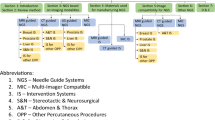
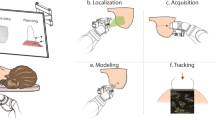
Abstract
Medical robotics is an interdisciplinary field that came into existence to improve medical procedures utilizing robotics technology. Medical robotics range from minimally invasive surgeries using robots to robots that support patients in rehabilitation to image-guided systems for different medical interventions. Different advantages of robots made them appealing to be used for medical interventions. Among these advantages are being precise, untiring, dexterous, and the ability to work in environments that are not safe to human clinicians. Steerable needles are a type of medical devices that can steer around obstacles to reach a target location and thus can improve the accuracy of medical procedures. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the state-of-the-art and research challenges in robotic needle steering. First off, the motivations, including clinical motivations behind needle steering, are demonstrated, and then the state of the art of the different needle steering techniques in the literature are analyzed. This includes their modeling, path planning, control, and clinical applications. Finally, a discussion of the advantages and limitations of the existing techniques that hindered the clinical acceptance of the steerable needles, along with suggestions to get these needles closer to their clinical applications, as well as concluding remarks, is provided.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayazid M, Roesthuis RJ, Reilink R, Misra S (2012) Integrating deflection models and image feedback for real-time flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Rob 29(2):542–553
Abayazid M, Moreira P, Shahriari N, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Misra S (2015) Ultrasound-guided three-dimensional needle steering in biological tissue with curved surfaces. Med Eng Phys 37(1):145–150
Abayazid M, Kemp M, Misra S (2013) 3d flexible needle steering in soft-tissue phantoms using fiber Bragg grating sensors. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 5843–5849
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2007) Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med Eng Phys 29(4):413–431
Adebar TK, Okamura AM (2014) Recursive estimation of needle pose for control of 3d-ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 4303–4308
Adebar TK, Fletcher AE, Okamura AM (2014) 3-d ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering in biological tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(12):2899–2910
Adebar TK, Greer JD, Laeseke PF, Hwang GL, Okamura AM (2015) Methods for improving the curvature of steerable needles in biological tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(6):1167–1177
Adebar TK, Greer JD, Laeseke PF, Hwang GL, Okamura AM (2016) Methods for improving the curvature of steerable needles in biological tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63(6):1167–1177
Alterovitz R, Goldberg KY, Pouliot J, Hsu IC (2008) Sensorless motion planning for medical needle insertion in deformable tissues. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 13(2):217–225
Alterovitz R, Goldberg K, Okamura A (2005) Planning for steerable bevel-tip needle insertion through 2d soft tissue with obstacles. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 1640–1645
Alterovitz R, Lim A, Goldberg K, Chirikjian GS, Okamura AM (2005) Steering flexible needles under Markov motion uncertainty. In: 2005 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 1570–1575
Alterovitz R, Siméon T, Goldberg K (2007) The stochastic motion roadmap: a sampling framework for planning with Markov motion uncertainty. Robotics: In Science and Systems, Atlanta, United States. ffhal-01987480f
Ayvali E, Liang CP, Ho M, Chen Y, Desai JP (2012) Towards a discretely actuated steerable cannula for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Int J Robot Res 31(5):588–603
Babaiasl M, Boccelli S, Chen Y, Yang, F, Ding JL, Swensen JP (2020) Predictive mechanics based model for depth of cut (DOC) of waterjet in soft tissue for waterjet-assisted medical applications. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 58(8): 1845–1872
Babaiasl M, Yang F, Boccelli S, Swensen JP (2020) Fracture-directed waterjet needle steering: design, modeling, and path planning. In: 2020 international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics (BioRob). IEEE
Babaiasl M, Yang F, Chen Y, Ding JL, Swensen JP (2019) Predicting depth of cut of water-jet in soft tissue simulants based on finite element analysis with the application to fracture-directed water-jet steerable needles. In: 2019 international symposium on medical robotics (ISMR). IEEE, pp 1–7
