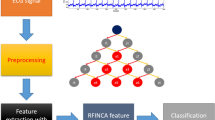
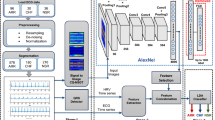
Abstract
Electrocardiogram (ECG) biometric recognition has emerged as a hot research topic in the past decade. Although some promising results have been reported, especially using sparse representation learning (SRL) and deep neural network, robust identification for small-scale data is still a challenge. To address this issue, we integrate SRL into a deep cascade model, and propose a multi-scale deep cascade bi-forest (MDCBF) model for ECG biometric recognition. We design the bi-forest based feature generator by fusing L1-norm sparsity and L2-norm collaborative representation to efficiently deal with noise. Then we propose a deep cascade framework, which includes multi-scale signal coding and deep cascade coding. In the former, we design an adaptive weighted pooling operation, which can fully explore the discriminative information of segments with low noise. In deep cascade coding, we propose level-wise class coding without backpropagation to mine more discriminative features. Extensive experiments are conducted on four small-scale ECG databases, and the results demonstrate that the proposed method performs competitively with state-of-the-art methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Odinaka I, Lai P H, Kaplan A D, Osullivan J A, Sire-vaag E J, Rohrbaugh J W. ECG biometric recognition: A comparative analysis. IEEE Trans. Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(6): 1812-1824. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2012.2215324.
Kim M, Pan S B. Deep learning based on 1-D ensemble networks using ECG for real time user recognition. IEEE Trans. Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(10): 5656-5663. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2909730.
Wang J, She M, Nahavandi S, Kouzani A Z. Human identification from ECG signals via sparse representation of local segments. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(10): 937-940. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2013.2267593.
Jaafar H, Ramli N, Nasir A S A. Implementation of kernel sparse representation classifier for ECG biometric system. Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering, 2018, 10(1-13): 89-94
Li R, Yang G, Wang K, Huang Y, Yuan F, Yin Y. Robust ECG biometrics using GNMF and sparse representation. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 129: 70-76. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.005.
Goshvarpour A, Goshvarpour A. Human identification using a new matching pursuit-based feature set of ECG. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2019, 172: 87-94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.02.009.
Zhang L, Liu J, Zhang B, Zhang D, Zhu C. Deep cascade model-based face recognition: When deep-layered learning meets small data. IEEE Trans. Image Process, 2019, 29: 1016-1029. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2938307.
Abdeldayem S S, Bourlai T. A novel approach for ECG-based human identification using spectral correlation and deep learning. IEEE Trans. Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 2020, 2(1): 1-14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBIOM.2019.2947434.
Labati R D, Munoz E, Piuri V, Sassi R, Scotti F. Deep-ECG: Convolutional neural networks for ECG biometric recognition. Pattern Recognition Letter, 2019, 126: 78-85. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.03.028.
da Silva Luz E, Moreira G, Oliveira L S, Schwartz W R, Menotti D. Learning deep off-the-person heart biometrics representations. IEEE Trans. Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 13(5): 1258-1270. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2017.2784362.
Hammad M, Liu Y, Wang K. Multimodal biometric authentication systems using convolution neural network based on different level fusion of ECG and fingerprint. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 26527-26542. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/AC-CESS.2018.2886573.
Zhang Y, Xiao Z, Guo Z, Wang Z. ECG-based personal recognition using a convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognition Letter, 2019, 125: 668-676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.07.009.
Zhou Z, Feng J. Deep forest: Towards an alternative to deep neural networks. In Proc. the 26th Int. Artificial Intelligence, August 2017, pp.3553-3559. DOI: 10.24963/ij-cai.2017/497.
Liu X B, Wang R, Cai Z, Cai Y, Yin X. Deep multi-grained cascade forest for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 8169-8183. DOI: 0.1109/TGRS.2019.2918587.
Wen H, Zhang J, Lin Q, Yang K, Huang P. Multi-level deep cascade trees for conversion rate prediction in recommendation system. In Proc. the 23rd Int. Artificial Intelligence, May 2019, pp.338-345. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.3301338.
Lim C, Woo W L, Dlay S, Gao B. Heartrate-dependent heartwave biometric identification with thresholding-based GMM-HMM methodology. IEEE Trans. Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(1): 45-53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2874462.
Meltzer D, Luengo D. Fiducial ECG-based biometry: Comparison of classifiers and dimensionality reduction methods. In Proc. the 42nd Int. Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Jul. 2019, pp.552-556. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2019.8768891.
Diab M O, Seif A, El-Abed M, Sabbah M. Individual identification using ECG signals. Journal of Computer and Communications, 2018, 6: 74-80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2018.61008.
Dong X, Si W, Huang W. ECG-based identity recognition via deterministic learning. Biotechnology & Biotech-nological Equipment, 2018, 32(3): 769-777. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2018.1428500.
Rahman S A E. Biometric human recognition system based on ECG. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(3): 17555-17572. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7152-0.
Srivastva R, Singh Y N. Human recognition using discrete cosine transform and discriminant analysis of ECG. In Proc. the 4th Int. Image Information Processing, Dec. 2017, pp.368-372. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIIP.2017.8313742.
Bassiouni M M, El-Dahshan E A, Khalefa W, Salem A M. Intelligent hybrid approaches for human ECG signals identification. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2018, 12(5): 941-949. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1237-5.
Ur Rehman U, Kamal K, Iqbal J, Sheikh M F. Biometric identification through ECG signal using a hybridized approach. In Proc. the 5th Int. Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Apr. 2019, pp.226-230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3330482.3330496.
