Abstract
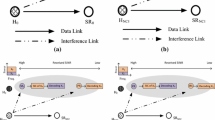
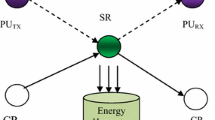
In wireless spectrum, the cognitive radio network (CRN) has the capability to automatically detect the channels so that it is possible to perform concurrent communication. One of the major challenges in hybrid CRNs is effective spectrum sharing. In the interweave scheme secondary user (SU) uses the spectrum, when primary user (PU) is absent. Further in the underlay scheme SU uses the spectrum concurrently with PU along with the interference constraint. In order to utilize the advantage of both the scheme hybrid CRN has been proposed in Chu et al. (IEEE Trans Commun 62(7):2183–2197, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcomm.2014.2325041). The major challenges in hybrid CRN are to select the scheme (interweave/underlay) and use the relays accordingly. To overcome this problem, the optimum relay selection and accurate cooperative spectrum sensing scheme are proposed in this paper which improves the SU performance in terms of throughput of hybrid CRN. By accurate cooperative spectrum sensing method, the accuracy of the decision to select the underlay/overlay scheme to transmit the data is improved. The SU uses relays to minimize interference with the PU while underlay scheme is selected for transmission. Here, the relay selection is optimized by an optimum relay selection method. Numerical results show that the proposed scheme improves the throughput of hybrid CRN. The experimental results show that the proposed method is performed better in terms of delay, delivery ratio, overhead, energy consumption, and throughput.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khalid, L., & Anpalagan, A. (2010). Emerging cognitive radio technology: Principles, challenges and opportunities. Computers & Electrical Engineering,36(2), 358–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2009.03.004.
Saleem, Y., & Rehmani, M. (2014). Primary radio user activity models for cognitive radio networks: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications,43, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2014.04.001.
Zhang, Y., Tay, W., Li, K., & Gaiti, D. (2014). Distributed boundary estimation for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,32(11), 1961–1973. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsac.2014.1411rp08.
Sun, H., Nallanathan, A., Wang, C.-X., & Chen, Y. (2013). Wideband spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Wireless Communications,20(2), 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1109/mwc.2013.6507397.
Zhao, Q., Wu, Z., & Li, X. (2016). Energy efficiency of compressed spectrum sensing in wideband cognitive radio networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0581-9.
Li, H., Xing, X., Zhu, J., Cheng, X., Li, K., Bie, R., et al. (2016). Utility-based cooperative spectrum sensing scheduling in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,66, 645–655.
Chen, R., Park, J.-M., Hou, Y., & Reed, J. (2008). Toward secure distributed spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine,46(4), 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcom.2008.4481340.
Sigg, S., Scholz, M., Shi, S., Ji, Y., & Beigl, M. (2014). Rf-sensing of activities from non-cooperative subjects in device-free recognition systems using ambient and local signals. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing,13(4), 907–920. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmc.2013.28.
Unnikrishnan, J., & Veeravalli, V. (2007). Cooperative spectrum sensing and detection for cognitive radio. In IEEE GLOBECOM 2007–2007 IEEE global telecommunications conference, Washington, DC, USA (pp. 2972–2976). https://doi.org/10.1109/glocom.2007.563.
Akyildiz, I., Lo, B., & Balakrishnan, R. (2011). Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: A survey. Physical Communication,4(1), 40–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2010.12.003.
He, D. (2013). Chaotic stochastic resonance energy detection fusion used in cooperative spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,62(2), 620–627. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2012.2224680.
Axell, E., Leus, G., Larsson, E., & Poor, H. (2012). Spectrum sensing for cognitive radio: State-of-the-art and recent advances. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,29(3), 101–116. https://doi.org/10.1109/msp.2012.2183771.
Zhao, Y., Kang, G., Wang, J., Liang, X., & Liu, Y. (2013). A soft fusion scheme for cooperative spectrum sensing based on the log-likelihood ratio. In 2013 IEEE 24th annual international symposium on personal, indoor, and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), London, UK (pp. 3150–3154). https://doi.org/10.1109/pimrc.2013.6666688.
Ahmed, A., Hu, Y., & Noras, J. (2014). Noise variance estimation for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. AASRI Procedia,9, 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasri.2014.09.008.