Babaiasl M, Yang F, Swensen JP (2018) Towards water-jet steerable needles. In: 2018 7th IEEE international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics (Biorob). IEEE, pp 601–608
Babaiasl M, Yang F, Swensen JP (2020) Duty cycling of waterjet can improve steerability and radius-of-curvature (roc) for waterjet steerable needles. In: 2020 international symposium on medical robotics (ISMR). IEEE
Bernardes MC, Adorno BV, Poignet P, Borges GA (2012) Semi-automatic needle steering system with robotic manipulator. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 1595–1600
Bernardes MC, Adorno BV, Poignet P, Zemiti N, Borges GA (2011) Adaptive path planning for steerable needles using duty-cycling. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 2545–2550
Bernardes M, Adorno BV, Poignet P, Borges G (2013) Robot-assisted automatic insertion of steerable needles with closed-loop imaging feedback and intraoperative trajectory replanning. Mechatronics 23(6):630–645
Bernardes MC, Adorno BV, Borges GA, Poignet P (2014) 3d robust online motion planning for steerable needles in dynamic workspaces using duty-cycled rotation. J Control Autom Electr Syst 25(2):216–227
Black RJ, Ryu S, Moslehi B, Costa JM (2014) Characterization of optically actuated MRI-compatible active needles for medical interventions. In: Behavior and mechanics of multifunctional materials and composites 2014, vol 9058. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 90580J
Bui VK, Park S, Park JO, Ko SY (2016) A novel curvature-controllable steerable needle for percutaneous intervention. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H] 230(8):727–738
Burgner J, Swaney PJ, Lathrop RA, Weaver KD, Webster RJ (2013) Debulking from within: a robotic steerable cannula for intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(9):2567–2575
Burrows C, Secoli R, y Baena FR (2013) Experimental characterisation of a biologically inspired 3D steering needle. In: 2013 13th international conference on control, automation and systems (ICCAS 2013). IEEE, pp 1252–1257
Cannon LM, Fagan AJ, Browne JE (2011) Novel tissue mimicking materials for high frequency breast ultrasound phantoms. Ultrasound Med Biol 37(1):122–135
Ceh D, Peters TM, Chen EC (2015) Acoustic characterization of polyvinyl chloride and self-healing silicone as phantom materials. In: Medical imaging 2015: physics of medical imaging, vol 9412. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 94123G
Chatelain P, Krupa A, Navab N (2015) 3d ultrasound-guided robotic steering of a flexible needle via visual servoing. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 2250–2255
Chen AI, Balter ML, Chen MI, Gross D, Alam SK, Maguire TJ, Yarmush ML (2016) Multilayered tissue mimicking skin and vessel phantoms with tunable mechanical, optical, and acoustic properties. Med Phys 43(6Part1):3117–3131
Chentanez N, Alterovitz R, Ritchie D, Cho L, Hauser KK, Goldberg K, Shewchuk JR, O’Brien JF (2009) Interactive simulation of surgical needle insertion and steering. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2009 papers, pp 1–10
Datla NV, Hutapea P (2015) Flexure-Based Active Needle for Enhanced Steering Within Soft Tissue. ASME J Med Devices 9(4): 041005
de Carvalho IM, De Matheo LL, Júnior JFSC, de Melo Borba C, von Krüger MA, Infantosi AFC, de Albuquerque Pereira WC (2016) Polyvinyl chloride plastisol breast phantoms for ultrasound imaging. Ultrasonics 70:98–106
De Falco I, Culmone C, Menciassi A, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2018) A variable stiffness mechanism for steerable percutaneous instruments: integration in a needle. Med Biol Eng Comput 56(12):2185–2199
de Jong TL, Pluymen LH, van Gerwen DJ, Kleinrensink GJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2017) PVA matches human liver in needle-tissue interaction. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 69:223–228
Dehghan E, Salcudean SE (2009) Needle insertion parameter optimization for brachytherapy. IEEE Trans Rob 25(2):303–315
DiMaio SP, Salcudean S (2003) Needle steering and model-based trajectory planning. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 33–40
DiMaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005) Interactive simulation of needle insertion models. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(7):1167–1179
DiMaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005) Needle steering and motion planning in soft tissues. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(6):965–974
Donder A, Baena FRY (2021) Kalman-filter-based, dynamic 3-d shape reconstruction for steerable needles with fiber bragg gratings in multicore fibers. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 38(4):2262–2275
Duindam V, Alterovitz R, Sastry S, Goldberg K (2008) Screw-based motion planning for bevel-tip flexible needles in 3D environments with obstacles. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 2483–2488
