Abstract
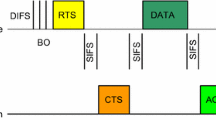
This paper presents a new reliable MAC protocol called “RMAC” supporting reliable multicast for wireless ad hoc networks. By utilizing the busy tones to realize the multicast reliability, RMAC has three novelties: (1) it uses a variable-length control frame to stipulate an order for the receivers to respond, thus solving the feedback collision problem; (2) it extends the usage of busy tone for preventing data frame collisions into the multicast scenario; and (3) it introduces a new usage of busy tone for acknowledging data frames positively. In addition, RMAC is generalized into a comprehensive MAC protocol that provides both reliable and unreliable services for all the three modes of communications: unicast, multicast, and broadcast, making it capable of supporting various upper-layer protocols. The evaluation shows that RMAC achieves high reliability with very limited overhead. RMAC is also compared with other reliable MAC protocols, showing that RMAC not only provides higher reliability but also involves lower cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEEE. Part 11: Wireless LAN MAC and PHY specifications. ANSI/IEEE Std. 802.11, 1999.
Mario Gerla, Ching-Chuan Chiang, Lixia Zhang. Tree multicast strategies in mobile multihop wireless networks. ACM/Balzter Mobile Network and Applications Journal, 1999, 4: 193–207.
Elizabeth M Royer, Charles E Perkins. Multicast operation of the ad hoc on-demand distance vector routing protocol. In Proc. ACM MobiCom'99, Seattle, Aug. 1999, pp.207–218.
Wu C, Tay Y. AMRIS: A multicast protocol for ad hoc wireless networks. In Proc. IEEE MILCOM'99, Atlantic City, NJ, Nov. 1999.
Bommaiah E, Liu M, McAuley A et al. AMRoute: Ad hoc multicast routing protocol. Internet Draft, IETF, Aug. 1998.
Lee S, Su W, Gerla M. Ad hoc wireless multicast with mobility prediction. In Proc. IEEE ICCCN'99, Boston, Oct. 1999.
Garcia-Luna-Aceves J J, Madruga E L. The core-assisted mesh protocol. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Aug. 1999, 17: 1380–1394.
Lee S J, Su W, Hsu J et al. A performance comparison study of ad hoc wireless multicast protocols. In Proc. IEEE INFOCOM'00, Tel Aviv, Israel, Mar. 2000.
David Eckhardt, Peter Steenkiste. Improving wireless LAN performance via adaptive local error control. In Proc. IEEE ICNP'98, 1998.
Yong Peng, Shi-Duan Cheng. Performance enhancement and bandwidth guarantee in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, Mar. 2004, 19(2): 150–157.
Don Towsley, James Kurose, Sridhar Pingali. A comparison of sender-initiated and receiver-initiated reliable multicast protocols. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Apr. 1997, 15: 398–406.
Kuri J, Kasera S K. Reliable multicast in multi-access wireless LANs. Wireless Networks, 2001, 7(3): 359–369.
Tang K, Gerla M. MAC reliable broadcast in ad hoc networks. In Proc. IEEE MILCOM 2001, Oct. 2001, pp.1008–1013.
Sun M T, Huang L, Arora A, Lai T H. MAC layer multicast in IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. In Proc. the International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP) 2002, 2002.
IEEE. Part 11: Wireless LAN MAC and PHY specifications: Higher-speed physical layer extension in the 2.4GHz band. ANSI/IEEE Std. 802.11b, 1999.
Gupta S K S, Shankar V, Lalwani S. Reliable multicast MAC protocol for wireless LANs. In Proc. IEEE ICC'03, May 2003.
Bertsekas D, Gallagher R G. Data Networks. Second Edtion. Prentice-Hall, 1992.
Tobagi F A, Kleinrock L. Packet switching in radio channels: Part II–-The hidden terminal problem in carrier sense multiple-access and the busy-tone solution. IEEE Trans. Communications, Dec. 1975, Com-23: 1417–1433.
Wu C. Li V O. Receiver-initiated busy-tone multiple access in packet radio networks. In Proc. ACM SIGCOMM'87, 1987, pp.336–342.
Haas Z, Deng J. Dual busy tone multiple access (DBTMA): A multiple access control scheme for ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans. Communications, June 2002, 50: 975–985.
Xiang Zeng, Rajive Bagrodia, Mario Gerla. GloMoSim: A library for parallel simulation of large-scale wireless networks. In Proc. the 12th Workshop on Parallel and Distributed Simulations, Alberta, Canada, May 1998.
Levis P, Culler D. Mate: A virtual machine for tiny networked sensors. In Proc. ACM Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, San Jose, CA, Oct. 2002, pp.207–218.
Christian Bettstetter. Mobility modeling in wireless networks: Categorization, smooth movement, and border effects. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 2001, 5(3): 55–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A previous version of this paper appeared in the Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP 2004), pp.494–501, IEEE Computer Society Press.
Wei-Sheng Si is currently a lecturer at Software School, Dalian Univ. Technology. He received his B.S. degree from Peking Univ. in 1997 and M.S. degree from Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in 2000. Both degrees are in computer science. From Aug. 2000 to Jan. 2004, he was a Ph.D. candidate at the Dept. Computer Science, Univ. Virginia (USA). He returned to China before completing his Ph.D. His research interests include P2P systems, wireless networking, and network security.
Cheng-Zhi Li is currently a visiting assistant professor at the Univ. Texas at Arlington (USA). He received his B.S. degree in applied mathematics and M.S. degree in operations research from Fuzhou Univ. and Xiamen Univ., China, respectively. He received his Ph.D. degree in computer engineering from Texas A&M Univ., USA in 1999. From 1999 to 2001, he was a postdoctoral fellow at Rice Univ., USA. From 2001 to 2003, he was a research scientist at the Univ. Virginia (USA). His research areas encompass wired and wireless networking.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, WS., Li, CZ. RMAC: A Reliable MAC Protocol Supporting Multicast for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. J Comput Sci Technol 20, 702–712 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-005-0702-0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-005-0702-0