Abstract
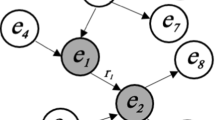
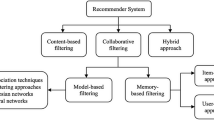
Knowledge graph-aware recommendation has become an important research topic in recent years. The user preference representation, which preserves the user’s taste towards items (e.g., movies, books.), is obtained through aggregating the information of entities or attributes in knowledge graphs directly. However, the fine-grained heterogeneity information, which can be derived from the groups of items or entities, remains barely exploited in the process of encoding the user interaction intention for the items. To fill up this gap, we propose a Multistage Clustering-based Hierarchical Attention (McHa) model to capture the user preference representation. In our work, we first group the items and their neighboring entities in the knowledge graph into item clusters and entity clusters (jointly referred to as multistage clusters), respectively. Then, the user preference representation is obtained by hierarchically aggregating the heterogeneity information derived from the multistage clusters with the weights generated by the hierarchical attention layers. We conduct extensive experimental comparisons with baselines and the variants. The experimental results indicate that McHa has achieved state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets in two scenarios.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, Q., Azizi, V., Chen, X., Zhang, Y.: Learning heterogeneous knowledge base embeddings for explainable recommendation. Algorithms 11(9), 137 (2018)
Auer, S., Bizer, C., Kobilarov, G., Lehmann, J., Cyganiak, R., et al.: Dbpedia: A nucleus for a web of open data. In: The Semantic Web, pp. 722–735. Springer (2007)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2787–2795 (2013)
Chen, H.-C., Wei, C.-P., Dai, Y.-S., Lin, Y.-K.: Exploiting item heterogeneity for collaborative filtering recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 4th China Summer Workshop on Information Management (2010)
Chen, T., Yin, H, Ye, G., Huang, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, M.: Try this instead: Personalized and interpretable substitute recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 891–900 (2020)
Chen, C., Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Ma, S.: Neural attentional rating regression with review-level explanations. In: Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, pp 1583–1592 (2018)
Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Qin, Z.: Dynamic explainable recommendation based on neural attentive models. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 53–60 (2019)
Chen, J., Yu, J., Lu, W., Qian, Y., Li, P.: Ir-rec: An interpretive rules-guided recommendation over knowledge graph. Information Sciences 563, 326–341 (2021)
Chicaiza, J., Valdiviezo-Diaz, P.: A comprehensive survey of knowledge graph-based recommender systems: Technologies, development, and contributions. Information 12(6), 232 (2021)
Eissa, A.H.B., El-Sharkawi, M.E., Mokhtar, H.M.O.: Towards recommendation using interest-based communities in attributed social networks. In: Companion Proceedings of the The Web Conference 2018, pp. 1235–1242 (2018)
Fu, Z., Xian, Y., Gao, R., Zhao, J., Huang, Q., Ge, Y, Xu, S., Geng, S., Shah, C., Zhang, Y., et al.: Fairness-aware explainable recommendation over knowledge graphs. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 69–78 (2020)
Gao, R., Shah, C.: How fair can we go: Detecting the boundaries of fairness optimization in information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGIR International Conference on Theory of Information Retrieval, pp. 229–236 (2019)
Gao, J., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Xie, X.: Explainable recommendation through attentive multi-view learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 3622–3629 (2019)
Ge, Y., Liu, S., Gao, R., Xian, Y., Li., Y., Zhao, X., Pei, C., Sun, F., Ge, J., Ou, W. et al.: Towards long-term fairness in recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 445–453 (2021)
Geyik, S.C., Ambler, S., Kenthapadi, K.: Fairness-aware ranking in search & recommendation systems with application to linkedin talent search. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2221–2231 (2019)
Guo, Q., Zhuang, F., Qin, C., Zhu, H., Xie, X., et al.: A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems. arXiv:2003.00911 (2020)
Hou, Y., Yang, N., Wu, Y., Yu, P.S.: Explainable recommendation with fusion of aspect information. World Wide Web 22(1), 221–240 (2019)