Dupont PE, Lock J, Itkowitz B, Butler E (2009) Design and control of concentric-tube robots. IEEE Trans Rob 26(2):209–225
Dupont P, Gosline A, Vasilyev N, Lock J, Butler E, Folk C, Cohen A, Chen R, Schmitz G, Ren H, et al (2012) Concentric tube robots for minimally invasive surgery. In: Hamlyn symposium on medical robotics, vol 7, p 8
Duriez C, Guébert C, Marchal M, Cotin S, Grisoni L (2009) Interactive simulation of flexible needle insertions based on constraint models. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 291–299
Engh JA, Podnar G, Kondziolka D, Riviere CN (2006) Toward effective needle steering in brain tissue. In: 2006 international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, pp 559–562
Engh JA, Minhas DS, Kondziolka D, Riviere CN (2010) Percutaneous intracerebral navigation by duty-cycled spinning of flexible bevel-tipped needles. Neurosurgery 67(4):1117–1123
Fallahi B, Rossa C, Sloboda RS, Usmani N, Tavakoli M (2016) Sliding-based switching control for image-guided needle steering in soft tissue. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 1(2):860–867
Farrer AI, Odéen H, de Bever J, Coats B, Parker DL, Payne A, Christensen DA (2015) Characterization and evaluation of tissue-mimicking gelatin phantoms for use with MRGFUS. J Ther Ultrasound 3(1):9
Fonseca M, Zeqiri B, Beard P, Cox B (2016) Characterisation of a phantom for multiwavelength quantitative photoacoustic imaging. Phys Med Biol 61(13):4950
Forte AE, Galvan S, Manieri F, y Baena FR, Dini D (2016) A composite hydrogel for brain tissue phantoms. Mater Des 112:227–238
Frasson L, Ko S, Turner A, Parittotokkaporn T, Vincent JF, Rodriguez y Baena F (2010) Sting: a soft-tissue intervention and neurosurgical guide to access deep brain lesions through curved trajectories. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H J Eng Med 224(6):775–788
Gerboni G, Greer JD, Laeseke PF, Hwang GL, Okamura AM (2017) Highly articulated robotic needle achieves distributed ablation of liver tissue. IEEE robotics and automation letters 2(3): 1367–1374
Gilbert HB, Neimat J, Webster RJ (2015) Concentric tube robots as steerable needles: achieving follow-the-leader deployment. IEEE Trans Rob 31(2):246–258
Glozman D, Shoham M (2007) Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Robot 23(3):459–467
Glozman D, Shoham M (2007) Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Rob 23(3):459–467
Glozman D, Shoham M (2004) Flexible needle steering and optimal trajectory planning for percutaneous therapies. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 137–144
Goksel O, Dehghan E, Salcudean SE (2009) Modeling and simulation of flexible needles. Med Eng Phys 31(9):1069–1078
Grimm PD, Blasko JC, Sylvester JE, Meier RM, Cavanagh W (2001) 10-year biochemical (prostate-specific antigen) control of prostate cancer with 125i brachytherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 51(1):31–40
Ha J, Fagogenis G, Dupont PE (2018) Modeling tube clearance and bounding the effect of friction in concentric tube robot kinematics. IEEE Trans Rob 35(2):353–370
Haddadi A, Hashtrudi-Zaad K (2011) Development of a dynamic model for bevel-tip flexible needle insertion into soft tissues. In: 2011 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, pp 7478–7482
Hamzé N, Peterlík I, Cotin S, Essert C (2016) Preoperative trajectory planning for percutaneous procedures in deformable environments. Comput Med Imaging Graph 47:16–28
Hauser K, Alterovitz R, Chentanez N, Okamura A, Goldberg K (2009) Feedback control for steering needles through 3d deformable tissue using helical paths. In: Robotics science and systems: online proceedings, vol 37
Hungr N, Long JA, Beix V, Troccaz J (2012) A realistic deformable prostate phantom for multimodal imaging and needle-insertion procedures. Med Phys 39(4):2031–2041
Ilami M, Ahmed RJ, Petras A, Beigzadeh B, Marvi H (2020) Magnetic needle steering in soft phantom tissue. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11
Jiang S, Liu S, Feng W (2011) PVA hydrogel properties for biomedical application. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(7):1228–1233
Jiang S, Su Z, Wang X, Liu S, Yu Y (2013) Development of a new tissue-equivalent material applied to optimizing surgical accuracy. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):3768–3774
Jiang S, Hata N, Kikinis R (2008) Needle insertion simulation for image-guided brachytherapy of prostate cancer. In: 2008 2nd international conference on bioinformatics and biomedical engineering. IEEE, pp 1682–1685
Joinié-Maurin M, Bayle B, Gangloff J (2011) Force feedback teleoperation with periodical disturbance compensation. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 4828–4833
Kallem V, Cowan NJ (2007) Image-guided control of flexible bevel-tip needles. In: Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE, pp 3015–3020
