartData.2017.103.
Outchakoucht, A., ES-Samaali, H., & Philippe, J. (2017). Dynamic access control policy based on blockchain and machine learning for the internet of things. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 8, 417–424.
Khan, M. A., & Salah, K. (2018). Iot security: Review, blockchain solutions, and open challenges. Future Generation Computer Systems, 82, 395–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.11.022.
Sharma, P. K., Singh, S., Jeong, Y., & Park, J. H. (2017). Distblocknet: A distributed blockchains-based secure sdn architecture for iot networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(9), 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1700041.
Ferreira Jesus, E., Chicarino, R. L. V., Albuquerque, C., & de Rocha, A. (2018). A survey of how to use blockchain to secure internet of things and the stalker attack. Security and Communication Networks, 2018, 1–27.
Xia, Q., Sifah, E. B., Smahi, A., Amofa, S., & Zhang, X. (2017). Bbds: Blockchain-based data sharing for electronic medical records in cloud environments. Information, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/info8020044. http://www.mdpi.com/2078-2489/8/2/44.
Al Omar, A., Rahman, M. S., Basu, A., & Kiyomoto, S. (2017). Medibchain: A blockchain based privacy preserving platform for healthcare data. In G. Wang, M. Atiquzzaman, Z. Yan, & K. K. R. Choo (Eds.), Security, Privacy, and Anonymity in Computation, Communication, and Storage (pp. 534–543). Cham: Springer.
Angeletti, F., Chatzigiannakis, I., & Vitaletti, A. (2017). Privacy preserving data management in recruiting participants for digital clinical trials (pp. 7–12).
Dorri, A., Kanhere, S. S., Jurdak, R., & Gauravaram, P. (2017). Blockchain for iot security and privacy: The case study of a smart home. In 2017 IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops (PerCom workshops) (pp. 618–623). https://doi.org/10.1109/PERCOMW.2017.7917634.
Collen, A., Nijdam, N. A., Augusto-Gonzalez, J., Katsikas, S. K., Giannoutakis, K. M., Spathoulas, G., et al. (2018). Ghost-safe-guarding home iot environments with personalised real-time risk control. In E. Gelenbe, P. Campegiani, T. Czachórski, S. K. Katsikas, I. Komnios, L. Romano, & D. Tzovaras (Eds.), Security in Computer and Information Sciences (pp. 68–78). Cham: Springer.
Gao, F., Zhu, L., Shen, M., Sharif, K., Wan, Z., & Ren, K. (2018). A blockchain-based privacy-preserving payment mechanism for vehicle-to-grid networks. IEEE Network, 99, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/MNET.2018.1700269.
Dorri, A., Steger, M., Kanhere, S. S., & Jurdak, R. (2017). Blockchain: A distributed solution to automotive security and privacy. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(12), 119–125. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1700879.
Mylrea, M., & Gourisetti, S. N. G. (2017). Blockchain for smart grid resilience: Exchanging distributed energy at speed, scale and security. In 2017 resilience week (RWS) (pp. 18–23). https://doi.org/10.1109/RWEEK.2017.8088642.
SDxCentral: Oracle builds a blockchain cloud service based on hyperledger. (2018). https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/oracle-blockchain-cloud-service-goes-public/2018/07/?utm_source=SDxCentral.com+Mailing+List&utm_campaign=8c5232b1c3-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2018_07_16&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_c2b6e504a2-8c5232b1c3-81947645. Accessed on 16 October 2018.
TechTarget: Cisco eyes blockchain messaging for better security. (2018). https://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/news/252439024/Cisco-eyes-blockchain-messaging-for-better-security?track=NL-1817&ad=920345&src=920345&asrc=EM_NLN_93606076&utm_medium=EM&utm_source=NLN&utm_campaign=20180416_Cisco%20looks%20at%20blockchain%20to%20secure%20group%20messaging. Accessed on 16 October 2018.
SDxCentral: Verizon to use ksi blockchain technology developed for estonia. (2018). https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/verizon-use-ksi-blockchain-technology-developed-estonia/2018/02/?utm_source=SDxCentral.com+Mailing+List&utm_campaign=e04f4588f7-SDxCentral+Newsletter+2018-02-13&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_c2b6e504a2-e04f4588f7-81947645. Accessed on 16 October 2018.
SDxCentral: Google is working on blockchain technology, too. (2018). https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/google-working-blockchain-technology/2018/03/?utm_source=SDxCentral.com+Mailing+List&utm_campaign=ab57972ecd-SDxCentral+Newsletter+2018-03-23&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_c2b6e504a2-ab57972ecd-81947645. Accessed on 16 October 2018.
Drops, I. https://icodrops.com. Accessed on 5 December 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakovic, V., Karamachoski, J., Atanasovski, V. et al. Blockchain Paradigm and Internet of Things. Wireless Pers Commun 106, 219–235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06270-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06270-9