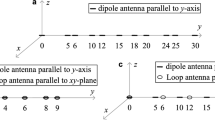
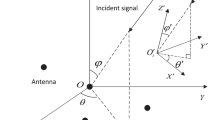
Abstract
Generally, multi-dimensional spectral peak search (SPS) in parameter estimation for polarization sensitive coprime linear arrays (PS-CLAs) requires heavy computational burden. To resolve this problem, we propose a search-free algorithm for multi-parameter estimation with PS-CLAs in this paper. Specifically, different from the decomposition algorithms, we first reconstruct the total received signal of PS-CLA as the signal extracted from a large uniform linear array, which enables to offer a spectrum function only with regard to direction of arrival (DOA) by utilizing rank reduction estimator. Subsequently, we employ the polynomial root finding technique instead of one-dimensional SPS to directly calculate the DOA estimates. Furthermore, a quadratic optimization problem is established for the polarization parameters and in particular, the closed-form solutions are provided by utilizing Lagrange multiplier approach. Finally, numerical simulations illustrate that the proposed search-free algorithm can obtain improved estimation accuracy with remarkably low complexity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
\(x \in \langle a, b\rangle\) refers to the set of integers which satisfies \(a \le x \le b.\)
\({\mathbf {I}}_{M}\) represents an \(M \times M\) identity matrix.
det\((\cdot )\) represents the determinant of the matrix.
References
Zhang, X. F., Xu, L. Y., Xu, L., & Xu, D. Z. (2010). Direction of departure (DOD) and direction of arrival (DOA) estimation in MIMO radar with reduced-dimension MUSIC. IEEE Communications Letters, 14(12), 1161–1163.
Li, J. F., Zhang, X. F., & Chen, H. (2012). Improved two-dimensional DOA estimation algorithm for two-parallel uniform linear arrays using propagator method. Signal Processing, 92(12), 3032–3038.
Wen, F. Q. (2019). Computationally efficient DOA estimation algorithm for MIMO radar with imperfect waveforms. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(6), 1037–1040.
Wang, H. F., Wan, L. T., & Dong, M. X. (2019). Assistant vehicle localization based on three collaborative base stations via SBL-based robust DOA estimation. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(3), 5766–5777.
Zhou, J., Wang, Y., & Kikuchi, H. (2016). Performance of a MIMO Y-shaped antenna array with electromagnetic vector sensors. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(3), 1141–1158.
Wang, L., Yang, L., Wang, G., & Wang, S. (2015). DOA and polarization estimation based on sparse COLD array. Wireless Personal Communications, 85(4), 2447–2462.
Ng, J. W. P., & Manikas, A. (2005). Polarisation-sensitive array in blind MIMO CDMA system. Electronics Letters, 41(17), 970–972.
Zhang, X. F., Chen, C., & Li, J. F. (2014). Blind DOA and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive array using dimension reduction MUSIC. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 25(1), 67–82.
Yuan, Q. W., Chen, Q., & Sawaya, K. (2006). MUSIC based DOA finding and polarization estimation using USV with polarization sensitive array antenna. In IEEE radio and wireless symposium (pp. 339–342).
Li, J., & Compton, R. T. (1991). Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 39(9), 1376–1383.
Li, J., & Compton, R. T. (1992). Two-dimensional angle and polarization estimation using the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 40(5), 550–555.
Zhang, X. F., Shi, Y., & Xu, D. Z. (2008). Novel blind joint direction of arrival and polarization estimation for polarization-sensitive uniform circular array. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, 86, 19–37.
Zhou, M., & Zhang, X. F. (2015). Joint estimation of angle and polarization for bistatic MIMO radar with polarization sensitive array using dimension reduction MUSIC. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(3), 1333–1345.
Si, W. J., Wang, Y., & Zhang, C. J. (2018). 2D-DOA and polarization estimation using a novel sparse representation of covariance matrix with COLD array. IEEE Access, 6, 66385–66395.
Han, Y., Fang, Q. Y., Yan, F. G., Jin, M., & Qiao, X. L. (2016). Joint DOA and polarization estimation for unequal power sources based on reconstructed noise subspace. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 27(3), 501–513.