Kato T, Okumura I, Song SE, Golby AJ, Hata N (2014) Tendon-driven continuum robot for endoscopic surgery: preclinical development and validation of a tension propagation model. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 20(5):2252–2263
Kaye DR, Stoianovici D, Han M (2014) Robotic ultrasound and needle guidance for prostate cancer management: review of the contemporary literature. Curr Opin Urol 24(1):75
Khadem M, Rossa C, Usmani N, Sloboda RS, Tavakoli M (2016) A two-body rigid/flexible model of needle steering dynamics in soft tissue. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 21(5):2352–2364
Khadem M, Rossa C, Usmani N, Sloboda RS, Tavakoli M (2017) Robotic-assisted needle steering around anatomical obstacles using notched steerable needles. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22(6):1917–1928
Khadem M, Fallahi B, Rossa C, Sloboda RS, Usmani N, Tavakoli M (2015) A mechanics-based model for simulation and control of flexible needle insertion in soft tissue. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA. IEEE), pp 2264–2269
Khadem M, Rossa C, Usmani N, Sloboda RS, Tavakoli M (2016) Introducing notched flexible needles with increased deflection curvature in soft tissue. In: Advanced intelligent mechatronics (AIM), 2016 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, pp 1186–1191
Kim Y, Parada GA, Liu S, Zhao X (2019) Ferromagnetic soft continuum robots. Science. Robotics 4(33):eaax7329
Ko SY, y Baena FR (2012) Toward a miniaturized needle steering system with path planning for obstacle avoidance. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(4):910–917
Ko SY, y Baena FR (2012) Trajectory following for a flexible probe with state/input constraints: an approach based on model predictive control. Robot Auton Syst 60(4):509–521
Ko SY, Frasson L, y Baena FR (2011) Closed-loop planar motion control of a steerable probe with a “programmable bevel’’ inspired by nature. IEEE Trans Rob 27(5):970–983
Konh B, Honarvar M, Darvish K, Hutapea P (2017) Simulation and experimental studies in needle-tissue interactions. J Clin Monit Comput 31(4):861–872
Konh B, Sasaki D, Podder TK, Ashrafiuon H (2020) 3d manipulation of an active steerable needle via actuation of multiple SMA wires. Robotica 38(3):410–426
Konh B, Motalleb M (2017) Evaluating the performance of an advanced smart needle prototype inside tissue. In: Active and passive smart structures and integrated systems 2017, vol 10164. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 101640G
Konh B, Podder TK (2017) Design and fabrication of a robust active needle using SMA wires. In: 2017 Design of medical devices conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection
Krupa A (2014) A new duty-cycling approach for 3d needle steering allowing the use of the classical visual servoing framework for targeting tasks. In: 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics. IEEE, pp 301–307
Lee J, Park W (2014) A probability-based path planning method using fuzzy logic. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 2978–2984
Lee J, Wang J, Park W (2018) Efficient Mechanism Design and Systematic Operation Planning for Tube-Wire Flexible Needles. ASME. J. Mechanisms Robotics 10(6): 065001
Lehmann T, Sloboda R, Usmani N, Tavakoli M (2018) Model-based needle steering in soft tissue via lateral needle actuation. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 3(4):3930–3936
Leibinger A, Forte AE, Tan Z, Oldfield MJ, Beyrau F, Dini D, y Baena FR (2016) Soft tissue phantoms for realistic needle insertion: a comparative study. Ann Biomed Eng 44(8):2442–2452
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Della Pina MC, Cioni D (2009) Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Abdom Imaging 34(5):547–556
Lezcano DA, Iordachita II, Kim JS (2020) Trajectory generation of FBG-sensorized needles for insertions into multi-layer tissue. In: 2020 IEEE SENSORS. IEEE, pp 1–4
Li P, Jiang S, Yu Y, Yang J, Yang Z (2015) Biomaterial characteristics and application of silicone rubber and PVA hydrogels mimicked in organ groups for prostate brachytherapy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 49:220–234
Li W, Belmont B, Shih A (2015) Design and manufacture of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tissue mimicking material for needle insertion. Procedia Manuf 1:866–878
Li W, Belmont B, Greve JM, Manders AB, Downey BC, Zhang X, Xu Z, Guo D, Shih A (2016) Polyvinyl chloride as a multimodal tissue-mimicking material with tuned mechanical and medical imaging properties. Med Phys 43(10):5577–5592
Li P, Yang Z, Jiang S (2018) Needle-tissue interactive mechanism and steering control in image-guided robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput 56(6):931–949
