Abstract
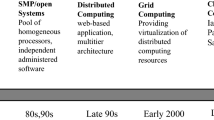
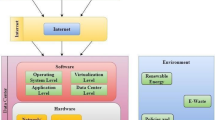
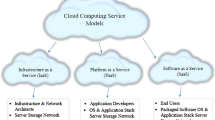
Cloud computing, after its success as a commercial infrastructure, is now emerging as a private infrastructure. The software platforms available to build private cloud computing infrastructure vary in their performance for management of cloud resources as well as in utilization of local physical resources. Organizations and individuals looking forward to reaping the benefits of private cloud computing need to understand which software platform would provide the efficient services and optimum utilization of cloud resources for their target applications. In this paper, we present our initial study on performance evaluation and comparison of three cloud computing software platforms from the perspective of common cloud users who intend to build their private clouds. We compare the performance of the selected software platforms from several respects describing their suitability for applications from different domains. Our results highlight the critical parameters for performance evaluation of a software platform and the best software platform for different application domains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaquero L M, Rodero-Merino L, Caceres J, Lindner M. A break in the Clouds: Towards a cloud definition. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev., 2009, 39(1): 50–55.
Shafer J. I/O virtualization bottlenecks in cloud computing today. In Proc. the 2nd Workshop on I/O Virtualization, March 2010, pp.5–12. http://li46-224.members.linode.com/publications/papers/shafer-wiov2010.pdf, Dec. 2014.
Wardley S, Goyer E, Barcet N. Ubuntu enterprise Cloud architecture. Technical White Paper, Ubuntu, 2009. http://www.ubuntu.com/sites/default/files/active/White-%20Paper%20Ubuntu%20Enterprise%20Cloud%20Architecture%20v1.pdf, Apr. 2015.
Nurmi D, Wolski R, Grzegorczyk C, Obertelli G, Soman S, Youseff L, Zagorodnov D. Eucalyptus: An open-source cloud computing infrastructure. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2009, 180(1): 012051.
Saavedra R H, Smith A J. Analysis of benchmark characteristics and benchmark performance prediction. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst., 1996, 14(4): 344–384.
Pu X, Liu L, Mei Y, Sivathanu S, Koh Y, Pu C. Understanding performance interference of I/O workload in virtualized cloud environments. In Proc. the 3rd IEEE CLOUD, July 2010, pp.51–58.
Mucci P J, London K, Thurman J. The CacheBench report. Technical Report, ut-cs-98-394, University of Tennessee, 1998. http://icl.cs.utk.edu/projects/llcbench/cachebench.pdf, Jan. 2015.
Schüller F. Grid computing with and standard test cases for a meteorological limited area model [Master Thesis]. Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Innsbruck, 2007. http://imgi.uibk.ac.at/file/157/download?token=KQL58LB2, Jan. 2015.
Deshane T, Shepherd Z, Matthews J, Ben-Yehuda M, Shah A, Rao B. Quantitative comparison of Xen and KVM. In Proc. Xen Summit, June 2008. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228772586Quantitative_comparison_of_Xen_and_KVM/links/004635229734fe42f6000000, Jan. 2015.
Reddy V V, Rajamani L. Evaluation of different hypervisors performance in the private cloud with SIGAR framework. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2014, 5(2): 60–66.
Palankar M R, Iamnitchi A, Ripeanu M, Garfinkel S. Amazon S3 for science grids: A viable solution? In Proc. the 2008 International Workshop on Data-Aware Distributed Computing, June 2008, pp.55–64.
Stantchev V. Performance evaluation of cloud computing offerings. In Proc. the 3rd International Conference on Advanced Engineering Computing and Applications in Sciences, Oct. 2009, pp.187–192.
Khurshid A, Al-Nayeem A, Gupta I. Performance evaluation of the Illinois cloud computing testbed. Technical Report, Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2009.
Iosup A, Ostermann S, Yigitbasi M N, Prodan R, Fahringer T, Epema D H. Performance analysis of cloud computing services for many-tasks scientific computing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2011, 22(6): 931–945.
Garfinkel S. An evaluation of Amazon’s Grid computing services: EC2, S3 and SQS. Technical Report, TR-08-07, School for Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, 2007.
