Abstract
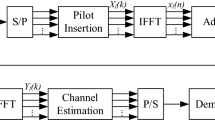
This paper is concerned with the problem of channel estimation for amplify-and-forward (AF) cooperative relay networks with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. The algorithm is based on both the least square (LS) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) technique with a superimposed training strategy. Specifically, both the source and relay superimpose their own training signal onto data stream prior to transmission so as to estimate the separate channel state information of the source to relay link and the relay to destination link. We also present the performance analysis and derive the approximated closed-form expressions for the MSE of separate channel estimation of source to relay link and the relay to destination link, respectively, from which we compute the optimal training signal as well as the relay power-amplification factor. To further improve the performance of channel estimation, we adopt a weighted average process to enhance the estimation performance over multiple OFDM blocks, from which we compute the optimal tracking factor. Simulation results are provided to corroborate the proposed scheme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laneman J N, Tse D N C, Wornell G W. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2004, 15: 3062–3080
Seol D Y, Kwon U K, Im G H. Performance of single carrier transmission with cooperative diversity over fast fading channels. IEEE Trans Commun, 2009, 57: 2799–2807
Sendonaris A, Erkip E, Aazhang B. User cooperation diversity: Part I. system description. IEEE Trans Commun, 2003, 51: 1927–1938
Herdin M. A chunk based OFDM amplify-and-forward relaying scheme for 4G mobile radio systems. P IEEE, 2006, 10: 4507–4512
Li Y, Wang W, Kong J, et al. Subcarrier paring for amplify-and-forward and decode-and-forward OFDM relay links. IEEE Commun Lett, 2009, 13: 209–211
Ng D W K, Schober R. Resource allocation and scheduling in multi-cell OFDMA systems with decode-and-forward relaying. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2011, 10: 2246–2258
Song M G, Kim D, Im G H. Recursive channel estimation method for OFDM-based cooperative systems. IEEE Commun Lett, 2010, 14: 1029–1031
Velasquez L C, Le H N, Ngoc T L. Double selective cascaded channel estimation in amplify-and-forward relay systems. P IEEE, 2011, 1: 1–4
Abdallah S, Psaromiligkos I N. Semi-blind channel estimation for amplify-and-forward two-way relay networks employing constant modulus constellations. In: Proceedings of CISS 10. Princeton: IEEE, 2010. 1–5
Tang X, Hua Y. Optimal design of non-regenerative MIMO wireless relays. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2007, 6: 1398–1407
Christos M, Rontogiannis A, Berberids K, et al. Training design in single relay AF cooperative systems with correlated channels. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICASSP 11. Prague: IEEE, 2011. 3316–3319
Gao F, Jiang B, Gao X Q, et al. Superimposed training based channel estimation for OFDM modulated amplify-andforward relay networks. IEEE Trans Commun, 2011, 59: 2029–2039
Wang G, Gao F, Tellambura C. Channel estimation and training design for two-way relay networks in timeselective fading environments. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2011, 10: 2681–2691
Zhou G T, Viberg M, McKelvey T. A first-order statistical method for channel estimation. IEEE Signal Proc Lett, 2003, 10: 57–60
Ghogho M, McLernon D, Hernandez E A, et al. Channel estimation and symbol detection for block transmission using data-dependent superimposed training. IEEE Signal Proc Lett, 2005, 12: 226–229
Dai X, Zhang H, Li D. Linearly time-varying channel estimation for MIMO/OFDM systems using superimposed training. IEEE Trans Commun, 2010, 58: 681–692
Cui T, Tellambura C. Superimposed-pilot symbols for channel estimation in OFDM systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE Global COM. Vol 4. 2005. 2229–2233
Zhang H, Dai X H, Da R P. Linearly time-varying channel estimation and training power allocation for OFDM/MIMO systems using superimposed training. Sci China Inf Sci, 2011, 54: 1456–1470
Kay S M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1993
Barhumi I, Leus G, Moonen M. Optimal training design for MIMO OFDM systems in mobile wireless channels. IEEE Trans Signal Proces, 2003, 51: 1615–1624
Jakes W. Microwave Mobile Communications. Piscataway: IEEE, 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Pan, D., Cui, H. et al. Superimposed training for channel estimation of OFDM modulated amplify-and-forward relay networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 56, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4714-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4714-4