Li P, Yang Z, Jiang S (2018) Tissue mimicking materials in image-guided needle-based interventions: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 93:1116–1131
Liu Y, Ge Z, Yang S, Walker ID, Ju Z (2019) Elephant’s trunk robot: an extremely versatile under-actuated continuum robot driven by a single motor. J Mech Robot 11(5)
Lobo JR, Moradi M, Chng N, Dehghan E, Morris WJ, Fichtinger G, Salcudean SE (2011) Use of needle track detection to quantify the displacement of stranded seeds following prostate brachytherapy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(3):738–748
Losey DP, York PA, Swaney PJ, Burgner J, Webster III R.J (2013) A flexure-based wrist for needle-sized surgical robots. In: Medical imaging 2013: image-guided procedures, robotic interventions, and modeling, vol 8671. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 86711G
Lyons LA, Webster RJ, Alterovitz R (2010) Planning active cannula configurations through tubular anatomy. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 2082–2087
Maghsoudi A, Jahed M (2012) Needle dynamics modelling and control in prostate brachytherapy. IET Control Theory Appl 6(11):1671–1681
Majewicz A, Marra SP, Van Vledder MG, Lin M, Choti MA, Song DY, Okamura AM (2012) Behavior of tip-steerable needles in ex vivo and in vivo tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(10):2705–2715
Majewicz A, Okamura AM (2013) Cartesian and joint space teleoperation for nonholonomic steerable needles. In: 2013 world haptics conference (WHC). IEEE, pp 395–400
Majewicz A, Siegel JJ, Stanley AA, Okamura AM (2014) Design and evaluation of duty-cycling steering algorithms for robotically-driven steerable needles. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 5883–5888
Majewicz A, Wedlick TR, Reed KB, Okamura AM (2010) Evaluation of robotic needle steering in ex vivo tissue. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 2068–2073
Mallapragada VG, Sarkar N, Podder TK (2009) Robot-assisted real-time tumor manipulation for breast biopsy. IEEE Trans Rob 25(2):316–324
Matheson E, Secoli R, Burrows C, Leibinger A, Rodriguez y Baena F (2019) Cyclic motion control for programmable bevel-tip needles to reduce tissue deformation. J Med Robot Res 4(01):1842001
Meltsner M, Ferrier N, Thomadsen B (2007) Observations on rotating needle insertions using a brachytherapy robot. Phys Med Biol 52(19):6027
Mignon P, Poignet P, Troccaz J (2018) Automatic robotic steering of flexible needles from 3D ultrasound images in phantoms and ex vivo biological tissue. Ann Biomed Eng 46(9):1385–1396
Mignon P, Poignet P, Troccaz J (2016) Beveled-tip needle-steering using 3d ultrasound, mechanical-based Kalman filter and curvilinear ROI prediction. In: 2016 14th international conference on control, automation, robotics and vision (ICARCV). IEEE, pp 1–6
Minhas DS, Engh JA, Fenske MM, Riviere CN (2007) Modeling of needle steering via duty-cycled spinning. In: 2007 29th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, pp 2756–2759
Minton JA, Iravani A, Yousefi AM (2012) Improving the homogeneity of tissue-mimicking cryogel phantoms for medical imaging. Med Phys 39(11):6796–6807
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW, Ramesh K, Okamura AM (2010) Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int J Robot Res 29(13):1640–1660
Misra S, Reed KB, Douglas AS, Ramesh K, Okamura AM (2008) Needle-tissue interaction forces for bevel-tip steerable needles. In: Biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, 2008. BioRob 2008. 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on. IEEE, pp 224–231
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW, Ramesh K, Okamura AM (2009) Observations and models for needle-tissue interactions. In: 2009 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 2687–2692
Mora OC, Zanne P, Zorn L, Nageotte F, Zulina N, Gravelyn S, Montgomery P, de Mathelin M, Dallemagne B, Gora MJ (2020) Steerable oct catheter for real-time assistance during teleoperated endoscopic treatment of colorectal cancer. Biomed Opt Express 11(3):1231–1243
Moreira P, Misra S (2015) Biomechanics-based curvature estimation for ultrasound-guided flexible needle steering in biological tissues. Ann Biomed Eng 43(8):1716–1726
Moreira P, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Misra S (2014) Needle steering in biological tissue using ultrasound-based online curvature estimation. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 4368–4373
Narayan M, Choti MA, Fey AM (2019) Data-driven detection of needle buckling events in robotic needle steering. J Med Robot Res 4(02):1850005
Neubach Z, Shoham M (2009) Ultrasound-guided robot for flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(4):799–805
O’Brien K, Boyer ZR, Mart BG, Brolliar CT, Carroll TL, Fichera L (2019) Towards flexible steerable instruments for office-based laryngeal surgery. In: 2019 design of medical devices conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection
