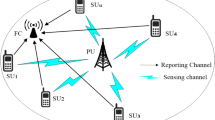
Abstract
A critical problem with Cooperative Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Network is the presence of Malicious Users (MUs) reporting false information to the Fusion Centre (FC) about the Primary User (PU) spectrum availability. This paper outline different techniques to mitigate the damaging effects of the false sensing in Soft Decision Fusion (SDF) schemes using One-to-Many Sensing-Distances and Z-Score. FC employs these schemes to separate the sensing information received from MUs and Secondary Users and feed the results to the Hampel’s test for MUs detection. After segregating all potential MUs FC takes a final decision about the availability of PU spectrum using the proposed SDF schemes. The suggested scheme is tested in an environment of opposite, random opposite, always yes and always no types of MUs. Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed scheme, which surpass the existing SDF schemes in reliability, precision and efficiency.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghasemi, A., & Sousa, E. S. (2008). Spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: Requirements, challenges and design trade-offs. IEEE Communications Magazine, 46(4), 32–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2008.4481338.
Chen, R., Park, J. M., Hou, Y. T., & Reed, J. H. (2008). Toward secure distributed spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 46(4), 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2008.4481340.
Mishra, S., Sahai, A., & Brodersen, R. (2006). Cooperative sensing among cognitive radios. In IEEE international conference on communications (vol. 4, pp. 1658–1663). Istanbul. https://doi.org/10.1109/icc.2006.254957.
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(2), 201–220. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2004.839380.
Axell, E., Leus, G., Larsson, E. G., & Poor, H. V. (2012). Spectrum sensing for cognitive radio: State-of-the-art and recent advances. In IEEE signal processing magazine (vol. 29, pp. 101–116). https://doi.org/10.1109/msp.2012.2183771.
Zhai, L., Wang, H., & Gao, C. (2016). A spectrum access based on quality of service (QoS) in cognitive radio networks. PLoS ONE, 11(5), 2005–2009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155074.
Ben Letaief, K., & Zhang, W. (2009). Cooperative communications for cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE (vol. 97, pp. 878–893).
Monemian, M., & Mahdavi, M. (2014). Analysis of a new energy-based sensor selection method for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(9), 3021–3032. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2014.2322034.
Lee, D. (2015). Adaptive random access for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(2), 831–840.
He, Y., Xue, J., Ratnarajah, T., Sellathurai, M., & Khan, F. (2016). On the performance of cooperative spectrum sensing in random cognitive radio networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 12(1), 881–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2016.2554464.
Li, H., & Han, Z. (2010). Catch me if you can: An abnormality detection approach for collaborative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(11), 3554–3565. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2010.091510.100315.
Kar, S., Sethi, S., & Sahoo, R. K. (2017). A multi-factor trust management scheme for secure spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 97(2), 2523–2540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4621-5.
Vu-Van, H., & Koo, I. (2012). A robust cooperative spectrum sensing based on Kullback-Leibler divergence. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E95-B(4), 1286–1290. https://doi.org/10.1587/trans.e0.
Sharifi, A. A., & Niya, J. M. (2016). Securing collaborative spectrum sensing against malicious attackers in cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 90(1), 75–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3331-8.
Zeng, K., Pawełczak, P., & Čabrić, D. (2010). Reputation-based cooperative spectrum sensing with trusted nodes assistance. IEEE Communications Letters, 14(3), 226–228. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2010.03.092240.
Nabil, M. (2014). A cooperative spectrum sensing scheme based on task assignment algorithm for cognitive radio networks. In 2014 international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC) (pp. 151–156). Nicosia, Cyprus.
Penna, F., Sun, Y., Dolecek, L., & Cabric, D. (2012). Detecting and counteracting statistical attacks in cooperative spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(4), 1806–1822. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2011.2181839.
Sharifi, A. A., Sharifi, M., & MuseviNiya, M. J. (2016). Collaborative spectrum sensing under primary user emulation attack in cognitive radio networks. IETE Journal of Research, 62(2), 205–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2015.1083907.
Kaligineedi, P., Khabbazian, M., & Bhargava, V. K. (2010). Malicious user detection in a cognitive radio cooperative sensing system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(8), 2488–2497.
Van, H.-V., & Koo, I. (2012). A sequential cooperative spectrum sensing scheme based on cognitive user reputation. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 58(4), 1147–1152. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2012.6414979.
Gul, N., Qureshi, I. M., Omar, A., Elahi, A., & Khan, M. S. (2017). History based forward and feedback mechanism in cooperative spectrum sensing including malicious users in cognitive radio network. PLoS ONE, 12(8), e0183387.
Gul, N., Qureshi, I. M., Akbar, S., Kamran, M., & Rasool, I. (2018). One-to-many relationship based Kullback–Leibler divergence against malicious users in cooperative spectrum sensing. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3153915.
