Abstract
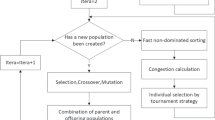
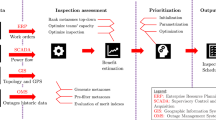
Large-scale power grids, especially smart grid systems, consist of a huge amount of complex computerized electronic devices, such as smart meters. A smart maintenance system is desired to schedule and send maintenance worker to locations where any computerized devices become faulty. A grid management system (GMS) is purposely designed in the way that the following three conditions are generally fulfilled: 1) all workers are working on full capacity everyday; 2) the highest severity level faulty devices are fixed the quickest; and 3) the overall traveling distance/time is minimized. In this study, two intelligent grid maintenance framework are proposed considering the above three conditioned based on two state-of-arts algorithms, namely, genetic algorithm and K-mediods clustering method, respectively. Five real-world datasets collected from five different local cities/counties in eastern China are adopted and applied to verify the effectiveness of the two proposed intelligent grid maintenance frameworks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jarrah, O.Y., Yoo, P.D., Muhaidat, S., Karagiannidis, G.K., Taha, K.: Efficient machine learning for big data: a review. Big Data Research 2(3), 87–93 (2015)
Berge, C., Minieka, E.: Graphs and hypergraphs (1973)
Bhanu, B., Lee, S., Ming, J.: Adaptive image segmentation using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 25(12), 1543–1567 (1995)
Bishnu, P.S., Bhattacherjee, V.: Application of k-medoids with kd-tree for software fault prediction. ACM SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes 36(2), 1–6 (2011)
Bui, N., Castellani, A.P., Casari, P., Zorzi, M.: The internet of energy: a Web-enabled smart grid system. IEEE Netw. 26(4), 39–45 (2012)
Cai, B., Huang, L., Xie, M.: Bayesian networks in fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 13(5), 2227–2240 (2017)
Chen, X.W., Lin, X.: Big data deep learning: challenges and perspectives. IEEE access 2, 514–525 (2014)
Colak, I.: Introduction to smart grid. In: Smart Grid Workshop and Certificate Program (ISGWCP). International, pp. 1–5, IEEE (2016)
Desai, B., Lebow, M.: Needed: asap approach, intelligent fleet management for transformers: a risk-based approach. IEEE Power Energ. Mag. 8(6), 53–60 (2010)
Domingos, P.: A few useful things to know about machine learning. Commun. ACM 55(10), 78–87 (2012)
Fan, W., Bifet, A.: Mining big data: current status, and forecast to the future. ACM sIGKDD Explorations Newsletter 14(2), 1–5 (2013)
Fei, S.w., Zhang, X.b.: Fault diagnosis of power transformer based on support vector machine with genetic algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications 36(8), 11:352–11:357 (2009)
Feng, J.X., Kusiak, A.: Data mining applications in engineering design, manufacturing and logistics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 44(14), 2689–2694 (2006)
Germán, M O, Molina, J.D., Romero, A.A., Gómez, H.D., García, E.: Power asset management: methods and experiences in colombian power system. In: Transmission & Distribution Conference and Exposition-Latin America (PES T&D-LA), 2014 IEEE PES, pp. 1–6, IEEE (2014)
Ijjina, E.P., Chalavadi, K.M.: Human action recognition using genetic algorithms and convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 59, 199–212 (2016)
Isermann, R.: Fault-diagnosis applications: model-based condition monitoring: actuators, drives, machinery, plants, sensors, and fault-tolerant systems. Springer Science & Business Media (2011)
Jardine, A.K., Lin, D., Banjevic, D.: A review on machinery diagnostics and prognostics implementing condition-based maintenance. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 20 (7), 1483–1510 (2006)
Jiang, H., Zhang, J.J., Gao, W., Wu, Z.: Fault detection, identification, and location in smart grid based on data-driven computational methods. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 5(6), 2947–2956 (2014)
Jordan, M.I., Mitchell, T.M.: Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 349(6245), 255–260 (2015)
Juntunen, T., Kostakos, V., Perttunen, M., Ferreira, D.: Web tool for traffic engineers: direct manipulation and visualization of vehicular traffic using google maps. In: Proceeding of the International Academic Mindtrek Conference, pp 209–210 (2012)
Kaufman, L., Rousseeuw, P.: Clustering by means of medoids. North-Holland (1987)
Lee, J., Ni, J., Djurdjanovic, D., Qiu, H., Liao, H.: Intelligent prognostics tools and e-maintenance. Comput. Ind. 57(6), 476–489 (2006)
Lei, R., Xue, L., Le, X., Liu, W.: Coordinated energy cost management of distributed internet data centers in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(1), 50–58 (2012)
Lei, Y., He, Z., Zi, Y., Chen, X.: New clustering algorithm-based fault diagnosis using compensation distance evaluation technique. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 22(2), 419–435 (2008)
