Abstract
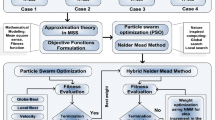
In this study, optimum channel estimation in MIMO network is investigated by an integrated computing paradigm using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Nelder Mead Method (NMM). The efficacy of global optimization is exploited through PSO while for fine-tuning of channel coefficients, the strength of NMM as an efficient local optimization technique is utilized. Hybrid swarm intelligence framework is applied for square channel matrix having identical array elements at both transmitter and receiver end. Different signal–noise ratios are applied for analyzing the response of complex received signal from flat fading Additive White Gaussian Noise channel. Numerical simulations are done for evaluating Mean Square Error among true and estimated channel coefficients. Performance analysis is conducted not only for a single run of proposed hybrid swarm intelligence but also on extensive simulations on multiple independent trials to prove the worth of the scheme.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Althahab, A. Q. J., et al. (2019). A comprehensive review on various estimation techniques for multi input multi output channel. Journal of University of Babylon for Engineering Sciences, 27(1), 262–274.
Huang, H., et al. (2018). Deep learning for super-resolution channel estimation and DOA estimation based massive MIMO system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(9), 8549–8560.
Telatar, E. (1999). Capacity of multi-antenna Gaussian channels. European Transactions on Telecommunications, 10(6), 585–596.
Foschini, G. J. (1996). Layered space-time architecture for wireless communication in fading environments when using multi-element antennas. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 1(2), 41–59.
Molisch, A. (2005). Wireless Communications. Hoboken: Wiley.
Gesbert, D., Shafi, M., Shiu, D., Smith, P., & Naguib, A. (2003). From theory to practice: an overview of MIMO space-time coded wireless systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 21(3), 281–302.
Dai, L., Zhou, S., Zhuang, H., & Yao, Y. (2002). Closed-loop MIMO architecture based on water filling. Electronics Letters, 38(25), 1718–1720.
Zheng, K., Huang, L., Wang, W., & Yang, G. (2005). TD-CDM-OFDM: Evolution of TD-SCDMA toward 4G. IEEE Communications Magazine, 43(1), 45–52.
Sampath, H., Talwar, S., Tellado, J., Erceg, V., & Paulraj, A. (2002). A fourth-generation MIMO-OFDM broadband wireless system: design, performance, and field trial results. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(9), 143–149.
Garg, J., et al. (2013). Performance analysis of MIMO wireless communications over fading channels—A review. International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, 2(4), 1272–1302.
Joseph, W. et al (2007). Influence of channel models and MIMO on the performance of a system based on IEEE 802.16, wireless communications and networking conference, ISBN 1-4244-0659-5, (pp. 1826–1830).
Qiao, Y. T., Yu, S., Su, P., & Zhang, L. (2005). Research on an iterative algorithm of LS channel estimation in MIMO OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 51(1), 149–153.
Tsoulos, G. (2006). MIMO system technology for wireless communications. Boca Raton: CRC Publisher.
Ali, M., et al. (2017). MIMO channel estimation using the LS and MMSE algorithm. IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, 12(1), 13–22.
Pinar, C., & Besdok, E. (2016). A conceptual comparison of the Cuckoo-search, particle swarm optimization, differential evolution and artificial bee colony algorithms. Artificial Intelligence Review, 39(4), 315–346.
Yang, X.S., Deb, S. (2009). Cuckoo search via levy flights world congress on nature and biologically inspired computing. Nabic-2009, (vol. 4, pp. 210–214). Coimbatore, India.
Geem, Z. W., Kim, J. H., & Loganathan, G. V. (2001). A new heuristic optimization algorithm: Harmony search. Simulation, 76, 60–68.
Goldberg, D. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Alias, M. Y., Chen, S., & Hanzo, L. (2005). Multiple-antenna-aided OFDM employing genetic-algorithm-assisted minimum bit error rate multiuser detection. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 54(5), 1713–1721.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks, (pp. 1942–1948).
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. C. (2001). Swarm intelligence. Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann.
Gao, Y., Li, Z., Hu, X., & Liu, H. (2007). A multi-population particle swarm optimizer and its application to blind multichannel estimation. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on natural computation (ICNC’07), Haikou, China.
Bodur, H., Tunc, C. A., Aktas, D., Erturk, V. B., & Altintas, A. (2007). Particle swarm optimization for SAGE maximization step in channel parameter estimation. In Proceedings of the 2nd European conference on antennas and propagation (EuCAP’07), Ankara, Turkey.
Schmeink, K., Block, R., Knievel, C., & Hoeher, P. A. (2010). Joint channel and parameter estimation for combined communication and navigation using particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 7th workshop on positioning navigation and communication (WPNC’10), Dresden, Germany.
Cheng, C. -H., Hsu, H. -C., Huang, Y. -F., Wen, J. -H., & Hsu, L. -C. (2010). Performance of an adaptive PSO parallel interference canceller for CDMA communication systems. In Proceedings of the 5th annual ICST wireless internet conference (WICON’10), Singapore.
Soo, K. K., Siu, Y. M., Chan, W. S., Yang, L., & Chen, R. S. (2007). Particle-swarm-optimization-based multiuser detector for CDMA communications. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 56(5), 3006–3013.
Palally, H., Chen, S., Yao, W., & Hanzo, L. (2009). Particle swarm optimisation aided semi-blind joint maximum likelihood channel estimation and data detection for MIMO systems. In Journal of electrical and computer engineering proceedings of the IEEE/SP 15th workshop on statistical signal processing (SSP’09), (pp. 309–312).
Vidhya, K., & Kumar, K. R. S. (2014). Channel estimation of MIMO–OFDM system using PSO and GA. Arabian Journal for Science & Engineering, 39(5), 4047–4056.
Khan, J. A., Raja, M. A. Z., Rashidi, M. M., Syam, M. I., & Wazwaz, A. M. (2015). Nature-inspired computing approach for solving non-linear singular Emden-Fowler problem arising in electromagnetic theory. Connection Sciences, 27(4), 377–396.
Akbar, S., Raja, M. A. Z., Zaman, F., Mehmood, T. & Khan, M. A. R. (2017). Design of bio-inspired heuristic techniques hybridized with sequential quadratic programming for joint parameters estimation of electromagnetic plane waves. Wireless Personal Communications, 96(1), 1475–1494.
Christopher, K., & Hoeher, P. A. (2012). On particle swarm optimization for MIMO channel estimation. London: Hindawi Publishing Corp.
Tao, S., Jiadong, X., & Kai, Z. (2007). Blind MIMO identification using particle swarm algorithm. In Proceedings of the international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WiCom’07), Shanghai, China.
Dong, W., Li, J., & Lu, Z. (2008). Joint frequency offset and channel estimation for MIMO systems based on particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE 67th vehicular technology conference (VTC’08-Spring), Singapore.
Ali, W., & Li, Y. (2019). Design of Nature Inspired Computing Approach for Estimation of Channel Coefficients in MIMO Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 107(4), 2047–2069.
Tyagi, M. M. (2017) Mimo channel estimation using fast converging evolutionary optimization algorithm. International Journal of Advance Research, Ideas and Innovations in Technology, 3(3), 130–136.
AsadUllah, M. et al. (2018). Blind channel and data estimation using fuzzy logic-empowered opposite learning-based mutant particle swarm optimization. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 6759526. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6759526.
Funding
This research is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Grant Nos. 11574250 and 11874302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, W., Li, Y., Tanoli, S.A.K. et al. Integrated Swarming Computing Paradigm for Efficient Estimation of Channel Parameters in MIMO System. Wireless Pers Commun 115, 77–102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07562-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07562-1