Abstract
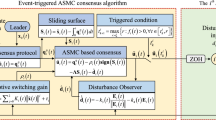
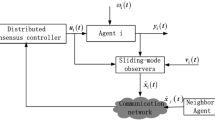
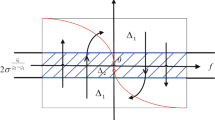
This paper proposes a finite-time consensus control algorithm based on nonlinear integral sliding-mode control for second-order multi-agent systems (MASs) with mismatched and matched disturbances. Firstly, a nonlinear finite-time disturbance observer is established to estimate the states and mismatched disturbances of the agent. Secondly, a dynamic integral sliding-mode (ISM) surface is designed by employing the estimates of mismatched disturbances. Then, based on the designed ISM and disturbance observer, the discontinuous or continuous campsite control protocols are respectively developed to guarantee the consensus for MASs in finite time with active anti-disturbance control. Finally, numerical simulation results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed consensus control algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin L, He X, and Zhou D, Distributed proportion-integration-derivation formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with communication time delays, Neurocomputing, 2017, 267: 271–282.
Yang H Y, Zhang Z, and Zhang S, Consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with exogenous disturbances, International Journal of Robust & Nonlinear Control, 2011, 21(9): 945–956.
Sun Y, Wang Y, and Zhao D, Flocking of multi-agent systems with multiplicative and independent measurement noises, Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2015, 440(60): 81–89.
Lin P, Ren W, and Song Y, Distributed multi-agent optimization subject to nonidentical constraints and communication delays, Automatica, 2016, 65: 120–131.
Wang X, Liu X, She K, et al., Pinning impulsive synchronization of complex dynamical networks with various time-varying delay sizes, Nonlinear Analysis Hybrid Systems, 2017, 26: 307–318.
Yang H, Zhu Z, and Zhang S, Consensus of second-order delayed multi-agent systems with leader-following, European Journal of Control, 2010, 16(2): 188–199.
Zhang G, Deng Y, Zhang W, et al., Novel DVS guidance and path-following control for under-actuated ships in presence of multiple static and moving obstacles, Ocean Engineering, 2018, 170(11): 100–110.
Chen Y, Ai X, and Zhang Y, Spherical formation tracking control for second-order agents with unknown general flowfields and strongly connected topologies, International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2019, 29(11): 3715–3736.
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y, et al., A geometric extension design for spherical formation tracking control of second-order agents in unknown spatiotemporal flowfields, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 88(2): 1173–1186.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, and Wang Z, An adaptive backstepping design for formation tracking motion in an unknown Eulerian specification flowfield, Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354(14): 6217–6233.
Mo L, Niu Y, and Pan T, Consensus of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with switching jointly-connected interconnection, Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2015, 427: 132–140.
Wang Q, Fu J, and Wang J, Fully distributed containment control of high-order multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics, Systems & Control Letters, 2017, 99: 33–39.
Hu J, Xiao Z, and Zhou Y, Robust consensus tracking control of a second-order leader-follower multi-agent system, IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46(20): 130–135.
Li W, Xie L, and Zhang J F, Containment control of leader-following multi-agent systems with Markovian switching network topologies and measurement noises, Automatica, 2015, 51: 263–267.
Fu J and Wang J, Robust finite-time containment control of general linear multi-agent systems under directed communication graphs, Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2016, 353(12): 2670–2689.
Wang F Y, Yang H Y, Liu Z X, et al., Containment control of leader-following multi-agent systems with jointly-connected topologies and time-varying delays, Neurocomputing, 2017, 260: 341–348.
Yang H, Wang F, and Han F, Containment control of fractional order multi-agent systems with time delays, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(3): 727–732.
Bhat S P and Bernstein D S, Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems, SIAM J. Contr. Opti., 2000, 38(3): 751–766.
Xiao Q Y, Wu Z H, and Peng L, Fast finite-time consensus tracking of second-order multi-agent systems with a virtual leader, Journal of Networks, 2014, 9(12): 3268–3274.
Wang X, Li S, and Shi P, Distributed finite-time containment control for double-integrator multiagent systems, IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 44(9): 1518–1528.
Cortes J, Finite-time convergent gradient flows with applications to network consensus, Automatica, 2006, 42(11): 1993–2000.
