Abstract
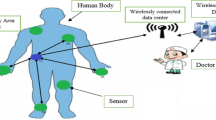
Wireless body area network (WBAN) is the subfield of Wireless Sensor Network, employs in the area of monitoring the health of the patient. WBAN is also known as wireless body sensor network in which sensor nodes are fused inside the body of the person to detect their physiological changes. After processing or comparing those obtained data with the pre-stored default value, the packets are transmitted to the base station. Due to the inner-body sensor node, replacement of the battery may hazardous for the person. So, storing up and saving of energy is the main focus inside the WBANs. In this research, we employ the critical data routing code for transmitting the relevant data from inner-body node to the on-body medical super sensor (MSS) node. Here, MSS act as a controller that can manage all the injected sensor node inside the body of the person as their member. And, if inner-body sensor node is detecting any corporal activities from the human body then it compares those data with the pre-stored threshold level value of that sensor node, and if sensor obtained more deviation in their results then it follows the critical data routing (CDR) for the transmission process, unless it goes to the rest mode. In other words, the sensor node can only be transmitted the critical packet data to their near-by controller and avoiding the redundant picking of normal packet data. By following this procedure we can save the maximum of energy for the sensor so that it alive for the greatest period of time that lead to continuous monitoring of the patient and also maximizes the lifespan of the network. Simulation can be done on MATLAB that can show the finest outcomes in terms of energy spending, network lifespan, throughput- efficiency, hold up by any one of the steering protocol when there is a comparison between CDR, REEC, and SIMPLE respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 January 2020
In the original article, the captions to Figs. 4 and 5 were incorrect and incomplete, respectively. They should read as follows.
References
Movassaghi, S., Abolhasan, M., & Lipman, J. (2013). A review of routing protocols in wireless body area networks. Journal of Networks,8(3), 559–575.
Ababneh, N., & et al. (2012) Energy-balanced rate assignment and routing protocol for body area network. In 26th international conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops (WAINA). IEEE.
Tsouri, G. R., Gill, R., Prieto, A., & Argade, N. (2012). On increasing network lifetime in body area networks using global routing with energy consumption balancing. Sensors,12(10), 13088–13108.
Latre, B., & et al. (2007). A low-delay protocol for multihop wireless body area networks. In Fourth annual international conference on mobile and ubiquitous systems: Networking and services, 2007. MobiQuitous 2007. IEEE.
Quwaider, M., & Biswas, S. (2009). On-body packet routing algorithms for body sensor networks. In First international conference on networks and communications, 2009. NETCOM’09. IEEE.
Ehyaie, A., Hashemi, M., & Khadivi, P. (2009). Using relay network to increase lifetime in wireless body area sensor networks. In IEEE international symposium on world of wireless, mobile and multimedia networks, and workshops, 2009. WoWMoM 2009. IEEE.
Nabi, M., & et al. (2010). A robust protocol stack for multi-hop wireless body area networks with transmit power adaptation. In Proceedings of the fifth international conference on body area networks. ACM.
Guo, C., Venkatesha Prasad, R., & Jacobsson, M. (2010). Packet forwarding with minimum energy consumption in body area sensor networks. In 2010 7th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference (CCNC). IEEE.
Tsouri, Gill R., Sapio, Adrian, & Wilczewski, Jeff. (2011). An investigation into relaying of creeping waves for reliable low-power body sensor networking. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems,5(4), 307–319.
Sapio, A., & Tsouri, G. R. (2010). Low-power body sensor network for wireless ECG based on relaying of creeping waves at 2.4 GHz. In 2010 international conference on body sensor networks (BSN). IEEE.
Javaid, N.,, Yaqoob, M., Khan, M. Y., Khan, M. A., Javaid, A., & Khan, Z. A. (2013). Analyzing delay in wireless multi-hop heterogeneous body area networks. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering, and Technology.
Javaid, N., Israr, I., Khan, M. A., Javaid, A., Bouk, S. H., & Khan, Z. A. (2013). Analyzing medium access techniques in wireless body area networks. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology.
Quwaider, M., & Biswas, S. (2009). Probabilistic routing in on-body sensor networks with postural disconnections. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM international symposium on Mobility management and wireless access. ACM.
