Abstract
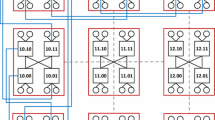
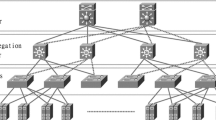
The capability of the data center network largely decides the performance of cloud computing. However, the number of servers in the data center network becomes increasingly huge, because of the continuous growth of the application requirements. The performance improvement of cloud computing faces great challenges of how to connect a large number of servers in building a data center network with promising performance. Traditional tree-based data center networks have issues of bandwidth bottleneck, failure of single switch, etc. Recently proposed data center networks such as DCell, FiConn, and BCube, have larger bandwidth and better fault-tolerance with respect to traditional tree-based data center networks. Nonetheless, for DCell and FiConn, the fault-tolerant length of path between servers increases in case of failure of switches; BCube requires higher performance in switches when its scale is enlarged. Based on the above considerations, we propose a new server-centric data center network, called BCDC, based on crossed cube with excellent performance. Then, we study the connectivity of BCDC networks. Furthermore, we propose communication algorithms and fault-tolerant routing algorithm of BCDC networks. Moreover, we analyze the performance and time complexities of the proposed algorithms in BCDC networks. Our research will provide the basis for design and implementation of a new family of data center networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris D. Ballmer’s millionserver claim doesn’t seem so crazy. https://gigaom.com/2013/07/17/ballmers-million-server-claim-doesnt-seem-so-crazy/#comments, July 2013.
Dignan L. AWS financials on deck: The road to 3 million servers in operation. http://www.zdnet.com/article/aws-financials-on-deck-the-road-to-3-million-servers-in-operation/, April 2015.
Al-Fares M, Loukissas A, Vahdat A. A scalable, commodity data center network architecture. In Proc. the ACM SIGCOMM Conf. Data Communication, August 2008, pp.63-74.
Guo C X, Wu H T, Tan K, Shi L, Zhang Y G, Lu S W. DCell: A scalable and fault-tolerant network structure for data centers. In Proc. the ACM SIGCOMM Conf. Data Communication, August 2008, pp.75-86.
Li D, Guo C X, Wu H T, Tan K, Zhang Y G, Lu S W. Fi-Conn: Using backup port for server interconnection in data centers. In Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, April 2009, pp.2276-2285.
Guo C X, Lu G H, Li D, Wu H T, Zhang X, Shi Y F, Tian C, Zhang Y G, Lu S W. BCube: A high performance, server-centric network architecture for modular data centers. In Proc. the ACM SIGCOMM Conf. Data Communication, August 2009, pp.63-74.
Greenberg A, Hamilton J R, Jain N, Kandula S, Kim C, Lahiri P, Maltz D A, Patel P, Sengupta S. VL2: A scalable and flexible data center network. In Proc. the ACM SIGCOMM Conf. Data Communication, August 2009, pp.51-62.
Abu-Libdeh H, Costa P, Rowstron A, O’Shea G, Donnelly A. Symbiotic routing in future data centers. In Proc. ACM SIGCOMM, Aug.30-Sept.3, 2010, pp.51-62.
Yu Y, Qian C. Space shuffle: A scalable, flexible, and high-performance data center network. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2016, 27(11): 3351-3365.
Zheng K, Wang L, Yang B H, Sun Y, Uhlig S. LazyCtrl: A scalable hybrid network control plane design for cloud data centers. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2017, 28(1): 115-127.
Bhuyan L N, Agrawal D P. Generalized hypercube and hyperbus structures for a computer network. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1984, C-33(4): 323-333.
Leiserson C E. Fat-trees: Universal networks for hardware-efficient supercomputing. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1985, 34(10): 892-901.
Dally W J. Performance analysis of k-ary n-cube interconnection networks. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1990, 39(6): 775-785.
Xiang D, Zhang Y L, Pan Y. Practical deadlock-free fault-tolerant routing in meshes based on the planar network fault model. IEEE Trans. Computers, 2009, 58(5): 620-633.
Xiang D. Deadlock-free adaptive routing in meshes with fault-tolerance ability based on channel overlapping. IEEE Trans. Dependable and Secure Computing, 2011, 8(1): 74-88.
Lin D, Liu Y, Hamdi M, Muppala J. FlatNet: Towards a flatter data center network. In Proc. IEEE Global Communications Conf., December 2012, pp.2499-2504.
