Abstract
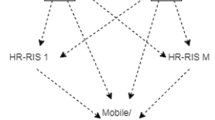
Terahertz (THz) multiuser massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) has been envisioned as a promising technique to support massive connectivity in next-generation wireless networks. However, due to ultra-high frequency band, the path attenuation of THz channels is extremely severe, resulting in limited wireless coverage. In this paper, we propose an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted THz multiuser massive MIMO technique to enhance coverage. First, we design an IRS-assisted THz communication framework with a low-cost sub-connected hybrid precoding architecture, including uplink data transmission and downlink data transmission. In particular, precoding errors due to the limitations of physical devices and environments are taken into consideration. Then, we derive the closed-form expressions for uplink and downlink spectral efficiencies, and reveal the impacts of system parameters. Finally, we conduct extensive simulations to verify the effectiveness of the proposed IRS-assisted THz multiuser massive MIMO technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X M, Ng D W K, Yu W, et al. Massive access for 5G and beyond. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2021, 39: 615–637
Ahmed N, De D, Hussain I. Internet of Things (IoT) for smart precision agriculture and farming in rural areas. IEEE Int Things J, 2018, 5: 4890–4899
Qi Q, Chen X M, Zhong C J, et al. Physical layer security for massive access in cellular Internet of Things. Sci China Inf Sci, 2020, 63: 121301
Han C, Wu Y Z, Chen Z, et al. Terahertz communications (TeraCom): challenges and impact on 6G wireless systems. 2019. ArXiv:1912.06040v2
Zhang Z Q, Xiao Y, Ma Z, et al. 6G wireless networks: vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies. IEEE Veh Technol Mag, 2019, 14: 28–41
Boulogeorgos A A A, Alexiou A, Merkle T, et al. Terahertz technologies to deliver optical network quality of experience in wireless systems beyond 5G. IEEE Commun Mag, 2018, 56: 144–151
Hu X L, Zhong C J, Chen X M, et al. Cell-free massive MIMO systems with low resolution ADCs. IEEE Trans Commun, 2019, 67: 6844–6857
Zhao F R, Zhong C J, Chen X M, et al. Energy efficiency of massive MIMO downlink WPT with mixed-ADCs. IEEE Commun Lett, 2019, 23: 2316–2320
Jia R D, Chen X M, Zhong C J, et al. Design of non-orthogonal beamspace multiple access for cellular Internet-of-Things. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process, 2019, 13: 538–552
Chen X M, Zhang Z Y, Zhong C J, et al. Exploiting multiple-antenna techniques for non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2017, 35: 2207–2220
Rappaport T S, Xing Y C, Kanhere O, et al. Wireless communications and applications above 100 GHz: opportunities and challenges for 6G and beyond. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 78729–78757
Wang P, Li Y H, Song L Y, et al. Multi-gigabit millimeter wave wireless communications for 5G: from fixed access to cellular networks. IEEE Commun Mag, 2015, 53: 168–178
Yang P, Xiao Y, Xiao M, et al. 6G wireless communications: vision and potential techniques. IEEE Netw, 2019, 33: 70–75
Yuan Y F, Zhao Y J, Zong B Q, et al. Potential key technologies for 6G mobile communications. Sci China Inf Sci, 2020, 63: 183301
Song H J, Nagatsuma T. Present and future of Terahertz communications. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol, 2011, 1: 256–263
Jornet J M, Akyildiz I F. Channel modeling and capacity analysis for electromagnetic wireless nanonetworks in the Terahertz band. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2011, 10: 3211–3221
Han C, Bicen A O, Akyildiz I F. Multi-ray channel modeling and wideband characterization for wireless communications in the Terahertz band. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2015, 14: 2402–2412
Afsharinejad A, Davy A, Jennings B, et al. A path-loss model incorporating shadowing for THz band propagation in vegetation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2015. 1–6
Ekti A R, Boyaci A, Alparslan A, et al. Statistical modeling of propagation channels for Terahertz band. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), 2017. 275–280
You X H, Wang C X, Huang J, et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts. Sci China Inf Sci, 2021, 64: 110301
Hu X L, Wang J W, Zhong C J. Statistical CSI based design for intelligent reflecting surface assisted MISO systems. Sci China Inf Sci, 2020, 63: 222303
Yu G H, Chen X M, Zhong C J, et al. Design, analysis, and optimization of a large intelligent reflecting surface-aided B5G cellular Internet of Things. IEEE Int Things J, 2020, 7: 8902–8916
Hu S, Rusek F, Edfors O. The potential of using large antenna arrays on intelligent surfaces. In: Proceedings of the 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), 2017. 1–6
Tang W K, Li X, Dai J Y, et al. Wireless communications with programmable metasurface: transceiver design and experimental results. China Commun, 2019, 16: 46–61
Ning B Y, Chen Z, Chen W R, et al. Channel estimation and transmission for intelligent reflecting surface assisted THz communications. In: Proceedigs of IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 2020. 1–7
Li Z X, Chen Z, Ma X Y, et al. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface enabled Terahertz MIMO systems: a deep learning perspective. In: Proceedigs of IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), 2020. 75–79
Ma X Y, Chen Z, Chen W J, et al. Joint channel estimation and data rate maximization for intelligent reflecting surface assisted Terahertz MIMO communication systems. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 99565–99581
Chen W J, Ma X Y, Li Z X, et al. Sum-rate maximization for intelligent reflecting surface based Terahertz communication systems. In: Proceedigs of IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications Workshops in China (ICCC Workshops), 2019. 153–157
Qiao J P, Alouini M S. Secure transmission for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted mmwave and Terahertz systems. IEEE Wirel Commun Lett, 2020, 9: 1743–1747
Hu X L, Zhong C J, Chen X M, et al. Cluster grouping and power control for angle-domain MmWave MIMO NOMA systems. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process, 2019, 13: 1167–1180
Alkhateeb A, El Ayach O, Leus G, et al. Channel estimation and hybrid precoding for millimeter wave cellular systems. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process, 2014, 8: 831–846
Han S F, Chih-Lin I, Xu Z K, et al. Large-scale antenna systems with hybrid analog and digital beamforming for millimeter wave 5G. IEEE Commun Mag, 2015, 53: 186–194
Maruthi S P, Panigrahi T, Hassan M. Improving the reliability of pulse-based Terahertz communication using intelligent reflective surface. In: Proceedigs of IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), 2020. 1–6
Croswell W. Antenna theory, analysis, and design. IEEE Antennas Propag Soc Newsl, 1982, 24: 28–29
Hur S, Kim T, Love D J, et al. Millimeter wave beamforming for wireless backhaul and access in small cell networks. IEEE Trans Commun, 2013, 61: 4391–4403
Chen X M, Zhang Z Y, Zhong C J, et al. Fully non-orthogonal communication for massive access. IEEE Trans Commun, 2018, 66: 1717–1731
Björnson E, Hoydis J, Sanguinetti L. Massive MIMO networks: spectral, energy, and hardware efficiency. FNT Signal Process, 2017, 11: 154–655
Chen J, Chen X M, Gerstacker W H, et al. Resource allocation for a massive MIMO relay aided secure communication. IEEE Trans Inform Forensic Secur, 2016, 11: 1700–1711
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFB1805703), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61871344), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LR20F010002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, G., Chen, X., Shao, X. et al. Low-cost intelligent reflecting surface aided Terahertz multiuser massive MIMO: design and analysis. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 64, 200302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3281-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-021-3281-7