Djenouri, D., & Balasingham, I. (2009) New QoS and geographical routing in wireless biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of 6th IEEE international ICST conference on broadband communications, networks, and systems (pp. 1–8). Madrid, Spain.
Reusens, E., et al. (2009). Characterization of on-body communication channel and energy efficient topology design for wireless body area network. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine,13(6), 933–945.
Sandhu, M. M., Akbar, M., Behzad, M., Javaid, N., Khan, Z. A., & Qasim, U. (2014). REEC: Reliable energy efficient critical data routing in wireless body area network. In 2014 ninth international conference on broadband and wireless computing, communication, and applications.
Javaid, N., Abbas, Z., Farid, M. S., Khan, Z. A., & Alrajeh, N. (2013). M-ATTEMPT: A new energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. In The 4th international conference on ambient systems, networks and technologies (ANT 2013) (Vol. 19, pp. 224–231), Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, Procedia Computer Science, ISSN 1877-0509.
Nadeem, Q., Javaid, N., Mohammad, S. N., Khan, M. Y., Sarfraz, S., & Gull, M. (2013). SIMPLE: Stable increased-throughput multi-hop protocol for link efficiency in broadband and wireless computing. In Proceedings of the eighth international conference on broadband and wireless computing, communication and applications (BWCCA) (pp. 221–226), Compiegne, France.
Rohokale, V. M., Prasad, N. R., & Prasad R. (2011). A cooperative internet of things (IoT) for rural healthcare monitoring and control. In 2nd international conference wireless VITAE. ISBN:978-1-4577-0787-2.
Mainwaring, A., Polastre, J., Szewczyk, R., Culler, D., & Anderson, J. (2002).Wireless sensor networks for habitat monitoring. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on wireless sensor networks and applications (pp. 88–97). ACM Press.
Manzoor, B., Javaid, N., Rehman, O., Akbar, M., Nadeem, Q., Iqbal, A., et al. (2013). Q-LEACH: A new routing protocol for WSNs. Procedia Computer Science,19, 926–931.
Razzaque, M. A., Hong, C. S., & Lee, S. (2011). Data-centric multiobjective QoS-aware routing protocol for body sensor networks. Sensors (Basel),11(1), 917–937.
Khan, Z. A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Robertson, B. (2013). A QoS-aware routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in hospital body area networks. Procedia Computer Science,19, 171–179.
Khan, Z, Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Robertson, B. (2012). QPRD: QoS-aware peering routing protocol for delay sensitive data in hospital body area network communication. In Proceedings of 7th IEEE international conference on broadband, wireless computing, communication and applications (pp. 178–185). Victoria, BC, Canada.
Woo, A., & Culler, D. (2003) Evaluation of efficient link reliability estimators for low-power wireless networks. Computer Science Division, University of California, 1–20.
Monowar, M. M., Hassan, M. M., Bajaber, F., Hamid, M. A., & Alamri, A. (2014). Thermal-aware multiconstrained intrabody QoS routing for wireless body area networks. International Journal of Sensor Networks,2014(676312), 1–14.
Balanis, C. A. (2006). Antenna theory, analysis and design (3rd ed., p. 1073). Hoboken: Wiley.
Tang, Q., Tummala, N., Gupta, S. K. S., & Schwiebert, L. (2005). TARA : Thermal-aware routing algorithm for implanted sensor networks. In Proceedings of 1st IEEE international conference on distributed computing in sensor systems (pp. 206–217). Marina del Rey, CA, USA.
Pennes, H. H. (1948). Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperature in the resting human forearm. Journal of Applied Physiology,1(2), 93–122.
Bangash, J. I., Abdullah, A. H., Khan, A. W., Razzaque, M. A., & Yusof, R. (2015). Critical data routing (CDR) for intra wireless body sensor networks. Telkomnika,13(1), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.12928/telkomnika.v13i1.365.
Zhou, Q., Cao, X., Chen, S., & Lin, G. (2009). A solution to error and loss in wireless network transfer. In International conference on wireless networks and information systems, WNIS ‘09 (Vol., pp. 312, 315). 28–29 December 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sagar, A.K., Singh, S. & Kumar, A. Energy-Aware WBAN for Health Monitoring Using Critical Data Routing (CDR). Wireless Pers Commun 112, 273–302 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07026-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07026-6