Wang T, Su Z Y, Xia Y, Qin B, Hamdi M. NovaCube: A low latency Torus-based network architecture for data centers. In Proc. IEEE Global Communications Conf., December 2014, pp.2252-2257.
Wang T, Su Z Y, Xia Y, Liu Y, Muppala J, Hamdi M. SprintNet: A high performance servercentric network architecture for data centers. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Communications, June 2014, pp.4005-4010.
Wang T, Su Z Y, Xia Y, Muppala J, Hamdi M. Designing efficient high performance server-centric data center network architecture. Computer Networks, 2015, 79: 283-296.
Wang T, Su Z Y, Xia Y, Hamdi M. CLOT: A cost-effective low-latency overlaid Torus-based network architecture for data centers. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Communications, June 2015, pp.5479-5484.
Li D W, Wu J, Liu Z Y, Zhang F. Towards the tradeoffs in designing data center network architectures. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2017, 28(1): 260-273.
Efe K. A variation on the hypercube with lower diameter. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1991, 40(11): 1312-1316.
Cull P, Larson S M. The Möbius cubes. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1995, 44(5): 647-659.
Abraham S, Padmanabhan K. The twisted cube topology for multiprocessors: A study in network asymmetry. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 1991, 13(1): 104-110.
Fan J X, He L Q. BC interconnection networks and their properties. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2003, 26(1): 84-90. (in Chinese)
Wang D J. Hamiltonian embedding in crossed cubes with failed links. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2012, 23(11): 2117-2124.
Kulasinghe P, Bettayeb S. Embedding binary trees into crossed cubes. IEEE Trans. Computers, 1995, 44(7): 923-929.
Fan J, Lin X, Jia X. Optimal path embedding in crossed cubes. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2005, 16(12): 1190-1200.
Efe K. The crossed cube architecture for parallel computation. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 1992, 3(5): 513-524.
Chang C P, Sung T Y, Hsu L H. Edge congestion and topological properties of crossed cubes. IEEE Trans. Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2000, 11(1): 64-80.
Efe K, Blackwell P K, Slough W, Shiau T. Topological properties of the crossed cube architecture. Parallel Computing, 1994, 20(12): 1763-1775.
Kulasinghe P D. Connectivity of the crossed cube. Information Processing Letters, 1997, 61(4): 221-226.
Fan J X, Jia X H. Edge-pancyclicity and path-embeddability of bijective connection graphs. Information Sciences, 2008, 178(2): 340-351.
Yang X F, Dong Q, Tang Y Y. Embedding meshes/tori in faulty crossed cubes. Information Processing Letters, 2010, 110(14/15): 559-564.
Zhou S M. The conditional diagnosability of crossed cubes under the comparison model. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 2010, 87(15): 3387-3396.
Dong Q, Zhou J L, Fu Y, Yang X F. Embedding a mesh of trees in the crossed cube. Information Processing Letters, 2012, 112(14/15): 599-603.
Cheng B L, Fan J X, Jia X H, Zhang S K. Independent spanning trees in crossed cubes. Information Sciences, 2013, 233: 276-289.
Cheng B L, Fan J X, Jia X H, Wang J. Dimension-adjacent trees and parallel construction of independent spanning trees on crossed cubes. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2013, 73(5): 641-652.
Chen H C, Kung T L, Hsu L Y. 2-disjoint-path-coverable panconnectedness of crossed cubes. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2015, 71(7): 2767-2782.
Chen H C, Zou Y H, Wang Y L, Pai K J. A note on path embedding in crossed cubes with faulty vertices. Information Processing Letters, 2017, 121: 34-38.
Cheng B L, Wang D J, Fan J X. Constructing completely independent spanning trees in crossed cubes. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 2017, 219: 100-109.
Diestel R. Graph Theory (4th edition). Springer, 2010.
Ghemawat S, Gobioff H, Leung S T. The Google file system. In Proc. the 19th ACM Symp. Operating Systems Principles, October 2003, pp.29-43.
Dean J, Ghemawat S. MapReduce: Simplified data processing on large clusters. Communications of the ACM, 2008, 51(1): 107-113.
Acknowledgment
We thank the anonymous reviewers and editors for their valuable suggestions that help to improve the presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 301 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Fan, JX., Lin, CK. et al. BCDC: A High-Performance, Server-Centric Data Center Network. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 33, 400–416 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-018-1826-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-018-1826-3