Okamura AM, Simone C, O’leary MD (2004) Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(10):1707–1716
Okazawa S, Ebrahimi R, Chuang J, Salcudean SE, Rohling R (2005) Hand-held steerable needle device. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 10(3):285–296
Park YL, Elayaperumal S, Daniel B, Ryu SC, Shin M, Savall J, Black RJ, Moslehi B, Cutkosky MR (2010) Real-time estimation of 3-d needle shape and deflection for MRI-guided interventions. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 15(6):906–915
Park W, Kim JS, Zhou Y, Cowan NJ, Okamura AM, Chirikjian GS (2005) Diffusion-based motion planning for a nonholonomic flexible needle model. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ieee international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 4600–4605
Park W, Reed KB, Okamura AM, Chirikjian GS (2010) Estimation of model parameters for steerable needles. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 3703–3708
Patel NA, van Katwijk T, Li G, Moreira P, Shang W, Misra S, Fischer GS (2015) Closed-loop asymmetric-tip needle steering under continuous intraoperative MRI guidance. In: 2015 37th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE, pp 4869–4874
Patil S et al (2011) Motion planning under uncertainty in highly deformable environments. In: Robotics science and systems: online proceedings
Patil S, Burgner J, Webster RJ, Alterovitz R (2014) Needle steering in 3-d via rapid replanning. IEEE Trans Rob 30(4):853–864
Patil S, Alterovitz R (2010) Interactive motion planning for steerable needles in 3d environments with obstacles. In: 2010 3rd IEEE RAS & embs international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics. IEEE, pp 893–899
Piccin O, Barbe L, Bayle B, De Mathelin M, Gangi A (2009) A force feedback teleoperated needle insertion device for percutaneous procedures. Int J Robot Res 28(9):1154–1168
Pratt RL, Petruska AJ (2022) Empirically comparing magnetic needle steering models using expectation-maximization. Robotics 11(2):49
Reed KB, Kallem V, Alterovitz R, Goldbergxz K, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2008) Integrated planning and image-guided control for planar needle steering. In: 2008 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics. IEEE, pp 819–824
Reed KB, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2009) Controlling a robotically steered needle in the presence of torsional friction. In: 2009 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 3476–3481
Reed KB, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2009) Modeling and control of needles with torsional friction. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(12):2905–2916
Reed KB, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2009) Modeling and control of needles with torsional friction. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(12):2905–2916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2009.2029240
Reed KB, Majewicz A, Kallem V, Alterovitz R, Goldberg K, Cowan NJ, Okamura AM (2011) Robot-assisted needle steering. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 18(4):35–46
Ritter RC, Quate EG, Gillies GT, Grady MS, Howard M, Broaddus WC (1998) Measurement of friction on straight catheters in in vitro brain and phantom material. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 45(4):476–485
Roesthuis RJ, Abayazid M, Misra S (2012) Mechanics-based model for predicting in-plane needle deflection with multiple bends. In: 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics (BioRob). IEEE, pp 69–74
Roesthuis RJ, van de Berg NJ, van den Dobbelsteen JJ, Misra S (2015) Modeling and steering of a novel actuated-tip needle through a soft-tissue simulant using fiber Bragg grating sensors. In: Robotics and automation (ICRA), 2015 IEEE international conference on. IEEE, pp 2283–2289
Romano JM, Webster RJ, Okamura AM (2007) Teleoperation of steerable needles. In: Proceedings 2007 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 934–939
Ros-Freixedes L, Gao A, Liu N, Shen M, Yang GZ (2019) Design optimization of a contact-aided continuum robot for endobronchial interventions based on anatomical constraints. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 14(7):1137–1146
Rucker DC, Webster RJ (2008) Mechanics-based modeling of bending and torsion in active cannulas. In: 2008 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics. IEEE, pp 704–709
Rucker DC, Das J, Gilbert HB, Swaney PJ, Miga MI, Sarkar N, Webster RJ (2013) Sliding mode control of steerable needles. IEEE Trans Rob 29(5):1289–1299
Ryou M, Benias PC, Kumbhari V (2020) Initial clinical experience of a steerable access device for EUS-guided biliary drainage. Gastrointest Endosc 91(1):178–184