Hu, B., Shi, C., Zhao, W.X., Yu, P.S.: Leveraging meta-path based context for top-n recommendation with a neural co-attention model. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1531–1540 (2018)
Hu, X., Xu, J., Wang, W., Li, Z., Liu, A.: A graph embedding based model for fine-grained poi recommendation. Neurocomputing 428, 376–384 (2021)
Huang J., et al.: Improving sequential recommendation with knowledge-enhanced memory networks. In: The 41st International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 505–514 (2018)
Huang, X., Fang, Q., Qian, S., Sang, J., Li, Y., Xu, C.: Explainable interaction-driven user modeling over knowledge graph for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 548–556 (2019)
Huang, Y., Zhao, F., Gui, X., Jin, H.: Path-enhanced explainable recommendation with knowledge graphs. World Wide Web 24(5), 1769–1789 (2021)
Ji, S., Pan, S., Cambria, E., Marttinen, P., Philip, S.Y.: A survey on knowledge graphs: Representation, acquisition, and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst (2021)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Koren, Y.: Factorization meets the neighborhood: a multifaceted collaborative filtering model. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 426–434 (2008)
Li, Q., Tang, X., Wang, T., Yang, H., Song, H.: Unifying task-oriented knowledge graph learning and recommendation. IEEE Access 7, 115816–115828 (2019)
Lin, H., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Yue, Y., Lin, Z.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge resolution. Procedia Computer Science 108, 345–354 (2017)
Liu, J., Duan, L.: A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems. In: 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), vol. 5, pp. 2450–2453. IEEE (2021)
Liu, F., Xue, S., Wu, J., Zhou, C., Hu, W., Paris, C., Nepal, S., Yang, J., Yu, P.S.: Deep learning for community detection: Progress, challenges and opportunities. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 5, pp. 4981–4987 (2020)
Lops, P., Gemmis, M.D., Semeraro, G.: Content-based recommender systems: state of the art and trends. Springer, US (2011)
Lu, L., Shin, Y., Su, Y., Karniadakis, G.E.: Dying relu and initialization: Theory and numerical examples. arXiv:1903.06733 (2019)
Ma, X., Wu, J., Xue, S., Yang, J., Zhou, C., Sheng, Q.Z., Xiong, H., Akoglu, L.: A comprehensive survey on graph anomaly detection with deep learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng, 1–1 (2021)
Ma, W., Zhang, M., Cao, Y., Jin, W., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Ma, S., Ren, X.: Jointly learning explainable rules for recommendation with knowledge graph. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 1210–1221 (2019)
Mansoury, M., Abdollahpouri, H., Pechenizkiy, M., Mobasher, B., Burke, R.: Fairmatch: A graph-based approach for improving aggregate diversity in recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization, pp. 154–162 (2020)
Paleti, L., Krishna, P.R., Murthy, J.V.R.: Approaching the cold-start problem using community detection based alternating least square factorization in recommendation systems. Evolutionary Intelligence 14(2), 835–849 (2021)
Palumbo, E., Rizzo, G., Troncy, R.: Entity2rec: Learning user-item relatedness from knowledge graphs for top-n item recommendation. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 32–36 (2017)
Qian, R.: Understand your world with bing. Bing search blog (2013)
Qu, Y., Bai, T., Zhang, W., Nie, J., Tang, J.: An end-to-end neighborhood-based interaction model for knowledge-enhanced recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Deep Learning Practice for High-Dimensional Sparse Data, pp. 1–9 (2019)
Rendle, S., Freudenthaler, C., Gantner, Z., Schmidt-Thieme, L.: Bpr: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback. arXiv:1205.2618 (2012)
Satuluri, V., Wu, Y., Zheng, X., Qian, Y., Wichers, B., Dai, Q., Tang, G.M., Jiang, J., Lin, J.: Simclusters: Community-based representations for heterogeneous recommendations at twitter. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 3183–3193 (2020)
Seo, S., Huang, J., Yang, H., Liu, Y.: Interpretable convolutional neural networks with dual local and global attention for review rating prediction. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 297–305 (2017)
Shafqat, W., Byun, Y.-C.: Incorporating similarity measures to optimize graph convolutional neural networks for product recommendation. Applied Sciences 11(4), 1366 (2021)
Su, X., Xue, S., Liu, F., Wu, J., Yang, J., Zhou, C., Hu, W., Paris, C., Nepal, S., Jin, D., Sheng, Q.Z., Yu, P.S.: A comprehensive survey on community detection with deep learning. arXiv:2105.12584 (2021)
