Abstract
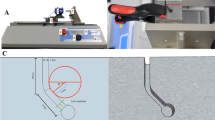
Nickel–titanium (NiTi) instruments are extensively used in endodontic treatment because of their outstanding mechanical properties. However, unexpected fracture of NiTi rotary instruments occurs during endodontic procedures. Therefore, a reliable method to detect the structural status of a used NiTi instrument is needed. The aim of this study is to use natural frequency for monitoring structural changes of a NiTi instrument during and after the instrumentation process. In this study, laboratory modal testing experiments were performed on cyclic fatigue-loaded NiTi rotary instruments with a natural frequency detecting device. In addition, three-dimensional finite element (FE) models were established for assessing the structural changes that take place in repeatedly loaded NiTi instruments. Repeated rotational loading resulted in a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in natural frequency (with a decreasing ratio of 5.6%) when the tested instruments reached 77–85% of their total life limit. In FE analysis, a strong correlation between natural frequency and change in elastic modulus of the NiTi instrument was found. These findings indicated that natural frequency may represent an effective parameter for evaluating the micro-structural status of NiTi rotary instruments subjected to fatigue loadings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankrum MT, Hartwell GR, Truitt JE (2004) K3 Endo, ProTaper, and ProFile systems: breakage and distortion in severely curved roots of molars. J Endod 30:234–237
Arens FC, Hoen MM, Steiman HR et al (2003) Evaluation of single-use rotary nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod 29:664–666
Barbosa FOG, Gomes JACP, de Araújo MCP (2008) Fractographic analysis of K3 nickel-titanium rotary instruments submitted to different modes of mechanical loading. J Endod 34:994–998
Berutti E, Chiandussi G, Gaviglio I, Ibba A (2003) Comparative analysis of torsional and bending stresses in two mathematical models of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: ProTaper versus ProFile. J Endod 29:15–19
Chang WJ, Lee SY, Wu CC et al (2007) A newly designed natural frequency analysis device for dental implants stability detection. Dent Mat J 25:665–671
Gambarini G (2001) Cyclic fatigue of ProFile rotary instruments after prolonged clinical use. Int Endod J 34:386–389
Hassiotis S, Jeong GD (1995) Identification of stiffness reductions using natural frequencies. J Eng Mech 121:1106–1113
Huang HM, Cheng KY, Chen CF et al (2005) Design and examination of a stability-detecting device for dental implants. Proc Inst Mech Eng H: J Eng Med 219:203–211
Huang HM, Chiu CL, Yeh CY (2003) Factors influencing the natural frequency of dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:1184–1188
Huang HM, Liu DZ, Shiau YY et al (2004) Natural frequency assessment of the stability of root keeper magnetic devices. Med Biol Eng Comput 42:388–393
Kay MW, Roe SC, Stikeleather LF et al (1998) Axial vibration of threaded external fixation pins: detection of pin loosening. Ann Biomed Eng 26:361–368
Li UM, Lee BS, Shih CT (2002) Cyclic fatigue of endodontic nickel titanium rotary instruments: static and dynamic tests. J Endod 28:448–451
Li UM, Shin CS, Lan WH (2006) Application of nondestructive testing in cyclic fatigue evaluation of endodontic Ni-Ti rotary instruments. Dent Mater J 25:247–252
Lu CL, Wu TX, Yu JG (2004) On torsional stiffness and natural frequency of bellows. Proc Inst Mech Eng C: J Mech Eng Sci 218:263–271
Meredith N (1998) A review of nondestructive test methods and their application to measure the stability and osseiontegration of bone anchored endosseous implants. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 26:275–291
Miyai K, Ebihara A, Hayashi Y (2006) Influence of phase transformation on the torsional and bending properties of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments. Int Endod J 39:119–126
Necchi S, Taschieri S, Petrini L, Migliavacca F (2008) Mechanical behaviour of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments in simulated clinical conditions: a computational study. Int Endod J 41:939–949
Parashos P, Messer HH (2006) Rotary NiTi instrument fracture and its consequences. J Endod 32:1031–1043
Thompson SA (2000) An overview of nickel–titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int Endod J 33:297–310
Torrisi L (1999) The NiTi superelastic alloy application to the dentistry field. Biomed Mater Eng 9:39–47
Xu X, Eng M, Zheng Y, Eng D (2006) Comparative study of torsional and bending properties for six models of nickel-titanium root canal instruments with different cross-sections. J Endod 32:372–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, SC., Lee, SY., Ciou, CY. et al. Non-destructive natural frequency tests of cyclic fatigue-loaded nickel–titanium rotary instruments. Med Biol Eng Comput 48, 555–560 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0605-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0605-2