Lu, H., Chen, J., Yan, K., Jin, Q., Xue, Y., Gao, Z.: A hybrid feature selection algorithm for gene expression data classification. Neurocomputing 256, 56–62 (2017)
Mühlenbein, H., Schomisch, M., Born, J.: The parallel genetic algorithm as function optimizer. Parallel Comput. 17(6-7), 619–632 (1991)
Najafabadi, M.M., Villanustre, F., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Seliya, N., Wald, R., Muharemagic, E.: Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. Journal of Big Data 2(1), 1 (2015)
Nelson, V.P.: Fault-tolerant computing: Fundamental concepts. Computer 23 (7), 19–25 (1990)
Qin, S.J.: Survey on data-driven industrial process monitoring and diagnosis. Annu. Rev. Control. 36(2), 220–234 (2012)
Rai, A., Upadhyay, S.: Bearing performance degradation assessment based on a combination of empirical mode decomposition and k-medoids clustering. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 93, 16–29 (2017)
Siewiorek, D.P., Swarz, R.S.: The theory and practice of reliable system design. Digital press (1982)
Singh, S.S., Chauhan, N.: K-means v/s k-medoids: A comparative study. In: National Conference on Recent Trends in Engineering & Technology, vol. 13 (2011)
Skiena, S.: Dijkstra algorithm. Implementing Discrete mathematics: Combinatorics and Graph Theory with Mathematica, pp 225–227. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1990)
Spears, W.M.: Crossover or mutation? In: Foundations of Genetic Algorithms, vol 2. pp 221–237, Elsevier (1993)
Srinivas, M., Patnaik, L.M.: Adaptive probabilities of crossover and mutation in genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 24(4), 656–667 (1994)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement learning: An introduction. MIT press (2018)
Venkatasubramanian, V., Rengaswamy, R., Kavuri, S.N., Yin, K.: A review of process fault detection and diagnosis: Part iii: Process history based methods. Comput. Chem. Eng. 27(3), 327–346 (2003)
Viswanadham, N., Johnson, T.: Fault detection and diagnosis of automated manufacturing systems. In: Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 1988, pp. 2301–2306. IEEE (1988)
Wang, W., Chen, H., Lou, B., Jin, N., Lou, X., Yan, K.: Data-driven intelligent maintenance planning of smart meter reparations for large-scale smart electric power grid. In: 2018 IEEE Smartworld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced & Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Cloud & Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation (SmartWorld/SCALCOM/UIC/ATC/CBDCom/IOP/SCI), pp. 1929–1935. IEEE (2018)
Whitley, D.: A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat. Comput. 4(2), 65–85 (1994)
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Hall, M.A., Pal, C.J.: Data Mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann (2016)
Wu, X., Zhu, X., Wu, G.Q., Ding, W.: Data mining with big data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(1), 97–107 (2014)
Wu, Y.J., Wang, Y., Qian, D.: A google-map-based arterial traffic information system. In: Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, 2007. ITSC 2007, pp. 968?-973. IEEE (2007)
Yan, K., Ji, Z., Lu, H., Huang, J., Shen, W., Xue, Y.: Fast and accurate classification of time series data using extended elm: Application in fault diagnosis of air handling units. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems (2017)
Yan, K., Zhong, C., Ji, Z., Huang, J.: Semi-supervised learning for early detection and diagnosis of various air handling unit faults. Energ. Buildings 181, 75–83 (2018)
Yang, J., Wu, C., Lee, H.P., Liang, Y.: Solving traveling salesman problems using generalized chromosome genetic algorithm. Prog. Nat. Sci. 18(7), 887–892 (2008)
Zhong, C., Yan, K., Dai, Y., Jin, N., Lou, B.: Energy efficiency solutions for buildings: Automated fault diagnosis of air handling units using generative adversarial networks. Energies 12(3), 527 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61850410531). It is also partially supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LY19F020016 and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61602431). A previous version of this paper titled ‘Data-Driven Intelligent Maintenance Planning of Smart Meter Reparations for Large-Scale Smart Electric Power Grid’ was published with The 4th IEEE International Conference on Internet of People (IoP 2018) on October 8-12, 2018, at Guangzhou in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Smart Computing and Cyber Technology for Cyberization
Guest Editors: Xiaokang Zhou, Flavia C. Delicato, Kevin Wang, and Runhe Huang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Lou, B., Li, X. et al. Intelligent maintenance frameworks of large-scale grid using genetic algorithm and K-Mediods clustering methods. World Wide Web 23, 1177–1195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00705-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00705-w