Abstract
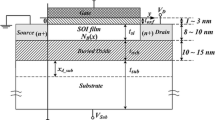
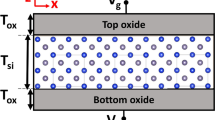
The high frequency performances of nano-scale ultra-thin-body (UTB) Schottky-barrier n-MOSFETs (SB-nMOSFETs) are investigated using 2D full-band self-consistent ensemble Monte Carlo method. The UTB SB-nMOSFET devices offer excellent RF performance with high values of f T and f max. The significant dependence of f T and f max on gate voltage and weak dependence on barrier height are demonstrated. Meanwhile, the significant dependence of g m and g ds on both gate voltage and SB height are shown. Moreover, the scalability of f T is outstanding and close to the ideal case (f T ∝ 1/L 2g ). The high frequency performances of 45 nm channel length SB-nMOSFETs at ballistic transport limit are also investigated. Results show that scattering strongly affects the capacitances C gs, C gd and C ds. At ballistic transport limit the f T and f max are almost 10 times larger. The Scattering effects in nano-scale SB-nMOSFETs cannot be neglected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kedzierski J, Xuan P Q, Anderson E H, et al. Complementary silicide source/drain thin-body MOSFETs for the 20 nm gate length regime. International Electron Devices Meeting Technical Digest. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2000. 57–60
Huang C K, Zhang W, Yang C. Two-dimensional numerical simulation of Schottky barrier MOSFET with channel length to 10 nm. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 1998, 45: 842
Winstead B, Ravaioli U. Simulation of Schottky barrier MOSFETs with a coupled quantum injection Monte Carlo technique. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2000, 47: 1241
Zhao Q, Klinkhammer F, Dolle M, et al. Nanometer patterning of epitaxial CoSi2/Si(100) for ultrashort channel Schottky barrier metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 74: 454
Connelly D, Clifton P, Faulkner C, et al. Ultra-thin-body fully depleted SOI metal source/drain n-MOSFETs and ITRS low-standby-power targets through 2018. International Electron Devices Meeting Technical Digest. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005. 972–975
Larson J M, Snyder J P. Overview and status of metal S/D Schottky-barrier MOSFET technology. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2006, 53: 1048–1057
Knoch J, Zhang M, Appenzelle J, et al. Physics of ultrathin-body silicon-on-insulator Schottky-barrier field-effect transistors. Appl Phys A, 2007, 87: 351–357
Saha A R, Chattopadhyay S, Bose C, et al. Technology CAD of silicided Schottky barrier MOSFET for elevated source C drain engineering. Mat Sci Eng B, 2005, 124–125: 424–430
Jang M, Kim Y, Shin J, et al. A 50-nm-gate-length erbium-silicided n-type Schottky barrier metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 741–743
Knoch J, Appenzeller J. Impact of the channel thickness on the performance of Schottky barrier metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81: 3082
Jing G, Lundstrom M S. A computational study of thin-body, double-gate, Schottky barrier MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2002, 49: 1897
Valentin R, Dubois E, Raskin J P, et al. RF small-signal analysis of Schottky-barrier p-MOSFET. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2008, 55: 1192–1202
Fritze M, Chen C L, Calawa S, et al. High-speed Schottky-barrier pMOSFET with f T = 280 GHz. IEEE Electr Device L, 2004, 25: 220–222
Pearman D J, Pailloncy G, Raskin J P, et al. Static and high-frequency behavior and performance of Schottky-barrier p-MOSFET devices. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2007, 54: 2796–2802
Du G, Liu X Y, Sun L, et al. Quantum Boltzmann equation solved by Monte Carlo method for nano-scale semiconductor devices simulation. Chinese Phys, 2006, 15: 177
Sun L, Liu X Y, Du G, et al. Monte Carlo simulation of Schottky contact with direct tunneling model. Semicond Sci Tech, 2003, 18: 576
Sze S M, Crowell C R, Kahng D. Photoelectric determination of the image force dielectric constant for hot electrons in Schottky barriers. J Appl Phys, 1964, 35: 2534–2536
Chelikowsky J R, Cohen M L. Nonlocal pseudopotential calculations for the electronic structure of eleven diamond and zinc-blende semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 1976, 14: 556
Fiegna C. Physics-based analysis of RF performance of small geometry MOSFETs: methodology and application to the evaluation of the effects of scaling. International Electron Devices Meeting Technical Digest. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1999. 543–546
Babiker S, Asenov A, Cameron N, et al. Complete Monte Carlo RF analysis of “real” short-channel compound FET’s. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 1998, 45: 1644–1652
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, G., Liu, X. & Han, R. High frequency performance of nano-scale ultra-thin-body Schottky-barrier n-MOSFETs. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 54, 1756–1761 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4267-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4267-y