Abstract
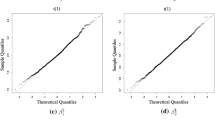
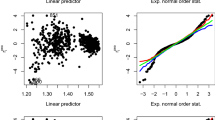
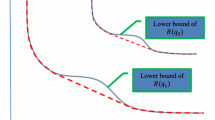
This paper proposes a double penalized quantile regression for linear mixed effects model, which can select fixed and random effects simultaneously. Instead of using two tuning parameters, the proposed iterative algorithm enables only one optimal tuning parameter in each step and is more efficient. The authors establish asymptotic normality for the proposed estimators of quantile regression coefficients. Simulation studies show that the new method is robust to a variety of error distributions at different quantiles. It outperforms the traditional regression models under a wide array of simulated data models and is flexible enough to accommodate changes in fixed and random effects. For the high dimensional data scenarios, the new method still can correctly select important variables and exclude noise variables with high probability. A case study based on a hierarchical education data illustrates a practical utility of the proposed approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koenker R, Quantite Regression, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2005.
Yu K, Lu Z, and Stander J, Quantile regression: Applications and current research areas, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series D, 2003, 52: 331–350.
Fan J and Li R, Variable selection via non-concave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2001, 96: 1348–1360.
Tibshirani R J, Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Ser. B, 1996, 58: 267–288.
Tian M Z and Chen G M, Hierarchical linear regression models for conditional quantiles, Science in China Series A: Mathematics, 2006, 49: 11–16.
Wu X and Tian M Z, A longitudinal study of the effects of family background factors on mathematics achievements using quantile regression, Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica (English Series), 2008, 24: 85–98.
Lange N and Laird N M, The effect of covariance structures on variance estimation in balance growth-curve models with random parameters, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1989, 84: 241–247.
Akaike H, A new look at the statistical model identification, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1974, 19: 716–723.
Schwarz G, Estimating the dimension of a model, Annals of Statistics, 1978, 6: 461–464.
Rao C R and Wu Y, A strongly consistent procedure for model selection in regression problems, Biometrika, 1989, 76: 369–374.
Vaida F and Blanchard S, Conditional Akaike information for mixed-effects models, Biometrika, 2005, 92: 351–370.
Niu F and Pu P, Selecting mixed-effects models based on generalized information criterion, Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 2006, 97: 733–758.
Wolfinger R D, Covariance structure selection in general mixed models, Communications in Statistics: Simulation and Computation, 1993, 22: 1079–1106.
Diggle P J, Liang K Y, and Zeger S L, Analysis of Longitudinal Data, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1994.
Bondell H D, Krishna A, and Ghosh S K, Joint variable selection for fixed and random effects in linear mixed-effects models, Biometrics, 2010, 66: 1069–1077.
Koenker R, Quantile regression for longitudinal data, Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 2004, 91: 74–89.
Harville D A, Extension of the Gauss-Markov theorem to include the estimation of random effects, Annals of Statistics, 1976, 4: 384–395.
Robinson G, That BLUP is a good thing: The estimation of random effects, Statistical Science, 1991, 6: 15–31.
Henderson C, Estimation of genetic parameters (Abstract), Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1950, 21: 309–310.
Goldberger A, Best linear unbiased prediction in the generalized linear regression model, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1962, 57: 369–375.
Rao C R, Linear Statistical Inference and Its Applications, Wiley, New York, 1973.
Koenker R and Bassett G, Regression quantiles, Econometrica, 1978, 46: 33–50.
Li Y and Zhu J, L1-norm quantile regressions, Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2008, 17: 1–23.
Rockafellar R T, Convex Analysis (Princeton Landmarks in Mathematics and Physics), Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, 1997.
Schwarz G, Estimating the dimension of a model, Annals of Statistics, 1978, 6: 461–464.
Koenker R, Ng P, and Portnoy S, Quantile smoothing splines, Biometrika, 1994, 81: 673–680.
Yuan M, GACV for quantile smoothing splines, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2006, 5: 813–829.
Knight K, Limiting distribution for L1 regression estimators under general conditions, Annals of Statistics, 1998, 26: 755–770.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the National Social Science Fund under Grant No. 17BJY210.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor SUN Liuquan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, Y. & Luo, Y. Double Penalized Quantile Regression for the Linear Mixed Effects Model. J Syst Sci Complex 33, 2080–2102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9065-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9065-4