Abstract
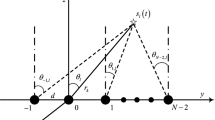
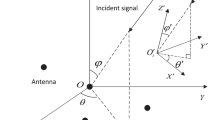
This paper proposes a new algorithm for joint frequency, two-dimensional (2-D) directions-of-arrival (DOA), and polarization estimation using parallel factor (PARAFAC) analysis model and cumulant. The proposed algorithm designs a new array configuration, and extends the PARAFAC analysis model from the common data-domain and subspace-domain to the cumulant one, and forms three-way arrays by using the three cumulant matrices obtained from the properly chosen dipole outputs, and analyzes the uniqueness of low-rank decomposition of the three-way arrays, and then jointly estimates the source parameters via the low-rank decomposition of the constructed PARAFAC model. In comparison with the conventional methods, the proposed method alleviates the aperture loss, and avoids pairing parameter. Finally, the simulation results are presented to validate the performance of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhuang Z W, Xu Z H, Xiao S P. Polarization Sensitive Array Signal Processing. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2005
Zhuang Z W, Xiao S P, Wang X S. Radar Polarization Information Processing and Applications. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1999
Johnson R. Antenna Engineering Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993
Lo Y T, Lee S W. Antenna Handbook Theory, Applications, and Design. Newyork: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, 1988
Balanis C A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design. New York: Harper & Row, 1982
Zhang X D. Modern Signal Processing. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1997
Li J, Compton R T. Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array. IEEE Trans Anten Propag, 1991, 39(9): 1376–1383
Li J, Compton R T. Two-dimensional angle and polarization estimation using the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Trans Anten Propag, 1992, 40(5): 550–555
Hua Y. A pencil-MUSIC algorithm for finding two-dimensional angles and polarizations using crossed-dipoles. IEEE Trans Anten Propag, 1993, 41(3): 370–375
Cheng Q, Hua Y. Further study of the Pencil-MUSIC algorithm. IEEE Trans Aerospace Electron Syst, 1996, 32(1): 284–301
Wang J Y, Chen T L. Joint frequency, two dimensional arrival angles and the polarizations estimation using an L array. Acta Electron Sin, 1999, 27(11): 74–76
Wang J Y, Chen T L. Joint frequency 2D AOA and polarization estimation using fourth-order cumulants. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2000, 43(3): 297–303
Wang J Y, Wang J Y, Chen T L. Joint frequency, 2-D AOA and polarization estimation in broad-band. Sci China Ser FInf Sci, 2001, 44(3): 161–167
Zhou Y Z, Chen T L. Angles of arrival and polarizations estimation. Chin J Radio Sci, 1997, 12(2): 220–224
Roy R, Kailath T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans Acous, Speech Signal Proc, 1989, 37(7): 984–995
Schmidt R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Tran Anten Propag, 1986, 34(3): 276–280
Liu T H, Mendel J M. Azimuth and elevation direction finding using arbitrary array geometries. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1998, 46(2): 2061–2065
Dogan M C, Mendel J M. Applications of cumulants to array processing-Part I: aperture extension and array calibration. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1995, 43(5): 1200–1216
Liang J L. Joint azimuth and elevation direction finding using cumulant. IEEE Sens J, 2009, 9(4): 390–398
Chevalier P, Ferreol A, Albera L. High-resolution direction finding from higher order statistics: the 2q-MUSIC algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2006, 54(8): 2986–2997
Zhang X D. Time Series Analysis: Higher Order Statistics Methods. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1996
Chevalier P, Albera L, Comon P. On the virtual array concept for higher order array processing. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2005, 53(4): 1254–1271
Mendel J M. Tutorial on higher-order statistics (spectra) in signal processing and system theory: theoretical results and some applications. Proc IEEE, 1991, 79(3): 278–305
Wang Y L, Chen H, Peng Y N, et al. Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithm. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004
Bro R. PARAFAC: Tutorial and applications. Chemom Intell Lab Syst, 1997, 38(2): 149–171
Cattell R B. Parallel proportional profiles and other principles for determining the choice of factors by rotation. Psychometrika, 1944, (9): 267–283
Harshman R A. Foundation of the PARAFAC procedure: Model and conditions for an ‘explanatory’ multi-mode factor analysis. UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics, 1970, 16: 1–84
Carroll J D, Chang J. Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an N-way generalization of ‘Eckart-Young’ decomposition. Psychometrika, 1970, 35(3): 283–
Sidiropoulos N D, Giannakis G B, Bro R. Blind PARAFAC receivers for DS-CDMA systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2000, 48(3): 810–823
Sidiopoulos N D, Bro R, Giannakis G B. Parallel factor analysis in sensor array processing. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2000, 48(8): 2377–2388
Rong Y, Vorobyov S A, Gershman A B, et al. Blind spatial signature estimation via time-varying user power loading and parallel factor analysis. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2005, 53(5): 1697–1710
Kruskal J B. Three-way arrays: rank and uniqueness of trilinear decompositions, with application to arithmetic complexity and statistics. Linear Algebra Appl, 1977, 18: 95–138
Kruskal J B. Rank Decomposition, and Uniqueness for 3-way and N-way Arrays. Multiway Data Analysis: Coppi R, Bolasco S, eds. Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1988. 7–18
Jiang T, Sidiropouls N D. Kruskal’s permutation lemma and the identification of CANDECOMP/PARAFAC and bilinear models with constant modulus constraints. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2004, 52(9): 2625–2636
Smilde A, Bro R, Geladi P. Multi-way Analysis with Applications in the Chemical Sciences. New York: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2004
Tomasi G. Practical and computational aspects in chemometric data analysis. PhD thesis. Frederikcberg, Denmark: the Royal Veterinary and Agriculture University, 2006. http://www.models.kvl.dk/research/theses/.
Liang J L, Yang S Y, Zhang J Y, et al. 4-D near-field source localization using cumulant. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 2007, 2007: 1–10
Liang J L, Wang S J, Gao L, et al. A novel near-field source localization algorithm without pairing parameters. Acta Electron Sin, 2007, 35(6): 1122–1127
Liang J L, Yang S Y, Zhang J Y. A cumulant-based parameter estimation algorithm for near-field sources. Prog in Nat Sci, 2007, 17(8): 900–905
Cai Y, Ni Y. Simultaneous synchronous spectrofluorimetric determination of vitamin B1, B2 and B6 using parallel factor analysis. J Guangxi Norm Univ (Nat Sci Ed). 2003, 21(2): 312–313
Sidiropoulos N D. COMFAC: Matlab code for LS fitting of the complex PARAFAC model in 3-D. 1998, http://www.telecom.tuc.gr/~nikos
Liao G S, Bao Z. Blind estimates of angle-doppler frequency for fluctuating targets signals via new rotational invariance techniques. Acta Electron Sin, 1996, 24(12): 6–11
Chen J F, Zhu X L, Zhang X D. A new algorithm for joint range-DOA-frequency estimation of near-field sources. EURASIP J Appl Signal Process, 2004, 4(3): 386–392
Liang J L. 4-D parameter estimation of narrowband sources based on parallel factor analysis. Chinese Sci Bull, 2008, 53(4): 2239–2247
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60901059/F0103), the Educational Department Foundations of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 09JK629), and the Doctor Research Start Fund of Xi’an University of Technology (Grant No. 116-210903)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Liu, D. & Zhang, J. Joint frequency, 2-D DOA, and polarization estimation using parallel factor analysis. Sci. China Ser. F-Inf. Sci. 52, 1891–1904 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0171-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0171-0