Abstract
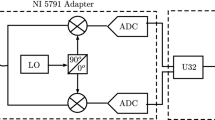
Automatic recognition of modulation scheme in blind environment plays a key role in many communication applications. A hierarchical and local density (HLD) approach is proposed to classify eight modulation schemes in a two stage process. In the first stage, the domain of modulation schemes (FSK, ASK, PSK, and QAM) is identified. FSK is identified based on feature extracted through complex envelope of downconverted signal. ASK scheme is identified using linear regression error. PSK and QAM modulation schemes are recognized based on the ratio of sixth and fourth order cumulant. In the latter stage, the order of modulation (ASK, PSK, and QAM) is classified through its respective ideal constellation points. HLD can correctly identify 2ASK, 4ASK, and QPSK modulation schemes in AWGN channel above 8 dB SNR and the other modulation schemes (8ASK, 8PSK, 16QAM, and 64QAM) above 16dB SNR. HLD is implemented in NI labVIEW and validated on the signals generated through PXIe-5673 and received using NI PXIe-5661. The proposed HLD classifier does not require any training to set thresholds as compared to more complex SVM, KNN, and Naive Bayes Classifier based techniques and shows an improved accuracy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmutalab, A., Assaleh, K., & El-Tarhuni, M. (2016). Automatic modulation classification based on high order cumulants and hierarchical polynomial classifiers. Physical Communication, 21, 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2016.08.001.
Ali, A., Yangyu, F., & Liu, S. (2017). Automatic modulation classification of digital modulation signals with stacked autoencoders. Digital Signal Processing, 71, 108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2017.09.005.
Aslam, M. W., Zhu, Z., & Nandi, A. K. (2012). Automatic modulation classification using combination of genetic programming and KNN. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(8), 2742–2750. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2012.060412.110460.
Chen, W., Xie, Z., Ma, L., Liu, J., & Liang, X. (2019). A faster maximum-likelihood modulation classification in flat fading non-Gaussian channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(3), 454–457.
Dobre, O.A., Bar-Ness, Y., & Su, W.: Higher-order cyclic cumulants for high order modulation classification. In Military communications conference, 2003. MILCOM’03. 2003 IEEE (Vol. 1, pp. 112–117). IEEE (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/MILCOM.2003.1290087
Ebrahimzadeh, A., & Ghazalian, R. (2011). Blind digital modulation classification in software radio using the optimized classifier and feature subset selection. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 24(1), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2010.08.008.
Ebrahimzadeh, A., & Mousavi, S. (2011). Classification of communications signals using an advanced technique. Applied Soft Computing, 11(1), 428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.12.001.
Hameed, F., Dobre, O. A., & Popescu, D. C. (2009). On the likelihood-based approach to modulation classification. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(12), 5884–5892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2009.12.080883.
Haykin, S. (2008). Communication systems. Hoboken: Wiley.
Hong, L., & Ho, K. (1999) . Identification of digital modulation types using the wavelet transform. In Military communications conference proceedings, 1999. MILCOM 1999. IEEE (Vol. 1, pp. 427–431). IEEE (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/MILCOM.1999.822719
Jajoo, G., Kumar, Y., Kumar, A., & Yadav, S. K. (2020). Implementation of modulation classifier over software defined radio. IET Communications, 14, 1467–1475. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-com.2019.0922.
Jajoo, G., Kumar, Y., & Yadav, S. K. (2019). Blind signal PSK/QAM recognition using clustering analysis of constellation signature in flat fading channel. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(10), 1853–1856.
Jajoo, G., Kumar, Y., Yadav, S. K., Adhikari, B., & Kumar, A. (2017). Blind signal modulation recognition through clustering analysis of constellation signature. Expert Systems with Applications, 90, 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.07.053.
Jajoo, G., Yadav, Y. K., & Yadav, S. (2018). Blind signal digital modulation classification through k-medoids clustering. In 2018 IEEE international conference on advanced networks and telecommunications systems (ANTS), Indore, India (pp. 1–5). https://doi.org/10.1109/ANTS.2018.8710107.
Keshk, M. E. H. M., El-Naby, M. A., Al-Makhlasawy, R. M., El-Khobby, H. A., Hamouda, W., Elnaby, M. M. A., et al. (2015). Automatic modulation recognition in wireless multi-carrier wireless systems with cepstral features. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(3), 1243–1288.
Kumar, Y., Sheoran, M., Jajoo, G., & Yadav, S. K. (2020). Automatic modulation classification based on constellation density using deep learning. IEEE Communications Letters, 24(6), 1275–1278. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2980840.
Mirarab, M., Sobhani, M. (2007). Robust modulation classification for PSK/QAM/ASK using higher-order cumulants. In 2007 6th International conference on information, communications and signal processing (pp. 1–4). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICS.2007.4449591
Mobasseri, B. G. (2000). Digital modulation classification using constellation shape. Signal Processing, 80(2), 251–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1684(99)00127-9.
Orlic, V. D., & Dukic, M. L. (2012). Automatic modulation classification: Sixth-order cumulant features as a solution for real-world challenges. In Telecommunications forum (TELFOR), 2012 20th (pp. 392–399). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/TELFOR.2012.6419230
Panagiotou, P., Anastasopoulos, A., & Polydoros, A. (2000). Likelihood ratio tests for modulation classification. In MILCOM 2000. 21st Century military communications conference proceedings (Vol. 2, pp. 670–674). https://doi.org/10.1109/MILCOM.2000.904013
Peng, S., Jiang, H., Wang, H., Alwageed, H., Zhou, Y., Sebdani, M. M., et al. (2019). Modulation classification based on signal constellation diagrams and deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 30(3), 718–727.
Phukan, G. J., & Bora, P. K. (2014). An algorithm for blind symbol rate estimation using second order cyclostationarity. In 2014 International conference on signal processing and communications (SPCOM) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPCOM.2014.6983923
Satija, U., Manikandan, M., & Ramkumar, B. (2014) . Performance study of cyclostationary based digital modulation classification schemes. In 2014 9th International conference on industrial and information systems (ICIIS) (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIINFS.2014.7036609
Sethi, A., & Ray, B. (2013) . Blind carrier/timing recovery and detection of modulation scheme. US Patent 8605830
Wong, M. D., & Nandi, A. K. (2001). Automatic digital modulation recognition using spectral and statistical features with multi-layer perceptrons. In Sixth international, symposium on signal processing and its applications, 2001 (Vol. 2, pp. 390–393). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSPA.2001.950162
Wong, M. D., Ting, S. K., & Nandi, A. K. (2008). Naive Bayes classification of adaptive broadband wireless modulation schemes with higher order cumulants. In 2nd International conference on signal processing and communication systems, 2008. ICSPCS 2008 (pp. 1–5). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSPCS.2008.4813755
Wu, H. C., Saquib, M., & Yun, Z. (2008). Novel automatic modulation classification using cumulant features for communications via multipath channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(8), 3098–3105. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2008.070015.
Yadav, Y. K., Jajoo, G., & Yadav, S. K. (2017). Modulation scheme detection of blind signal using constellation graphical representation. In: 2017 International conference on computer, communications and electronics (Comptelix) (pp. 231–235). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMPTELIX.2017.8003970
Acknowledgements
This project is funded by Defense Research and Development Organization under Grant number S/DRDO/SKY/20150004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jajoo, G., Kumar, Y., Kumar, A. et al. Blind Signal Modulation Recognition through Density Spread of Constellation Signature. Wireless Pers Commun 114, 3137–3156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07521-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07521-w