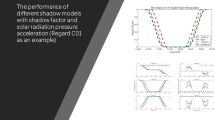
Abstract
The shadow effect is an important constraint to be considered during the implementation of exploration missions. In this paper, for the Earth-Moon Lagrange point L2 relay communication mission, shadow effect issues on a periodic orbit about L2 are investigated. A systematic analysis based on the time domain and phase space is performed including the distribution, duration, and frequency of shadows. First, the Lindstedt-Poincare and second-order differential correction methods are used in conjunction with the DE421 planetary ephemeris to achieve a mission trajectory family in a high-precision ephemeris model. Next, on the basis of a conical shadow model, the influence of different orbital phases and amplitudes on the shadow is analyzed. The distribution of the shadow is investigated as well. Finally, the configuration of the shadow and its characteristics are studied. This study provides an important reference and basis for mission orbit design and shadow avoidance for relay satellites at an Earth-Moon Lagrange point.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farquhar R W. Lunar communications with libration-point satellites. J Spacecraft Rockets, 1967, 4: 1383–1384
Xu M, Xu S J. Trajectory and correction maneuver during the transfer from Earth to halo orbit. Chin J Aeronaut, 2008, 21: 200–206
Li M T, Zheng J H. Impulsive lunar halo transfers using the stable manifolds and lunar flybys. Acta Astronaut, 2010, 66: 1481–1492
Canalias E, Masdemont J J. Computing natural transfers between Sun C Earth and Earth C Moon lissajous libration point orbits. Acta Astronaut, 2008, 63: 238–248
Parker J S. Families of low-energy lunar halo transfers. In: Proceedings of AAS/AIAA Spaceflight Dynamics Conference, Tampa, 2006. 06–132
Kulkami J, Campbell M. Asymptotic stabilization of motion about an unstable orbit: application to spacecraft flight in halo orbit. In: Proceeding of the 2004 American Control Conference, Boston, 2004. 1025–1030
Xu M, Zhou N, Wang J L. Robust adaptive strategy for station keeping of halo orbit. In: Proceedings of the 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Taiyuan, 2012. 3086–3091
Keeter T M. Station-keeping strategies for libration point orbit: target point and floquet mode approaches. Dissertation for Master’s Degree. Indiana: Purdue University, West Lafayette, 1994. 145–148
Liu L, Cao J F, Hu S J, et al. Maintenance of relay orbit about the Earth-Moon collinear libration points. J Deep Space Explor, 2015, 2: 318–324
Dong G L, Xu D Z, Li H T, et al. Initial result of the Chinese Deep Space Stations’ coordinates from Chinese domestic VLBI experiments. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 012203
Jorba A, Masdemond J. Dynamics in the centre manifold of the collinear points of the restricted three body problem. Phys D, 1999, 132: 189–213
Li M T. Low energy trajectory design and optimization for collinear libration points missions. Dissertation for Ph.D. Degree. Beijing: Center for Space Science and Applied Research Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010. 46–49
Montenbruck O, Gill E. Satellite Orbits: Models, Methods and Application. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2001. 80–81
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Lunar Exploration Program), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11572038), and Chang Jiang Scholars Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Wu, W., Qiao, D. et al. Effect of orbital shadow at an Earth-Moon Lagrange point on relay communication mission. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 60, 112301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-016-9069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-016-9069-9