Suchanek, F.M., Kasneci, G., Weikum, G.: Yago: a core of semantic knowledge. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 697–706 (2007)
Sun, Z., Yang, J., Zhang, J., Bozzon, A., Huang, L.-K., Xu, C.: Recurrent knowledge graph embedding for effective recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 297–305 (2018)
Tai, C.-Y., Wu, M.-R., Chu, Y.-W., Chu, S.-Y., Ku, L.-W.: Mvin: Learning multiview items for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 99–108 (2020)
Tang, X., et al.: Akupm: Attention-enhanced knowledge-aware user preference model for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 1891–1899 (2019)
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. arXiv:1710.10903 (2017)
Vrandečić, D.: Wikidata: A new platform for collaborative data collection. In: The World Wide Web Conference. pp. 1063–1064 (2012)
Wang, H., et al.: Multi-task feature learning for knowledge graph enhanced recommendation. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 2000–2010 (2019)
Wang, X., He, X., Cao, Y., Liu, M., Chua, T.-S.: Kgat: Knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 950–958 (2019)
Wang, X., Wang, D., Xu, C., He, X., Cao, Y., Chua, T.-S.: Explainable reasoning over knowledge graphs for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 5329–5336 (2019)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Aaai, vol. 14, pp. 1112–1119. Citeseer (2014)
Wang, H., Zhang, F., Hou, M., Xie, X., Guo, M., Liu, Q.: Shine: Signed heterogeneous information network embedding for sentiment link prediction. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 592–600 (2018)
Wang, H., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Zhao, M., Li, W., Xie, X., Guo, M.: Ripplenet: Propagating user preferences on the knowledge graph for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 417–426 (2018)
Wang, H., Zhao, M., et al.: Knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommender systems. In: The World Wide Web Conference, pp. 3307–3313 (2019)
Wu, L., Chen, L., Shao, P., Hong, R., Wang, X., Wang, M.: Learning fair representations for recommendation: A graph-based perspective. In: Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, pp. 2198–2208 (2021)
Xian, Y., Fu, Z., Muthukrishnan, S., De Melo, G., Zhang, Y.: Reinforcement knowledge graph reasoning for explainable recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 285–294 (2019)
Xian, Y., Zhao, T., Li, J., Chan, J., Kan, A., Ma, J., Dong, X.L., Faloutsos, C., Karypis, G., Muthukrishnan, S., Zhang Y.: Ex3: Explainable attribute-aware item-set recommendations. In: Fifteenth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 484–494 (2021)
Xie, L., Hu, Z., Cai, X., Zhang, W., Chen, J.: Explainable recommendation based on knowledge graph and multi-objective optimization. Complex & Intelligent Systems 7(3), 1241–1252 (2021)
Yang, Z., Yang, D., Dyer, C., He, X., Smola, A., Hovy, E.: Hierarchical attention networks for document classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 1480–1489 (2016)
Yu, X., Ren, X., Sun, Y., Sturt, B., Khandelwal, U., et al.: Recommendation in heterogeneous information networks with implicit user feedback. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 347–350 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Lai, G., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Ma, S.: Explicit factor models for explainable recommendation based on phrase-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 37th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research&; Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 83–92 (2014)
Zhang, F., Yuan, N.J., Lian, D., et al.: Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 353–362 (2016)
Zhao, H., Yao, Q., Li, J., Song, Y., Lee, D.L.: Meta-graph based recommendation fusion over heterogeneous information networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 635–644 (2017)
Zhao, J., Zhou, Z., Guan, Z., Zhao, W., Ning, W., Qiu, G., He, X.: Intentgc: a scalable graph convolution framework fusing heterogeneous information for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp. 2347–2357 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China (No.2018YFB1003804) and the Project of State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company (2020A-135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shi, Y., Li, D. et al. McHa: a multistage clustering-based hierarchical attention model for knowledge graph-aware recommendation. World Wide Web 25, 1103–1127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01022-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-022-01022-5