Zhang Y and Yang Y, Distributed finite-time tracking control for nonlinear multi-agent systems subject to external disturbances, International Journal of Control, 2013, 86(1): 29–40.
Chen G, Yue Y, and Song Y, Finite-time cooperative-tracking control for networked Euler-Lagrange systems, IET Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 7(11): 1487–1497.
Xiao F, Wang L, Chen J, et al., Finite-time formation control for multiagent systems, Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2605–2611.
Zhang G, Huang C, Zhang X, et al., Practical constrained dynamic positioning control for uncertain ship through the minimal learning parameter technique, IET Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 12(18): 2526–2533.
Lu Y, Zhang G, Sun Z, et al., Adaptive cooperative formation control of autonomous surface vessels with uncertain dynamics and external disturbances, Ocean Engineering, 2018, 167: 36–44.
Yang H, Yang Y, Han F, et al., Containment control of heterogeneous fractional-order multi-agent systems, Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(2): 752–765.
Zhang G, Tian B, Zhang W, et al., Optimized robust control for industrial unstable process via the mirror-mapping method, ISA Transactions, 2019, 86: 9–17.
Ou L L, Zhang W D, and Yu L, Low-order stabilization of LTI systems with time delay, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(4): 774–787.
Lu Y, Zhang G, Sun Z, et al., Robust adaptive formation control of underactuated autonomous surface vessels based on MLP and DOB, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 94(1): 503–519.
Wang M, Ren X, and Chen Q, Robust tracking and distributed synchronization control of a multi-motor servomechanism with H-infinity performance, ISA Transactions, 2017, 72: 147–160.
Sun Z, Zhang G, Lu Y, et al., Leader-follower formation control of underactuated surface vehicles based on sliding mode control and parameter estimation, ISA Transactions, 2017, 72: 15–24.
Zhao Q, Dong X, Liang Z, et al., Distributed cooperative guidance for multiple missiles with fixed and switching communication topologies, Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2017, 30(4): 1570–1581.
Yang J, Zolotas A, Chen W H, et al., Robust control of nonlinear MAGLEV suspension system with mismatched uncertainties via DOBC approach, ISA Transactions, 2011, 50(3): 389–396.
Li S H, Yang J, Chen W H, et al., Disturbance Observer-Based Control: Methods and Applications, CRC Press, Inc. 2014.
Yang J, Li S H, and Yu X H, Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 60(1): 160–169.
Wang X Y, Li S H, and Lam J, Distributed active anti-disturbance output consensus algorithms for higher-order multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances, Automatica, 2016, 74: 30–37.
Mondal S, Su R, and Xie L, Heterogeneous consensus of higher-order multi-agent systems with mismatched uncertainties using sliding mode control, International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2016, 27(13): 2303–2320.
Zhang Z, Li S, and Luo S, Terminal guidance laws of missile based on ISMC and NDOB with impact angle constraint, Aerospace Science & Technology, 2013, 31(1): 30–41.
Khalil H K, Nonlinear Systems, 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, New York, 2002.
Levant A, Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output-feedback control, International Journal of Control, 2003, 76(9–10): 924–942.
Shtessel Y B, Shkolnikov I A, and Levant A, Smooth second-order sliding modes: Missile guidance application, Automatica, 2007, 43(8): 1470–1476.
Davila A, Moreno J A, and Fridman L, Optimal Lyapunov function selection for reaching time estimation of super twisting algorithm, 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) Held Jointly with 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 2009, 8405–8410.
Hong Y G, Xu Y S, and Huang J, Finite-time control for robot manipulators, Systems & Control Letters, 2002, 46(4): 243–253.
Yu S and Long X, Finite-time consensus for second-order multi-agent systems with disturbances by integral sliding mode, Automatica, 2015, 54: 158–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61673200 and 61771231, the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China under Grant Nos. ZR2018ZC0438 and ZR2017MF010, and Key Research and Development Program of Yantai of China under Grant No. 2019XDHZ085.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor JIA Yingmin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Liu, F., Yang, H. et al. Distributed Finite-Time Integral Sliding-Mode Control for Multi-Agent Systems with Multiple Disturbances Based on Nonlinear Disturbance Observers. J Syst Sci Complex 34, 995–1013 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9152-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9152-6