Wu S C, Chen P T, Swindlehurst A L, Hung P L. Cancelable biometric recognition with ECGs: Subspace-based approaches. IEEE Trans. Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(5): 1323-1336. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2018.2876838.
He H, Tan Y. Automatic pattern recognition of ECG signals using entropy-based adaptive dimensionality reduction and clustering. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 55: 238-252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.02.001.
Srivastva R, Singh Y. ECG biometric analysis using Walsh-Hadamard transform. In Advances in Data and Information Sciences, Kolhe M L, Trivedi M C, Tiwari S, Singh V (eds.), Springer, 2018, pp.201-210. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-8360-0_19.
Zheng G, Wang Y, Sun X, Sun Y, Ji S. Study on Matthew effect based feature extraction for ECG biometric. In Proc. the 8th Int. Conf. Intelligent Science and Big Data Engineering, Aug. 2018, pp.623-634. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02698-1-54.
Pinto J R, Cardoso J S, Lourenço A. Evolution, current challenges, and future possibilities in ECG biometrics. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34746-34776. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/AC-CESS.2018.2849870.
Pal A, Singh Y. ECG biometric recognition. In Proc. the 4th Int. Conf. Mathematics and Computing, Jan. 2018, pp.61-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0023-37.
Hejazi M, Al-Haddad S A R, Singh Y P, Hashim S J, Aziz A F A. ECG biometric authentication based on non-fiducial approach using kernel methods. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 52: 72-86. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2016.02.008.
Chen H, Huang C, Huang Q, Zhang Q, Wang W. ECGadv: Generating adversarial electrocardiogram to misguide arrhythmia classification system. In Proc. the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Feb. 2020, pp.3446-3453. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5748.
Utkin L V, Ryabinin M A. Discriminative metric learning with deep forest. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Tools, 2017, 28(2): 195-204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218213019500076.
Su R, Liu X,Wei L, Zou Q. Deep-Resp-forest: A deep forest model to predict anti-cancer drug response. Methods, 2019, 166: 91-102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.02.009.
Pang M, Ting K M, Zhao P, Zhou Z. Improving deep forest by confidence screening. In Proc. the 20th Int. Data Mining, Nov. 2018, pp.1194-1199. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2018.00158.
Lan X, Zhang S, Yuen P C, Chellappa R. Learning common and feature-specific patterns: A novel multiple-sparse-representation-based tracker. IEEE Trans. Image Processing, 2017, 27(4): 2022-2037. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2777183.
Panagakis Y, Kotropoulos C, Arce G R. Music genre classification via joint sparse low-rank representation of audio features. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(12): 1905-1917. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2014.2355774.
Wright J, Yang A Y, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Ma Y. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(2): 210-227. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2008.79.
Moody G B, Mark R G. The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 2001, 20(3): 45-50. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/51.932724.
Bousseljot R, Kreiseler D, Schnabel A. Nutzung der EKG-signaldatenbank CARDIODAT der PTB uber das internet. Biomedizinische Technik/Biomedical Engineering, 2009, 40(s1): 317-318. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/bmte.1995.40.s1.317.
Da Silva H P, Lourenço A, Fred A, Raposo N, Airesde-Sousa M. Check your biosignals here: A new dataset for off-the-person ECG biometrics. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2014, 113(2): 503-514. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.11.017.
Pouryayevali S, Wahabi S, Hari S, Hatzinakos D. On establishing evaluation standards for ECG biometrics. In Proc. the 2014 Int. Conf. Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, May 2014, pp.3774-3778. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854307.
Pan J, Tompkins W J. A real-time QRS detection algo-rithm. IEEE Trans. Biomedical Engineering, 1985, BME-32(3): 230-236. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.1985.325532.
Biel L, Pettersson O, Philipson L, Wide P. ECG analysis: A new approach in human identification. IEEE Trans. Instrumentation and Measurement, 2001, 50(3): 808-812. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/19.930458.
Chan A A, Hamdy M M, Badre A, Badee V. Wavelet distance measure for person identification using electrocar-diograms. IEEE Trans. Instrumentation & Measurement, 2008, 57(2): 248-253. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2007.909996.
Yang J, Yu K, Gong Y, Huang T S. Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In Proc. the 2009 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2009, pp.1794-1801. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206757.
Wang K, Yang G, Huang Y, Yin Y. Multi-scale differential feature for ECG biometrics with collective matrix factorization. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 102: Article No. 107211. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107211.
Chu Y, Shen H, Huang K. ECG authentication method based on parallel multi-scale one-dimensional residual net-work with center and margin loss. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 51598-51607. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2912519.
Komeili M, Louis W, Armanfard N, Hatzinakos D. Feature selection for nonstationary data: Application to human recognition using medical biometrics. IEEE Trans. Cybern:, 2018, 48(5): 1446-1459. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2702059.
Huang Y W, Yang G P, Wang K K, Liu H Y, Yin Y L. Learning joint and specific patterns: A unified sparse representation for o_-the-person ECG biometric recognition. IEEE Trans. Information Forensics & Security, 2021, 16(1): 147-160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2020.3006384.
Lynn H M, Pan S B, Kim P. A deep bidirectional GRU net-work model for biometric electrocardiogram classification based on recurrent neural networks. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 145395-145405. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939947.
Louis W, Komeili M, Hatzinakos D. Continuous authentication using one-dimensional multi-resolution local binary patterns (1DMRLBP) in ECG biometrics. IEEE Trans. Information Forensics & Security, 2016, 11(12): 2818-2832. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2016.2599270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 170 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YW., Yang, GP., Wang, KK. et al. Multi-Scale Deep Cascade Bi-Forest for Electrocardiogram Biometric Recognition. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 36, 617–632 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1033-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1033-5