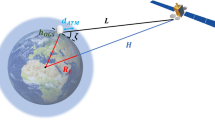
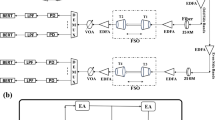
Abstract
The deep space probe is a vital technology for observing and exploring the universe. It is thus intensifying as an aerospace research focus on an international scale. Despite improving the frequency band, the conventional microwave communication technique has difficulty satisfying the increased demand for the enormous volume of scientific data returning to the Earth. With a carrier frequency that is several orders of magnitude higher than the microwave, free-space optical communication is a robust and promising method for achieving both high bit rates and long distances in deep space communication. In this article, the history of this technology is summarized and the objective laws are formulated, while key techniques and development trends are analyzed. Finally, useful concepts and suggestions are proposed for the development of deep space laser communication in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu W R, Liu W W, Qiao D, et al. Investigation on the development of deep space exploration. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 1086–1091
Wu W R, Dong G L, Li H T, et al. Engineering and Technology of Deep Space TT&C System (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 2013
Ning X L, Li Z, Wu W R, et al. Recursive adaptive filter using current innovation for celestial navigation during the Mars approach phase. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 032205
Wu W R, Yu D Y. Development of deep space exploration and its future key technologies (in Chinese). J Deep Space Explor, 2014, 1: 5–17
Fu K, Zhao G Q, Li X J, et al. Iterative spherical simplex unscented particle filter for CNS/Redshift integrated navigation system. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 042201
Cai Y G, Sun J F, Li G Y, et al. Self-homodyne free-space optical communication system based on orthogonally polarized binary phase shift keying. Appl Opt, 2016, 55: 4514
Ma J, Li K, Tan L Y, et al. Performance analysis of satellite-to-ground downlink coherent optical communications with spatial diversity over gamma-gamma atmospheric turbulence. Appl Opt, 2015, 54: 7575–7585
Meng L X, Li L, Zhang L Z, et al. Research on optic antenna of space laser communication networking. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging, Beijing, 2013
Luo J J, Li H Z, Tang Y F, et al. Research on laser communication technology development for deep space exploration (in Chinese). Spacecraft Eng, 2013, 22: 94–97
Ma J, Xu K H, Tan L Y, et al. Analysis for mars laser communications system in USA (in Chinese). Chin J Space Sci, 2006, 26: 364–369
Han H S, Chen J. 21st century foreign deep space exploration development plans and their progresses (in Chinese). Spacecraft Eng, 2008, 17: 1–22
James R L. Deep space optical communication development program. Proc SPIE, 1987, 56: 15–16
Boroson D M, Robinson B S. The lunar laser communication demonstration: NASA’s first step toward very high data rate support of science and exploration missions. Space Sci Rev, 2014, 185: 115–128
Boroson D M, Robinson B S, Murphy D V, et al. Overview and results of the lunar laser communication demonstration. Proc SPIE, 2014, 8971: 89710S
Grechukhin I A, Grigoriev V N, Danileiko N O, et al. Russian free-space laser communication experiment “SLS”. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Fujiyoshida, 2013
Grigoryev V, Kovalev V, Shargorodskiy V, et al. High-bit-rate laser space communication technology and results of onboard experiment. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Kobe, 2014
Renny A F, David A K, Harold T Y, et al. 5.625 Gbps bidirectional laser communications measurements between the NFIRE satellite and an optical ground station. Proc SPIE, 2011, 8184: 81840D
Heine F, Mühlnikel G, Zech H, et al. LCT for the European data relay system: in orbit commissioning of the alphasat and sentinel 1A LCTs. Proc SPIE, 2015, 9354: 93540G
Hideki T, Yoshihisa T, Yoshisada K, et al. Study on coding parameters for a small optical transponder. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Kobe. 2014
Mukai T, Inagawa S, Suzuki K, et al. A study of free space laser communication experiment on the ISS Japanese experiment module for space explorations. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), New Orleans, 2015
Hemmati H. Deep Space Optical Communications. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2005
Hemmati H. Status of free-space optical communications program at JPL. In: Proceedings of IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, 2000. 101–105
Hemmati H, Page N A. Preliminary opto-mechanical design for the X2000 transceiver. Proc SPIE, 1999, 3615: 206–211
Boroson D M, Roy S B, Scozzafava J J. Overview of high rate deep space laser communications options. Proc SPIE, 2004, 5338: 37–49
