Abstract
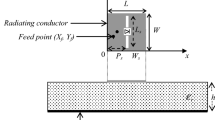
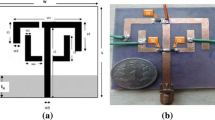
The modern wireless communication system requires high performance portable devices, thus designing of such communicating devices plays a major role. More particularly, meander shape is selected over the traditional shapes of microstrip patch antenna for the application of portable device antenna. Accordingly, in this paper, orthogonal meander architecture along with PIN diodes are proposed to achieve vertical and horizontal polarization. Further, to control switching of PIN diodes, Raspberry PI system is employed. In the proposed method, a novel meander-shaped antenna is designed and simulated using High-Frequency Structure Simulator-11 (HFSS-11) with an operating frequency of 2.4 GHz. However, the optimized design dimensions are used to fabricate the antenna and then the results are verified. This paper highlights the simulated and experimental results including, S-Parameter, radiation pattern, current distribution, co and cross polarization, path loss and impedance. Besides, the paper demonstrates the effect of cover on the antenna performance. Finally, the proposed meander shape reconfigurable antenna have validated as a portable device antenna from the obtained results for wireless communication applications.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, Ming-Chun, Zhou, B., & Ziolkowski, R. W. (2017). Low-profile, electrically small, huygens source antenna with pattern-reconfigurability that covers the entire azimuthal plane. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,65(3), 1063–1072.
Bouida, Zied, El-Sallabi, H., Ghrayeb, A., & Qaraqe, K. A. (2016). Reconfigurable antenna-based space-shift keying (SSK) for MIMO Rician channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,15(1), 446–457.
Yang, M., Jeon, S. W., & Kim, D. K. (2017). Linear degrees of freedom of MIMO broadcast channels with reconfigurable antennas in the absence of CSIT. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,63(1), 320–335.
Borda-Fortuny, Cristina, Tong, K.-F., Al-Armaghany, A., & Wong, K.-K. (2017). A low-cost fluid switch for frequency reconfigurable Vivaldi antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters,16, 3151–3154.
Ferrero, F., Lizzi, L., Staraj, R., & Ribero, J. M. (2016). Reconfigurable antenna for future spectrum reallocations in 5G communications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters,15, 1297–1300.
Ghassemiparvin, B., Shah, S., & Ghalichechian, N. (2017). Novel paraffin-based 100-GHz variable capacitors for reconfigurable antennas. In 2017 11th European conference on IEEE antennas and propagation (EUCAP) (pp. 3506–3510).
Poussot, Beno Ît, Laheurte, J.-M., Cirio, L., Picon, O., Delcroix, D., & Dussopt, L. (2008). Diversity measurements of a reconfigurable antenna with switched polarizations and patterns. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,56(1), 31–38.
Cai, Yong, Guo, Y. J., & Bird, T. S. (2012). A frequency reconfigurable printed Yagi-Uda dipole antenna for cognitive radio applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,60(6), 2905–2912.
Rodrigo, Daniel, & Cetiner, B. A. (2014). Frequency, radiation pattern and polarization reconfigurable antenna using a parasitic pixel layer. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,62(6), 3422–3427.
Rodriguez, E. G. (2016). Reconfigurable transceiver architecture for multiband RF-frontends. Berlin: Springer.
Rajagopalan, Harish, Rahmat-Samii, Y., & Imbriale, W. A. (2008). RF MEMS actuated reconfigurable reflectarray patch-slot element. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,56(12), 3689–3699.
Nikolaou, S., Bairavasubramanian, R., Lugo, C., Carrasquillo, I., Thompson, D. C., Ponchak, G. E., et al. (2006). Pattern and frequency reconfigurable annular slot antenna using PIN diodes. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,54(2), 439–448.
Lim, J. H., Back, G. T., Ko, Y. I., Song, C. W., & Yun, T. Y. (2010). A reconfigurable PIFA using a switchable PIN-diode and a fine-tuning varactor for USPCS/WCDMA/m-WiMAX/WLAN. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,58(7), 2404–2411.
Behdad, Nader, & Sarabandi, K. (2006). Dual-band reconfigurable antenna with a very wide tunability range. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,54(2), 409–416.
Zohur, A., Mopidevi, H., Rodrigo, D., Unlu, M., Jofre, L., & Cetiner, B. A. (2013). RF MEMS reconfigurable two-band antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters,12, 72–75.
Sanchez, L. F. (2015). Measurement of the radiation patterns of navy shipboard High Frequency (HF) antennas on a large warship, 0263-2241/_ 2015. Amsterdam: Elsevier Ltd.
Bittera, M., Smiesko, V., & Kovac, K. (2011). Modified uncertainty estimation of antenna factor measurement by standard site method. Amsterdam: Elsevier Ltd.
Kalteh, A. A., Zadeh, G. D., Naser-Moghadasi, M., et al. (2011). Implementation and investigation of circular slot UWB antenna with dual-band-notched Characteristics, Kalteh et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1499-2011-88.
Barousis, V. I., Kanatas, A. G., Kalis, A., Perruisseau-Carrier, J., et al. (2012). Reconfigurable parasitic antennas for compact mobile terminals in multiuser wireless systems, Barousis et al. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking,2012, 30.
Arun, V., & Marx, L. R. K. (2017). Micro-controlled tree shaped reconfigurable patch antenna with RF-energy harvesting. Wireless Personal Communications,94(4), 2769–2781.
Yadav, R., & Patel, P. N. (2017). EBG-inspired reconfigurable patch antenna for frequency diversity application. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,76, 2–59.
Barro, O. A., Himdi, M., & Lafond, O. (2016). Reconfigurable patch antenna radiations using plasma faraday shield effect. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters,15, 726–729.
Aoad, A., Simsek, M., & Aydin, Z. (2017). Knowledge based response correction method for design of reconfigurable N-shaped microstrip patch antenna using inverse ANNs. International Journal of Numerical Modelling: Electronic Networks, Devices and Fields,30(3–4), e2129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shashikant, K.R., Kulkarni, A. Reconfigurable Patch Antenna Design Using Pin Diodes and Raspberry PI for Portable Device Application. Wireless Pers Commun 112, 1809–1828 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07128-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07128-1