Ryu SC, Quek ZF, Koh JS, Renaud P, Black RJ, Moslehi B, Daniel BL, Cho KJ, Cutkosky MR (2014) Design of an optically controlled MR-compatible active needle. IEEE Trans Rob 31(1):1–11
Scali M, Kreeft D, Breedveld P, Dodou D (2017) Design and evaluation of a wasp-inspired steerable needle. In: Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication 2017, vol 10162. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 1016207
Scali M, Veldhoven PA, Henselmans PW, Dodou D, Breedveld P (2019) Design of an ultra-thin steerable probe for percutaneous interventions and preliminary evaluation in a gelatine phantom. PloS one 14(9): p.e0221165
Sears P, Dupont P (2006) A steerable needle technology using curved concentric tubes. In: 2006 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 2850–2856
Secoli R, y Baena FR (2013) Closed-loop 3d motion modeling and control of a steerable needle for soft tissue surgery. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 5831–5836
Seifabadi R, Song SE, Krieger A, Cho NB, Tokuda J, Fichtinger G, Iordachita I (2012) Robotic system for MRI-guided prostate biopsy: feasibility of teleoperated needle insertion and ex vivo phantom study. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7(2):181–190
Seifabadi R, Aalamifar F, Iordachita I, Fichtinger G (2016) Toward teleoperated needle steering under continuous MRI guidance for prostate percutaneous interventions. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 12(3):355–369
Shahriari N, Heerink W, Van Katwijk T, Hekman E, Oudkerk M, Misra S (2017) Computed tomography (CT)-compatible remote center of motion needle steering robot: fusing CT images and electromagnetic sensor data. Med Eng Phys 45:71–77
Sheng J, Deaton NJ, Desai JP (2019) A large-deflection FBG bending sensor for SMA bending modules for steerable surgical robots. In: 2019 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 900–906
Sitzman BT, Uncles DR (1996) The effects of needle type, gauge, and tip bend on spinal needle deflection. Anesth Analg 82(2):297–301
Sun W, Alterovitz R (2014) Motion planning under uncertainty for medical needle steering using optimization in belief space. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 1775–1781
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3): 209–249
Swaney PJ, Burgner J, Pheiffer TS, Rucker DC, Gilbert HB, Ondrake JE, Simpson AL, Burdette EC, Miga MI, Webster III RJ (2012) Tracked 3D ultrasound targeting with an active cannula. In: Medical imaging 2012: image-guided procedures, robotic interventions, and modeling, vol 8316. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 83160R
Swaney PJ, Gilbert HB, Hendrick RJ, Commichau O, Alterovitz R, Webster III RJ (2015) Transoral steerable needles in the lung: How non-annular concentric tube robots can improve targeting. In: Hamlyn symposium. Medical robotics
Swaney PJ, Burgner J, Gilbert HB, Webster RJ (2012) A flexure-based steerable needle: high curvature with reduced tissue damage. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(4):906–909
Swaney PJ, Mahoney AW, Hartley BI, Remirez AA, Lamers E, Feins RH, Alterovitz R, Webster RJ III (2017) Toward transoral peripheral lung access: combining continuum robots and steerable needles. J Med Robot Res 2(01):1750001
Swensen JP, Cowan NJ (2012) Torsional dynamics compensation enhances robotic control of tip-steerable needles. In: Robotics and automation (ICRA), 2012 IEEE international conference on. IEEE, 1601–1606
Swensen JP, Lin M, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2014) Torsional dynamics of steerable needles: modeling and fluoroscopic guidance. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(11):2707–2717
Tang W, Wan TR (2014) Constraint-based soft tissue simulation for virtual surgical training. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(11):2698–2706
Torabi M, Hauser K, Alterovitz R, Duindam V, Goldberg K (2009) Guiding medical needles using single-point tissue manipulation. In: 2009 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 2705–2710
van de Berg NJ, van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2014) Design choices in needle steering—a review. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 20(5):2172–2183
van de Berg NJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2015) Design of an actively controlled steerable needle with tendon actuation and FBG-based shape sensing. Med Eng Phys 37(6):617–622
van de Berg NJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2017) Endpoint accuracy in manual control of a steerable needle. J Vasc Interv Radiol 28(2):276–283
van de Berg NJ, de Jong TL, van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2017) The influence of tip shape on bending force during needle insertion. Sci Rep 7:40477
