Abstract
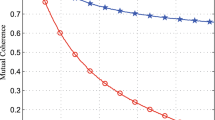
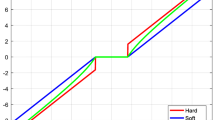
The article proposes a fast reconstruction algorithm for ℓ 0⩽p⩽1 norm nonconvex model, called Gradient projection nonconvex sparse recovery (GPNSR), which makes a good performance in high-quality image reconstruction. We apply the GPNSR into canonical multiple description coding theory and propose a robust high-quality compressed sensing-based coding method. Combined with iterative weighted technique and fast gradient descent method, the proposed method implicitly implements matrix inverse operations to highly reduce the storage pressure. Also the weighted norm method is taken to optimize the descent steps, which highly increases convergent speed of the algorithm. Taking an image has sparse Fourier representations as an example, the paper presents the detailed image sparse coding and fast reconstruction procedure. By integrating the compressive sensing multi-description coding framework, the simulation demonstrates the superior reconstruction performance of the proposed algorithm. Most importantly, with p close to zero, the reconstruction performance of GPNSR can approximate that of ℓ0 norm optimization result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Candès E J. Compressive sampling. In: Proceedings of International Congress of Mathematics. 2006. 1433–1452
Candès E J, Romberg J, Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2006, 52: 489–509
Candès E J, Romberg J. Quantitative robust uncertainty principles and optimally sparse decompositions. Found Comput Math, 2006, 6: 227–254
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2006, 52: 1289–1306
Candès E J, Romberg J. Practical signal recovery from random projections. Wavelet Appl Sig Image Proc XI, 2005, 5914: 1029228
Donoho D L, Tsaig Y. Extensions of compressed sensing. Signal Process, 2006, 86: 533–548
Goyal V K. Multiple description coding: compression meets the network. IEEE Signal Proc Mag, 2001, 18: 74–93
Carrillo R E, Barner K E, Aysal T C. Robust sampling and reconstruction methods for sparse signals in the presence of impulsive noise. IEEE J Sel Topic Signal Proc, 2010, 4: 132–408
Shi G M, Chen X Y, Song X X, et al. Signal matching wavelet for ultrasonic flaw detection in high background noise. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferr, 2011, 58: 776–787
Marcia R F, Willett R M, Harmany Z T. Compressive optical imaging: architectures and algorithms. In: Optical and Digital Image Processing: Fundamentals and Applications. 2011
Suzen M, Giannoula A, Durduran T. Compressed sensing in diffuse optical tomograph. Opt Express, 2010, 18: 23676–23690
Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly J M. Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58: 1182–1195
Chartrand R. Fast algorithms for nonconvex compressive sensing: MRI reconstruction from very few data. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). 2009. 262–265
Herman M, Strohmer T. High-resolution radar via compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2009, 57: 2275–2284
Easley P V M, Healy G R, Chellappa D M R. Compressed synthetic aperture radar. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Proc, 2010, 4: 244–254
Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J Roy Stat Soc B, 1996, 58: 267–288
Chen S, Donoho D, Saunders M. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J Sci Comput, 1998, 20: 33–61
Figueiredo M A T, Nowak R D, Wright S J. Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: application to compresed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Proc, 2007, 1: 586–597
Candes E, Wakin M, Boyd S. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l1 minimizaion. J Fourier Anal Appl, 2008, 14: 877–905
Chartrand R, Yin W. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Accoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. 2008. 3869–3872
Chartrand R. Exact reconstruction of sparse signal via nonconvex minimization. IEEE Signal Proc Lett, 2007, 14: 707–710
Rao B D, Kreutz-Delgado K. An affine scaling methodology for best basis selection. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1999, 47: 187–200
Rao B D, Engan K, Cotter S F, et al. Subset selection in noise based on diversity measure minimization. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2003, 51: 760–770
Gorodntisky I F, Rao B D. Sparse singal reconstruction from limited data using FOUSS: a reweighted minimim norm algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45: 600–616
Hager W W, Park S. The gradient projection method with exact line search. J Global Optim, 2004, 30: 103–118
Liu D H, Shi G M, Zhou J S, et al. New metod of multiple description coding for image based on compressed sensing. J Infrared Millim Wave, 2009, 28: 298–302
Donoho D L, Tsaig Y, Drori I, et al. Sparse solution of underdetermined linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2012, 58: 1094–1121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Shen, F., Wang, Z. et al. A high quality image reconstruction method based on nonconvex decoding. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 56, 1–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4712-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4712-6