Abstract
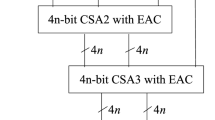
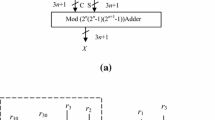
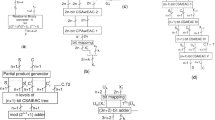
The conversion from residue to weighted binary representation plays an important role in the residue number system. Based on Chinese Remainder Theorem, a new residue-to-binary converter using arbitrary moduli set is proposed. The new converter uses the difference-correction algorithm for the conversion output and eliminates the modulo M operation, where M is the dynamic range of the residue number system. The sizes of the multipliers and modular multipliers in the new converter are small, thereby reducing the area and delay of the proposed converter. Simulation and synthesis results indicate that the new converter is more area-time efficient than the published converters based on Chinese Remainder Theorem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szabo N S, Tanaka R I. Residue Arithmetic and Its Applications to Computer Technology. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1967
Taylor F J. Residue arithmetic: a tutorial with examples. IEEE Comput, 1984, 17: 50–62
Beame P W, Cook S A, Hoover H J. Log depth circuits for division and related problems. SIAM J Comput, 1986, 15: 994–1003
Soderstrand M A, Jenkins W K, Jullien G A, et al. Residue Number System Arithmetic: Modern Applications in Digital Signal Processing. New York: IEEE Press, 1986
Leighton T. Introduction to Parallel Algorithms and Architectures: Array, Trees, Hypercubes. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1992
Lim K P, Premkumar A B. A modular approach to the computation of convolution sum using distributed arithmetic principles. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 1999, 46: 92–96
Koren I. Computer Arithmetic Algorithms. 2nd ed. Massachusetts: AK Peters Natick, 2002
Ma S, Hu J H, Zhang L, et al. An efficient RNS parity checker for moduli set 2n − 1, 2n + 1, 22n + 1 and its applications. Sci China Ser F-Inf Sci, 2008, 51: 1563–1571
Wang Y K. Residue-to-binary converters based on new Chinese remainder theorems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2000, 47: 197–205
Hariri A, Navi K, Rastegar R. A new high dynamic range moduli set with efficient reverse converter. Comput Math Appl, 2008, 55: 660–668
Cao B, Chang C H, Srikanthan. A residue-to-binary converter for a new five-moduli set. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2007, 54: 1041–1049
Wang W, Swamy M, Ahmad M. A high-speed residue-to-binary converter for three-moduli (2k, 2k − 1, 2k−1 − 1) RNS and a scheme for its VLSI implementation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2000, 47: 1576–1581
Al-Radadi E, Siy P. Four-moduli set (2, 2n − 1, 2n + 2n − 1 − 1, 2n+1 + 2n − 1) simplifies the residue to binary converters based on CRT II. Comput Math Appl, 2002, 44: 1581–1587
Mohan P V A, Premkumar A B. RNS-to-binary converters for two four-moduli sets 2n − 1, 2n, 2n + 1, 2n+1 − 1 and 2n − 1, 2n, 2n + 1, 2n+1 + 1. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2007, 54: 1245–1254
Lu M, Chiang J. A novel division algorithm for the residue number system. IEEE Trans Comput, 1992, 41: 1026–1032
Dimauro G, Impdedovo S, Pirlo G. A new technique for fast number comparison in the residue number systems. IEEE Trans Comput, 1993, 42: 608–612
Conway R, Nelson J. New CRT-based RNS converter using restricted moduli set. IEEE Trans Comput, 2003, 52: 572–578
Meehan S, O’neil S, Vaccaro J. An universal input and output RNS converter. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1990, 37: 799–803
Deng M J, Tan Y H, Sun Y Q. The Foundation of Number Theory. Harbin: Harbin Publishing House, 2000
Zhang C N, Shirazi B, Yun D. An efficient algorithm and parallel implementations for binary and residue number systems. J Symb Comput, 1993, 15: 451–462
Elleithy K, Bayoumi M. Fast and flexible architectures for RNS arithmetic decoding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1992, 39: 226–235
Kim J, Park K, Lee H. Efficient residue-to-binary conversion technique with rounding error compensation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1991, 38: 315–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Yao, R. Efficient CRT-based residue-to-binary converter for the arbitrary moduli set. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 54, 70–78 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-4133-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-4133-3