Van Den Berg J, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Abbeel P, Goldberg K (2010) LQG-based planning, sensing, and control of steerable needles. In: Algorithmic foundations of robotics IX. Springer, pp 373–389
Vandini A, Bergeles C, Lin FY, Yang GZ (2015) Vision-based intraoperative shape sensing of concentric tube robots. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS). IEEE, 2603–2610
Vogt WC, Jia C, Wear KA, Garra BS, Pfefer TJ (2016) Biologically relevant photoacoustic imaging phantoms with tunable optical and acoustic properties. J Biomed Opt 21(10):101405
Wan G, Wei Z, Gardi L, Downey DB, Fenster A (2005) Brachytherapy needle deflection evaluation and correction. Med Phys 32(4):902–909
Wang TW, Spector M (2009) Development of hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds for brain tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 5(7):2371–2384
Wang J, Ha J, Dupont PE (2019) Steering a multi-armed robotic sheath using eccentric precurved tubes. In: 2019 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 9834–9840
Wang J, Li X, Zheng J, Sun D (2013) Mechanics-based modeling of needle insertion into soft tissue. In: 2013 IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics. IEEE, pp 38–43
Wang Y, Tai BL, Yu H, Shih AJ (2014) Silicone-Based Tissue-Mimicking Phantom for Needle Insertion Simulation. ASME. J. Med. Devices 8(2): 021001
Watts T, Secoli R, y Baena FR (2018) A mechanics-based model for 3-d steering of programmable bevel-tip needles. IEEE Trans Rob 35(2):371–386
Webster RJ, Memisevic J, Okamura AM (2005) Design considerations for robotic needle steering. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 3588–3594
Webster RJ, Okamura AM, Cowan NJ (2006) Toward active cannulas: miniature snake-like surgical robots. In: 2006 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 2857–2863
Webster RJ, Romano JM, Cowan NJ (2008) Kinematics and calibration of active cannulas. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, pp 3888–3895
Webster RJ III, Kim JS, Cowan NJ, Chirikjian GS, Okamura AM (2006) Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int J Robot Res 25(5–6):509–525
Webster RJ III, Romano JM, Cowan NJ (2008) Mechanics of precurved-tube continuum robots. IEEE Trans Rob 25(1):67–78
Wedlick TR, Okamura AM (2009) Characterization of pre-curved needles for steering in tissue. In: Engineering in medicine and biology society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Annual International Conference of the IEEE. IEEE, pp 1200–1203
Wellborn PS, Swaney PJ, Webster RJ (2016) Curving clinical biopsy needles: can we steer needles and still obtain core biopsy samples? J Med Devices 10(3): 030904
Wood NA, Lehocky CA, Riviere CN (2013) Algorithm for three-dimensional control of needle steering via duty-cycled rotation. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on mechatronics (ICM). IEEE, pp 237–241
Wood NA, Shahrour K, Ost MC, Riviere CN (2010) Needle steering system using duty-cycled rotation for percutaneous kidney access. In: 2010 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology. IEEE, pp 5432–5435
Xu J, Duindam V, Alterovitz R, Goldberg K (2008) Motion planning for steerable needles in 3d environments with obstacles using rapidly-exploring random trees and backchaining. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering. IEEE, pp 41–46
Yamaguchi S, Tsutsui K, Satake K, Morikawa S, Shirai Y, Tanaka HT (2014) Dynamic analysis of a needle insertion for soft materials: arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian-based three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med 53:42–47
Yan KG, Podder T, Yu Y, Liu TI, Cheng CW, Ng WS (2008) Flexible needle-tissue interaction modeling with depth-varying mean parameter: preliminary study. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(2):255–262
Yang F, Babaiasl M, Swensen JP (2019) Fracture-directed steerable needles. J Med Robot Res 4(01):1842002
Zell K, Sperl JI, Vogel MW, Niessner R, Haisch C (2007) Acoustical properties of selected tissue phantom materials for ultrasound imaging. Phys Med Biol 52(20):N475
Zhou Y, Thiruvalluvan K, Krzeminski L, Moore WH, Xu Z, Liang Z (2013) Ct-guided robotic needle biopsy of lung nodules with respiratory motion-experimental system and preliminary test. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 9(3):317–330
Funding
No funding is received from external resources to prepare this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
No humans and/or animals studies are conducted in the current manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babaiasl, M., Yang, F. & Swensen, J.P. Robotic needle steering: state-of-the-art and research challenges. Intel Serv Robotics 15, 679–711 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-022-00446-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-022-00446-2