Abstract
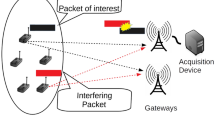
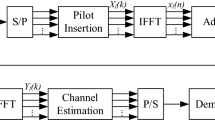
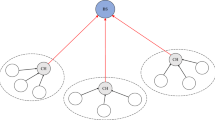
This paper proposes an adaptive equalization algorithm for asynchronous cooperative communications in ad hoc networks, where amplify-and-forward relays are adopted, each of which is equipped with single antenna. Adaptive equalization technique is carried out at the destination node in this paper to remove inter-symbol interference, which is caused by the retransmissions of the asynchronous relays. Least mean squares (LMS) has been regarded as an effective adaptive method, but it has difficulty in obtaining the optimal solution. In this paper, we present a hybrid adaptive scheme by combining particle swarm optimization (PSO) with conventional LMS algorithm, where PSO is utilized to search the optimal solution during the iterative process, and LMS is employed to avoid the local convergence, which is usually caused in PSO. Numerical simulation results show that, the proposed scheme outperforms conventional LMS algorithm in convergence performance over Rayleigh flat fading channel, and meanwhile, a signal–noise-ratio gain of 6 dB or so is obtained when BER is 10−3.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, T., Syue, S. J., Gauthier, V., Afifi, H., & Wang, C. L. (2011). CoopGeo: A beaconless geographic cross-layer protocol for cooperative wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,10(8), 2554–2565.
Wang, H., Xia, X. G., & Yin, Q. (2009). Computationally efficient equalization for asynchronous cooperative communications with multiple frequency offsets. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,8(2), 648–655.
Wang, H. M. (2017). Full-diversity uncoordinated cooperative transmission for asynchronous relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,66(1), 468–480.
Guo, X., & Xia, X. G. (2008). Distributed linear space-time convolutional codes achieving asynchronous full cooperative diversity with MMSE-DFE receivers (special paper). In IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Las Vegas, NV, 2008 (pp. 459–464).
Vahidnia, R., & Shahbazpanahi, S. (2013). Single-carrier equalization and distributed beamforming for asynchronous two-way relay networks. In 21st European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2013), Marrakech, 2013 (pp. 1–5).
Xiaohua, L., Fan, N., Jui-Te, H., & Mo, C. (2005). Channel equalization for stbc-encoded cooperative transmissions with asynchronous transmitters. In Conference Record of the Thirty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (pp. 457–461). Pacific Grove, CA.
Jiang, Y., Xiao, J., & You, X. (2012). A simplified equalization method for asynchronous cooperative relay systems. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW), Paris,2012, 258–262.
Gupta, A., & Joshi, S. (2008). Variable step-size LMS algorithm for fractal signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,56(4), 1411–1420.
Kwong, R. H., & Johnston, E. W. (1992). A variable step size LMS algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,40(7), 1633–1642.
Slock, D. T. M. (1993). On the convergence behavior of the LMS and the normalized LMS algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,41(9), 2811–2825.
Duttweiler, D. L. (2000). Proportionate normalized least-mean-squares adaptation in echo cancelers. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing,8(5), 508–518.
Iqbal, N., Zerguine, A., & Al-Dhahir, N. (2014). Adaptive equalisation using particle swarm optimisation for uplink SC-FDMA. Electronics Letters,50(6), 469–471.
Lakshmikanth, S., Natraj, K. R. & Rekha, K. R. (2014). Performance analysis of industrial noise cancellation with pso based wiener filter using adaptive LMS & NLMS. In 2014 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (pp. 363–368). Melmaruvathur.
Krusienski, D. J., & Jenkins, W. K. (2004). A particle swarm optimization-least mean squares algorithm for adaptive filtering. In Conference record of the 38th Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers (Vol. 1, pp. 241–245).
Wang, J., Yang, H., Xiaolin, H., & Wang, X. (2011). An adaline neural network-based multi-user detector improved by particle swarm optimization in CDMA Systems. Journal of Wireless Personal Communication,59(2), 191–203.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2017M623129. The work was also supported in part by Natural Science Foundation of China and in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant JB180112, and also in part by the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities under Grant B08038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JL., Zhi, K. & Zhang, R. A PSO-Based Hybrid Adaptive Equalization Algorithm for Asynchronous Cooperative Communications. Wireless Pers Commun 109, 2627–2635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06699-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06699-y