Abstract
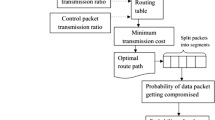
Existing energy efficient multi path routing protocol in Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) are not spatially disjoint and did not consider link availability and queuing delay. Hence an energy efficient disjoint multipath routing protocol using Simulated Annealing technique is proposed in this paper. In this protocol, routing will be performed based on the path cost and link cost metric, which in turn is dependent on the network and node characteristics like link availability, network load, battery drain rate, etc. Thus, the nodes selected for routing will be appropriate and will ensure successful data delivery at the destination. Since this technique takes into consideration all the minute network and node features, it can be assured that most of the network failure situations can be avoided, and thus guaranteeing efficient network operation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Rango, F., Guerriero, F., & Fazio, P. (2012). Link-Stability and Energy aware Routing Protocol in Distributed Wireless Networks. IEEE Transactions On Parallel And Distributed Systems, 23(4), 213–226
Xin Li, Zhe Li. (2009). LBAMR: A Load Balancing and Asymmetrical Multi-path Routing. In: 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, China.
Sungwook K (2014) Adaptive MANET Multipath Routing Algorithm Based on the Simulated Annealing Approach. Journal of scientific world. Article ID 872526, pp.1–8.
Nasehi, H., Javan, N. T., Aghababa, A. B., & Birgani, Y. G. (2013). Improving Energy Efficiency in MANETS By Multi-Path Routing. International Journal of Wireless & Mobile Networks, 5(1), 163–176
Aye, M. C., & Aung, A. M. (2014). Energy Efficient Multipath Routing For Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. International Journal of Information Technology, Modelling and Computing, 2(3), 11–18
Zhu, J., & Wang, X. (2011). Model and Protocol for Energy-Efficient Routing over Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing., 10(11), 1546–1557
Almobaideen, W., Al-Soub, R., & Sleit, A. (2013). MSDM: Maximally Spatial Disjoint Multipath Routing Protocol for MANET. Journal of Communications and Network, 5(4), 316–322
Sarkara, S., & Datta, R. (2015). A secure and energy-efficient stochastic multipath routing for self-organized mobile ad hoc networks. Journal of Ad-hoc networks, Elsevier, 37(2), 209–227
Jamali, S., Rezaei, L., & Gudakahriz, S. J. (2013). An Energy-efficient Routing Protocol for MANETs: A Particle Swarm Optimization Approach. Journal of Applied Research and Technology, 11(6), 803–812
Prabha, R., & Ramraj, N. (2015). An improved multipath MANET routing using link estimation and swarm intelligence. Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 9, 1–16.
Zhang, Y., Yan, T., Tian, J., Qi, H., Wang, G., & Li, Z. (2014). A topology-hiding Multipath routing protocol in mobile ad hoc networks. Elsevier. Ad-Hoc Networks, 21(6), 109–122
Ayyasamy, R., & Subramani, P. (2012). An Enhanced Distributed Certificate Authority Scheme for Authentication in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, 9(3), 2–39
Das, S. K., & Tripathi, S. (2018). Energy efficient routing formation algorithm for hybrid ad-hoc network: A geometric programming approach. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 12(1), 1102–1128
Das, S. K., & Tripathi, S. (2018). Adaptive and intelligent energy efficient routing for transparent heterogeneous ad-hoc network by fusion of game theory and linear programming. Applied Intelligence, 48(7), 1825–1845
Das, S. K., & Tripathi, S. (2018). Intelligent energy-aware efficient routing for MANET. Wireless Networks, 24(4), 1139–1159
Das, S. K., & Tripathi, S. (2017). Energy efficient routing formation technique for hybrid ad hoc network using fusion of artificial intelligence techniques. International journal of communication systems, 30(16), e3340
Harold Robinson, Y., & Rajaram, M. (2015). Energy-Aware Multipath Routing Scheme Based on Particle Swarm Optimization in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. The Scientific World Journal, 5, 1–9
Kim, S. (2014). Adaptive MANET multipath routing algorithm based on the simulated annealing approach. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. The Scientific World Journal, 4, 1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, C.N., Kukunuru, N. Energy Efficient Disjoint Multipath Routing Protocol Using Simulated Annealing in MANET. Wireless Pers Commun 120, 1027–1042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08502-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08502-3