Biswas A, Boroson D M, Edwards B L. Mars laser communication demonstration: what it would have been. Proc SPIE, 2006, 6105: 610502
Shaik K, Wonica D, Wilhelm M. Optical subnet concepts for the deep space network. Telecommun Data Acquisition Prog Rep, 1993, 42: 153–181
Wilson K E, Wright M, Cesarone R, et al. Cost and performance comparison of an earth-orbiting optical communication relay transceiver and a ground-based optical receiver subnet. Interpla Netw Prog Rep, 2003, 153: 1–12
Levitt B, Wilson K, Roberts T, et al. Hybrid optical DSN architecture: interleaved PPM concept. In: Proceedings of JPL Internal Conference, Pasadena, 2004
Badesha S S. SPARCL: a high altitude tethered balloon-based optical space-to-ground communication system. Proc SPIE, 2002, 4821: 181–193
Mecherle G S, Akle W, Starkus C, et al. Direct detection optical relay satellite for deep-space communication. Proc SPIE, 1994, 2123: 134–155
Boroson D M, Scozzafava J J, Murphy D V, et al. The lunar laser communications demonstration (LLCD). In: Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Space Mission Challenges for Information Technology, Pasadena, 2009. 23–28
Sun X L, Skillman D R, Hoffman E D, et al. Free space laser communication experiments from Earth to the lunar reconnaissance orbiter in lunar orbit. Opt Express, 2013, 21: 1865–1871
Sun X L, Skillman D R, Hoffman E D, et al. Simultaneous laser ranging and communication from an Earth-based satellite laser ranging station to the lunar reconnaissance orbiter in lunar orbit. Proc SPIE, 2013, 8610: 861003
Boroson D M, Robinson B S. Status of the lunar laser communication demonstration. Proc SPIE, 2013, 8610: 861002
Robinson B S, Boroson DM, Burianek D A, et al. The NASA lunar laser communication demonstration-successful highrate laser communications to and from the Moon. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Operations, Pasadena, 2014. 1–7
Boroson D M, Robinson B S, Burianek D A, et al. Overview and status of the lunar laser communications demonstration. Proc SPIE, 2014, 8971: 89710S
Constantine S, Elgin L E, Stevens M L, et al. Design of a high-speed space modem for the lunar laser communications demonstration. Proc SPIE, 2011, 7923: 792308
Burnside J W, Conrad S D, Pillsbury A D, et al. Design of an inertially stabilized telescope for the LLCD. Proc SPIE, 2011, 7923: 79230L
Murphy D V, Kansky J E, Grein M E, et al. LLCD operations using the lunar lasercom ground terminal. Proc SPIE, 2014, 8971: 89710V
Grein M E, Kerman A J, Dauler E A, et al. Design of a ground-based optical receiver for the lunar laser communications demonstration. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications, Santa Monica, 2011. 78–82
Caplan D O, Carney J J, Lafon R E, et al. Design of a 40 Watt 1.55 μm uplink transmitter for lunar laser communications. Proc SPIE, 2012, 8246: 82460M
Schulein R T, Lafonb R E, Taylora M B, et al. Nonlinearity mitigation of a 40 Watt 1.55 micron uplink transmitter for lunar laser communications. Proc SPIE, 2013, 8610: 86100F
Grein M E, Kerman A J, Dauler E A, et al. An optical receiver for the lunar laser communication demonstration based on photon-counting superconducting nanowires. Proc SPIE, 2015, 9492: 949208
Edwards B L, Israel D, Wilson K, et al. The laser communications relay demonstration. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Ajaccio, 2012. 1–9
Edwards B, Israel D, Caroglanian A, et al. A day in the life of the laser communications relay demonstration project. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Space Operations, Daejeon, 2016. 1–13
Cornwell D M. NASA’s optical communications program for 2015 and beyond. Proc SPIE, 2015, 9354: 93540E
Cornwell D M. NASA’s optical communications program for future planetary and near-Earth missions. Study Rep SCaN Program, 2016, 1–2
Fielhauer K B, Boone B G, Raible D E. Concurrent system engineering and risk reduction for dual-band (RF/optical) spacecraft communications. In: Proceedings of IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, 2012. 1–7
Raible D, Hylton A. Integrated RF/optical interplanetary networking preliminary explorations and empirical results. In: Proceedings of the 30th AIAA International Communications Satellite System Conference (ICSSC), Ottawa, 2012
Sodnik Z, Heese C, Carnelli I, et al. Multi-purpose laser communication system for the asteroid impact mission (AIM). In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), New Orleans, 2015. 1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Chen, M., Zhang, Z. et al. Overview of deep space laser communication. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61, 040301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9216-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9216-0