Wang, X. P., Wan, L. T., Huang, M. X., Shen, C., & Zhang, K. (2019). Polarization channel estimation for circular and non-circular signals in massive MIMO systems. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing,. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2925786.
Steinberg, B. D. (1976). Principles of aperture and array system design: Including random and adaptive arrays. New York: Wiley.
Vaidyanathan, P. P., & Pal, P. (2011). Theory of sparse coprime sensing in multiple dimensions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(8), 3592–3608.
Pal, P., & Vaidyanathan, P. P. (2010). A novel array structure for directions-of-arrival estimation with increased degrees of freedom. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (pp. 2606–2609).
Zhou, C. W., Gu, Y. J., Fan, X., Shi, Z. G., Mao, G. Q., & Zhang, Y. M. (2018). Direction-of-arrival estimation for coprime array via virtual array interpolation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 66(22), 5956–5971.
Shi, Z. G., Zhou, C. W., Gu, Y. J., Goodman, N., & Qu, F. Z. (2016). Source estimation using coprime array: A sparse reconstruction perspective. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(3), 755–765.
Tan, Z., Eldar, Y. C., & Nehorai, A. (2014). Direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays: A super resolution viewpoint. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(21), 5565–5576.
Zhou, C. W., Shi, Z. G., Gu, Y. J., & Shen, X. M. (2013). DECOM: DOA estimation with combined MUSIC for coprime array. In IEEE international conference on wireless communications and signal processing (pp. 1–5).
Sun, F. G., Lan, P., & Gao, B. (2015). Partial spectral search-based DOA estimation method for co-prime linear arrays. Electronics Letters, 51(24), 2053–2055.
Zhang, D., Zhang, Y. S., Zheng, G. M., Deng, B. Y., Feng, C. Q., & Tang, J. (2017). Improved DOA estimation algorithm for co-prime linear arrays using root-MUSIC algorithm. Electronics Letters, 53(18), 1277–1279.
Zheng, W., Zhang, X. F., Gong, P., & Zhai, H. (2017). DOA estimation for coprime linear arrays: An ambiguity-free method involving full DOFs. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(3), 562–565.
Liu, A. H., Yang, Q., Zhang, X., & Deng, W. B. (2018). Modified root MUSIC for co-prime linear arrays. Electronics Letters, 54(15), 949–951.
See, C. M. S., & Gershman, A. B. (2004). Direction-of-arrival estimation in partly calibrated subarray-based sensor arrays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(2), 329–338.
Zhang, Y., Xu, X., Sheikh, Y. A., & Ye, Z. F. (2016). A rank-reduction based 2-D DOA estimation algorithm for three parallel uniform linear arrays. Signal Processing, 120, 305–310.
Barabell, A. (1983). Improving the resolution performance of eigenstructure-based direction-finding algorithms. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (Vol. 8, pp. 336–339).
Zheng, W., Zhang, X. F., & Shi, Z. (2017). Two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation for coprime planar arrays via a computationally efficient one-dimensional partial spectral search approach. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 11(10), 1581–1588.
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1990). Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 38(10), 1783–1795.
He, J., & Liu, Z. (2009). Computationally efficient 2D direction finding and polarization estimation with arbitrarily spaced electromagnetic vector sensors at unknown locations using the propagator method. Digital Signal Processing, 19(3), 491–503.
Zhang, X. F., & Xu, D. Z. (2007). Blind PARAFAC signal detection for polarization sensitive array. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 1, 125–131.
Zhang, X. F., Zheng, W., Chen, W. Y., & Shi, Z. (2019). Two-dimensional DOA estimation for generalized coprime planar arrays: A fast-convergence trilinear decomposition approach. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 30, 239–256.
Rao, B. D., & Hari, K. V. S. (1989). Performance analysis of root-music. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 37(12), 1939–1949.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by China NSF Grants (61371169, 61631020, 61971218, 61601167), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NT2019013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, B. et al. Reduced-Dimensional Polynomial Rooting-Based Multiple Parameter Estimation for Polarization Sensitive Coprime Arrays: A Full Array Extraction Perspective. Wireless Pers Commun 114, 731–748 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07390-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07390-3