Guibene, W., Turki, M., Zayen, B., & Hayar, A. (2012). Spectrum sensing for cognitive radio exploiting spectrum discontinuities detection. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1499-2012-4.
Sun, M., Zhao, C., Yan, S., & Li, B. (2016). A novel spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks with noise uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2016.2596789.
Ejaz, W., Shah, G., Hasan, N., & Kim, H. (2014). Energy and throughput efficient cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio sensor networks. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies,26(7), 1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.2803.
Bouallegue, T., & Sethom, K. (2017). New threshold-based relay selection algorithm in dual hop cooperative network. Procedia Computer Science,109, 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.05.351.
Li, Y., & Nosratinia, A. (2013). Spectrum sharing with distributed relay selection and clustering. IEEE Transactions on Communications,61(1), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcomm.2012.091912.120062.
Nam, S., Vu, M., & Tarokh, V. (2008). Relay selection methods for wireless cooperative communications. In 2008 42nd Annual conference on information sciences and systems, Princeton, NJ, USA (pp. 859–864). https://doi.org/10.1109/ciss.2008.4558640.
Chinh Chu, T., Zepernick, H., & Phan, H. (2016). Hybrid spectrum access with relay assisting both primary and secondary networks under imperfect spectrum sensing. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0700-7.
Thakur, P., Kumar, A., Pandit, S., Singh, G., & Satashia, S. (2017). Advanced frame structures for hybrid spectrum access strategy in cognitive radio communication systems. IEEE Communications Letters,21(2), 410–413. https://doi.org/10.1109/lcomm.2016.2622260.
Ma, Y., Guo, Y., Niu, K., & Lin, J. (2012). Transmission capacity of secondary networks in hybrid overlaid/underlaid cognitive radio systems. In 2012 IEEE 14th international conference on communication technology, Chengdu, China (pp. 397–401). https://doi.org/10.1109/icct.2012.6511250.
Arjoune, Y., Mrabet, Z., Ghazi, H., & Tamtaoui, A. (2018). Spectrum sensing: Enhanced energy detection technique based on noise measurement. In 2018 IEEE 8th annual computing and communication workshop and conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA (pp. 828–834). https://doi.org/10.1109/ccwc.2018.8301619.
Cao, B., Feng, G., Li, Y., & Wang, C. (2014). Cooperative media access control with optimal relay selection in error-prone wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,63(1), 252–265. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2012.2226485.
Mietzner, J., Lampe, L., & Schober, R. (2009). Distributed transmit power allocation for multihop cognitive-radio systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,8(10), 5187–5201. https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2009.081318.
Ban, T., Choi, W., Jung, B., & Sung, D. (2009). Multi-user diversity in a spectrum sharing system. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,8(1), 102–106. https://doi.org/10.1109/t-wc.2009.080326.
Zou, Y., Zhu, J., Zheng, B., & Yao, Y.-D. (2010). An adaptive cooperation diversity scheme with best-relay selection in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsp.2010.2053708.
Seyfi, M., Muhaidat, S., & Liang, J. (2013). Relay selection in cognitive radio networks with interference constraints. IET Communications. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-com.2012.0415.
Zhao, Y., Adve, R., & Lim, T. J. (2007). Improving amplify-and-forward relay networks: Optimal power allocation versus selection. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications. https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2007.06026.
Martínez, D., & Andrade, Á. (2014). Reducing the effects of the noise uncertainty in energy detectors for cognitive radio networks. International Journal of Communication Systems,30(1), e2907. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.2907.
Althunibat, S., Di Renzo, M., & Granelli, F. (2013). Optimizing the K-out-of-N rule for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. In 2013 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), Atlanta, GA USA (pp. 1607–1611). https://doi.org/10.1109/glocom.2013.6831303.
Ruby, D., Vijayalakshmi, M., & Kannan, A. (2017). Intelligent relay selection and spectrum sharing techniques for cognitive radio networks. Cluster Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1102-2.
Aslam, S., & Lee, K. (2013). Spectrum sharing optimization with QoS guarantee in cognitive radio networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering,39(7), 2053–2067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.06.003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajaganapathi, R., Muthuchidambara Nathan, P. ORS-ACSS: Optimum Relay Selection and Accurate Cooperative Spectrum Sensing for Hybrid Cognitive Radio Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 110, 795–813 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06756-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06756-6