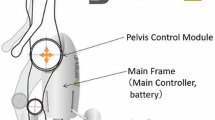
Abstract
This paper presents the design and control of a novel assistive robotic walker that we call “JAIST active robotic walker (JARoW)”. JARoW is developed to provide potential users with sufficient ambulatory capability in an efficient, cost-effective way. Specifically, our focus is placed on how to allow easier maneuverability by creating a natural interface between the user and JARoW. For the purpose, we develop a rotating infrared sensor to detect the user’s lower limb movement. The implementation details of the JARoW control algorithms based on the sensor measurements are explained, and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms is verified through experiments. Our results confirmed that JARoW can autonomously adjust its motion direction and velocity according to the user’s walking behavior without requiring any additional user effort.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Topping M (2000) An overview of development of Handy-1, a rehabilitation robot to assist the severely disabled. Artif Life Robot 4(4): 188–192
Soyama R, Ishii S, Fukase A (2003) The development of meal-assistance robot ‘My Spoon’. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE international conference on rehabilitation robotics, pp 88–91
Romer GRBE, Stuyt HJA, Peters G, Woerden KV (2003) The current and future processes for obtaining a ‘Manus’ (ARM) rehabrobot within the Netherlands. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE international conference on rehabilitation robotics, pp 9–12
Ikeda H, Katsumata Y, Shoji M, Takahashi T, Nakano E (2008) Cooperative strategy for a wheelchair and a robot to climb and descend a step. Adv Robot 22(13–14): 1439–1460
Kuo C-H, Yeh H-W, Wu C-E (2007) Development of autonomous navigation robotic wheelchairs using programmable system-on-chip based distributed computing architecture. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, pp 2939–2944
Shim I, Yoon J, Yoh M (2004) A human robot interactive system ‘RoJi’. Int J Control Automation Syst 2(3): 398–405
Yu H, Spenko M, Dubowsky S (2003) An adaptive shared control system for an intelligent mobility aid for the elderly. Auton Robot 15(1): 53–66
Mori Y, Okada J, Takayama K (2006) Development of a standing style transfer system ‘able’ for disabled lower limbs. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 11(4): 372–380
Kinnaird CR, Ferris DP (2009) Medial gastrocnemius myoelectric control of a robotic ankle exoskeleton. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 17(1): 31–37
Suzuki K, Mito G, Kawamoto H, Hasegawa Y, Sankai Y (2007) Intention-based walking support for paraplegia patients with robot suit HAL. Adv Robot 21(12): 1441–1469
Zoss AB, Kazerooni H, Chu A (2006) Biomechanical design of the berkeley lower extremity exoskeleton (BLEEX). IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 11(2): 128–138
Hirata Y, Hara A, Kosuge K (2007) Motion control of passive intelligent walker using servo brakes. IEEE Trans Robot 23(5): 981–990
Veg A, Popovic DB (2008) Walkaround: mobile balance support for therapy of walking. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 16(3): 264–269
Kulyukin V, Kutiyanawala A, LoPresti E, Matthews J, Simpson R (2008) iWalker: toward a rollator-mounted wayfinding system for the elderly. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on RFID, pp 303–311
Lacey GJ, Rodriguez-Losada D (2008) The evolution of guido. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 15(4): 75–83
Kong K, Jeon D (2006) Design and control of an exoskeleton for the elderly and patients. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 11(4): 428–432
Kobayashi H, Karato T, Tsuji T (2007) Development of an active walker as a new orthosis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on mechatronics and automation, pp 186–191
Tani M, Suzuki R, Furuya S, Kobayashi N (2004) Internal model control for assisting unit of wheeled walking frames. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on control applications, pp 928–933
Rentschler AJ, Simpson R, Cooper RA, Boninger ML (2008) Clinical evaluation of Guido robotic walker. J Rehabil Res Dev 45(9): 1281–1294
Hashimoto H, Sasaki A, Ohyama Y, Ishii C (2006) Walker with hand haptic interface for spatial recognition. In: Proceedings of the 9th IEEE international workshop on advanced motion control, pp 311–316
Morris A, Donamukkala R, Kapuria A, Steinfeld A., Matthews J, Dunbar-Jacobs J, Thrun S (2003) A robotic walker that provides guidance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 25–30
Lacey G, MacNamara S (2000) User involvement in the design and evaluation of a smart mobility aid. J Rehabil Res Dev 37(6): 709–723
Rentschler AJ, Cooper RA, Blasch B, Boninger ML (2003) Intelligent walkers for the elderly: performance and safety testing of VA-PAMAID robotic walker. J Rehabil Res Dev 40(5): 423–432
Graf B (2009) An adaptive guidance system for robotic walking aids. J Comput Inf Technol 17(1): 109–120
Shim H-M, Lee E-H, Shim J-H, Lee S-M, Hong S-H (2005) Implementation of an intelligent walking assistant robot for the elderly in outdoor environment. In: Proceedings of the 9th IEEE international conference on rehabilitation robotics, pp 452–455
Graf B, Hans M, Schraft RD (2004) Care-O-bot II—development of a next generation robotic home assistant. Auton Robots 16(2): 193–205
Kulyukin V (2004) Human–robot interaction through gesture-free spoken dialogue. Auton Robots 16(3): 239–257
MacNamara S, Lacey G (2000) A smart walker for the frail visually impaired. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1354–1359
Yano H, Hosomi Y, Aoki K, Nanba R, Hirotomi T, Satoru Okamoto (2008) Unstable motion detect system for four-casterd walker. IEICE technical report, Speech 107(434): 13–18 (in Japanese)
Rodriguez RV, Lewis RP, Mason JSD, Evans NWD (2008) Footstep recognition for a smart home environment. Int J Smart Home 2(2): 95–110
Hirasawa M, Okada H, Shimojo M (2007) The development of the plantar pressure sensor shoes for gait analysis. J Robot Mechatron 20(3): 324–330
Kong K, Tomizuka M (2008) Smooth and continuous human gait phase detection based on foot pressure patterns. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 3678–3683
Burnfield JM, Powers CM (2006) Normal and pathologic gait. In: Placzek JD, Boyce DA (eds) Orthopaedic physical therapy secrets. 2nd edn. Hanley and Belfus, Philadelphia
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2002) Digital image processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Vince J (2004) Geometry for computer graphics: formulae, examples and proofs. Springer, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G., Ohnuma, T. & Chong, N.Y. Design and control of JAIST active robotic walker. Intel Serv Robotics 3, 125–135 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-010-0064-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-010-0064-5