Juve G, Deelman E, Vahi K, Mehta G, Berriman B, Berman B P, Maechling P. Data sharing options for scientific workflows on Amazon EC2. In Proc. the 2010 ACM/IEEE International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Nov. 2010.
Kobayashi K, Mikami S, Kimura H, Tatebe O. The Gfarm file system on compute Clouds. In Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing Workshops and PhD Forum, May 2011, pp.1034–1041.
Wang L, Zhan J, Shi W, Liang Y. In Cloud, can scientific communities benefit from the economies of scale? IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2012, 23(2): 296–303.
Walker E. Benchmarking Amazon EC2 for highperformance scientific computing. ; Login, 2008, 33(5): 18–23.
Ostermann S, Iosup A, Yigitbasi N, Prodan R, Fahringer T, Epema D. A performance analysis of EC2 cloud computing services for scientific computing. In Proc. the 1st International Conference on Cloud Computing, Oct. 2009, pp.115–131.
Jackson K, Ramakrishnan L, Muriki K, Canon S, Cholia S, Shalf J, Wasserman H J, Wright N. Performance analysis of high performance computing applications on the Amazon web services cloud. In Proc. the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom), Nov.30–Dec.3, 2010, pp.159–168.
Ye X, Lv A, Zhao L. Research of high performance computing with clouds. In Proc. the 3rd International Symposium on Computer Science and Computational Technology, Aug. 2010, pp.289–293.
Ahuja S P, Man S. The state of high performance computing in the cloud. Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information Sciences, 2012, 3(2): 262–266.
Nadeem F, Fahringer T. Optimizing execution time predictions of scientific workflow applications in the Grid through evolutionary programming. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2013, 29(4): 926–935.
Gupta A, Milojicic D. Evaluation of HPC applications on cloud. In Proc. the 6th Open Cirrus Summit (OCS), Oct. 2011, pp.22–26.
Juve G, Deelman E, Berriman G, Berman B, Maechling P. An evaluation of the cost and performance of scientific workflows on Amazon EC2. Journal of Grid Computing, 2012, 10(1): 5–21.
Juve G, Deelman E, Vahi K, Mehta G, Berriman B, Berman B, Maechling P. Scientific workflow applications on Amazon EC2. In Proc. the 5th IEEE International Conference on E-Science Workshops, Dec. 2009, pp.59–66.
Vecchiola C, Pandey S, Buyya R. High performance cloud computing: A view of scientific applications. In Proc. the 10th International Symposium on Pervasive Systems, Algorithms, and Networks, Dec. 2009, pp.4–16.
Evangelinos C, Hill C N. Cloud computing for parallel scientific HPC applications: Feasibility of running coupled atmosphereocean climate models on Amazon’s EC2. In Proc. the 1st CCA, Oct. 2008.
Li A, Yang X, Kandula S, Zhang M. CloudCmp: Comparing public cloud providers. In Proc. the 10th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, Nov. 2010, pp.1–14.
Ward J S. A performance comparison of Clouds: Amazon EC2 and Ubuntu enterprise Cloud. Technical Report, Cloud Computing Co-laboratory. University of St Andrews, SICSA DemoFEST, 2009.
Tudoran R, Costan A, Antoniu G et al. A performance evaluation of Azure and Nimbus clouds for scientific applications. In Proc. the 2nd International Workshop on Cloud Computing Platforms, Apr. 2012, Article No. 4.
Voras I, Orlić M, Mihaljević B. An early comparison of commercial and open-source cloud platforms for scientific environments. In Proc. the 6th KES International Conference on Agent and MultiAgent Systems: Technologies and Applications, June 2012, pp.164–173.
Popović O, Jovanović Z, Jovanović N, Popović R. A comparison and security analysis of the cloud computing software platforms. In Proc. the 10th International Conference on Telecommunication in Modern Satellite Cable and Broadcasting Services (TELSIKS), Vol.2, Oct. 2011, pp.632–634.
Garg S K, Versteeg S, Buyya R. A framework for ranking of Cloud computing services. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2013, 29(4): 1012–1023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadeem, F., Qaiser, R. An Early Evaluation and Comparison of Three Private Cloud Computing Software Platforms. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 30, 639–654 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-015-1550-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-015-1550-1