Ma, J., Zhao, G., & Li, Y. (2008). Soft combination and detection for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(11), 4502–4507. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-WC.2008.070941.
Lee, Y. L., Saad, W. K., El-Saleh, A. A. B., & Ismail, M. (2013). Improved detection performance of cognitive radio networks in AWGN and rayleigh fading environments. Journal of Applied Research and Technology, 11(3), 437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-6423(13)71552-9.
Hamza, D., Aïssa, S., & Aniba, G. (2014). Equal gain combining for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(8), 4334–4345. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2014.2317788.
Teguig, D., Scheers, B., & Le Nir, V. (2012). Data fusion schemes for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. In 2012 military communications and information systems conference, MCC 2012 (pp. 104–110). Gdansk, Poland.
Jiang, T., & Qu, D. (2008). On minimum sensing error with spectrum sensing using counting rule in cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the 4th international ICST conference on wireless internet (pp. 1–9). Brussels, Belgium. https://doi.org/10.4108/icst.wicon2008.4954.
Marchang, N., Rajkumari, R., Brahmachary, S. B.,& Taggu, A. (2015). dynamic decision rule for cooperative spectrum. In 2015 IEEE international conference on electrical, computer and communication technologies (ICECCT) (pp. 1–5). Coimbatore, India, March 2015.
Unnikrishnan, J., & Veeravalli, V. V. (2007). Cooperative spectrum sensing and detection for cognitive radio. In IEEE global telecommunications conference ({GLOBECOM}) (pp. 2972–2976). Washington, DC. November 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/glocom.2007.563.
Liu, X., Yan, J., & Chen, K. (2016). Optimal energy harvest-based weighed cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio. In 2016 international workshop on sustainability, implementation and resilience of energy-aware networks, ICNC workshop (pp. 16–20). Kauai, HI, USA.
Bhattacharjee, S., Das, P., Mandal, S., & Sardar, B. (2015). Optimization of probability of false alarm and probability of detection in cognitive radio networks using GA. In Proceedings of ReTIS’15—2nd IEEE international conference on recent trends in information systems (pp. 53–57). Kolkata, India, July 2015.
Mehboob, U., Qadir, J., Ali, S., & Vasilakos, A. (2016). Genetic algorithms in wireless networking: Techniques, applications, and issues (Vol. 20)., Springer: Soft Computing Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2070-9.
Akbari, M., & Ghanbarisabagh, M. (2014). A novel evolutionary-based cooperative spectrum sensing mechanism for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 79(2), 1017–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1915-8.
Hossain, M. K., & Abd El-Saleh, A. (2013). Cognitive radio engine model utilizing soft fusion based genetic algorithm for cooperative spectrum optimization. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC), 2(3), 169–173.
Rashid, R. A., Hadi, A., Bin, F., Hamid, A., Fisal, N., Syed-yusof, S. K., et al. (2015). Efficient in-band spectrum sensing using swarm intelligence for cognitive radio network. Détectionspectraleintrabandeefficace en utilisantl’ optimisation par essaimsparticulaires pour un réseau sans filcognitif. Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 38(2), 106–115.
Gul, N., Qureshi, I. M., Elahi, A., & Rasool, I. (2018). Defense against malicious users in cooperative spectrum sensing using genetic algorithm. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2346317.
Gul, N., Naveed, A., Elahi, A., Khattak, T., & Qureshi, I. (2017). A combination of double sided neighbor distance and genetic algorithm in cooperative spectrum sensing against malicious users. In Proceedings of 2017 14th international Bhurban conference on applied sciences & technology (IBCAST) (pp. 746–753). Islamabad, Pakistan.
Herath, S. P., & Rajatheva, N. (2008). Analysis of equal gain combining in energy detection for cognitive radio over Nakagami channels. iN GLOBECOM—IEEE global telecommunications conference (pp. 2972–2976). https://doi.org/10.1109/glocom.2008.ecp.570.
Hampel, F. R. (1974). The influence curve and its role in robust estimation. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 69(346), 383–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1974.10482962.
Hampel, F. R. (1971). A general qualitative definition of robustness. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 42(6), 1887–1896. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177693054.
Liu, H., Shah, S., & Jiang, W. (2004). On-line outlier detection and data cleaning. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 28(9), 1635–1647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2004.01.009.
Pearson, R. K. (2002). Outliers in process modeling and identification. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 10(1), 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1109/87.974338.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Fazal Elahi (Late) for his continuous support and assistance during this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gul, N., Qureshi, I.M., Naveed, A. et al. Secured Soft Combination Schemes Against Malicious-Users in Cooperative Spectrum Sensing. Wireless Pers Commun 108, 389–408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06408-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06408-9