Abstract
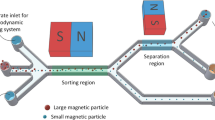
Magnetic nanoparticles for therapy and diagnosis are at the leading edge of the rapidly developing field of bionanotechnology. In this study, we have theoretically studied motion of magnetic nano- as well as micro-particles in the field of cylindrical Halbach array of permanent magnets. Magnetic flux density was modeled as magnetostatic problem by finite element method and particle motion was described using system of ordinary differential equations—Newton law. Computations were done for nanoparticles Nanomag®-D with radius 65 nm, which are often used in magnetic drug targeting, as well as microparticles DynaBeads-M280 with radius 1.4 µm, which can be used for magnetic separation. Analyzing snapshots of trajectories of hundred magnetite particles of each size in the water as well as in the air, we have found that optimally designed magnetic circuits of permanent magnets in quadrupolar Halbach array have substantially shorter capture time than simple blocks of permanent magnets commonly used in experiments, therefore, such a Halbach array may be useful as a potential source of magnetic field for magnetic separation and targeting of magnetic nanoparticles as well as microparticles for delivery of drugs, genes, and cells in various biomedical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radbruch A, Mechtold B, Thiel A, Miltenyi S, Pflüger E (1994) High-gradient magnetic cell sorting. Method Cell Biol B 42:387–403
Käppler T, Cerff M, Ottow K, Hobley T, Posten C (2009) In situ magnetic separation for extracellular protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:535–545
Babincová M, Čičmanec P, Altanerová V, Altaner Č, Babinec P (2002) AC-magnetic field controlled drug release from magnetoliposomes: design of a method for site-specific chemotherapy. Bioelectrochemistry 55:17–19
Babincová M, Leszczynska D, Sourivong P, Babinec P, Leszczynski J (2004) Principles of magnetodynamic chemotherapy. Med Hypotheses 62:375–377
Babinec P, Babincová M, Sourivong P, Leszczynska D (2005) Efficient treatment of pigmented B16 melanoma using photosensitized long-circulating magnetofullerenosomes. J Magn Magn Mater 293:394–397
Babincová M, Altanerová V, Altaner Č, Bergemann C, Babinec P (2008) In vitro analysis of cisplatin functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in combined cancer chemotherapy and electromagnetic hyperthermia. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 7:15–19
Babincová M, Babinec P, Bergemann C (2001) High-gradient magnetic capture of ferrofluids: implications for drug targeting and tumor embolization. Z Naturforsch C 56:909–911
Plank C, Schillinger U, Scherer F, Bergemann C, Rémy JS, Krötz F, Anton M, Lausier J, Rosenecker J (2003) The magnetofection method: using magnetic force to enhance gene delivery. Biol Chem 384:737–747
Schillinger U, Brill T, Rudolph C, Huth S, Gersting S, Krötz F, Hirschberger J, Bergemann C, Plank C (2005) Advances in magnetofection—magnetically guided nucleic acid delivery. J Magn Magn Mater 293:501–508
Babincová M, Altanerová V, Lampert M, Altaner C, Machová E, Srámka M, Babinec P (2000) Site-specific in vivo targeting of magnetoliposomes using externally applied magnetic field. Z Naturforsch C 55:278–281
Mykhaylyk O, Antequera YS, Vlaskou D, Plank C (2007) Generation of magnetic nonviral gene transfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nat Protoc 2:2391–2411
Zborowski M, Sun L, Moore LR, Williams PS, Chalmers JJ (1999) Continuous cell separation using novel magnetic quadrupole flow sorter. J Magn Magn Mater 194:224–230
Krafčík A, Babincová M, Babinec P (2009) Theoretical analysis of magnetic particle trajectory in high-current pulsed quadrupole: implications for magnetic cell separation, drug targeting, and gene therapy. Optoelectron Adv Mater Rapid Commun 3:226–233
Häfeli UO, Gilmour K, Zhou A, Lee S, Hayden ME (2007) Modeling of magnetic bandages for drug targeting: Button vs. Halbach arrays. J Magn Magn Mater 311:323–329
Furlani EP, Ng KC (2006) Analytical model of magnetic nanoparticle transport and capture in the microvasculature. Phys Rev E 73(061919):1–10
Furlani EP (2001) Permanent magnet and electromechanical devices: materials, analysis and applications. Academic Press, New York
Takayasu M, Gerber R, Friedlaender FJ (1983) Magnetic separation of submicron particles. IEEE Trans Magn 9:2112–2114
Jackson JD (2001) Classical electrodynamics. Wiley, New York
Meeker D Finite elements methods magnetics, V 4.2. http://femm.foster-miller.net.
Kanger JS, Subramaniam V, van Driel R (2008) Intracellular manipulation of chromatin using magnetic nanoparticles. Chromosome Res 16:511–522
Dames P, Gleich B, Flemmer A, Hajek K, Seidl N, Wiekhorst F, Eberbeck D, Bittmann I, Bergemann C, Weyh T, Trahms L, Rosenecker J, Rudolph C (2007) Targeted delivery of magnetic aerosol droplets to the lung. Nat Nanotechnol 2:495–499
Winkler M, Chichkine V, Behr KH, Geissel H, Eliseev S, Kalimov A, Li G, Munzenberg G, Plaß WR, Scheidenberger C, Wang Z, Weick H, Wollnik H (2003) Development and test of iron-free quadrupole lenses with high magnetic flux densities. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res B 204:454–459
Gerber R, Takayasu M, Friedlaender FJ (1983) Generalization of HGMS theory: the capture of ultra-fine particles. IEEE Trans Magn 19:2115–2117
Cregg PJ, Murphy K, Mardinoglu A (2008) Calculation of nanoparticle capture efficiency in magnetic drug targeting. J Magn Magn Mater 320:3272–3275
Cregg PJ, Murphy K, Mardinoglu A (2009) Inclusion of magnetic dipole–dipole and hydrodynamic interactions in implant-assisted magnetic drug targeting. J Magn Magn Mater 321:3893–3898
Wilson RJ, Hu W, Fu CWP, Koh AL, Gaster RS, Earhart CM, Fu A, Heilshorn SC, Sinclair S, Wang SX (2009) Formation and properties of magnetic chains for 100 nm nanoparticles used in separations of molecules and cells. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1452–1458
Hatch GP, Stelter RE (2001) Magnetic design considerations for devices and particles used for biological high-gradient magnetic separation (HGMS) systems. J Magn Magn Mater 225:262–276
Kopcansky P, Bano M, Repasan M, Potocova I, Timko M, Hrnciar V, Demjan S (2004) Magnetic targeted drug delivery using focused magnet. Magnetohydrodynamics 40:369–376
Rotariu O, Udrea LE, Strachan NJC, Baadescu V (2007) The guidance of magnetic colloids in simulated tissues for targeted drug delivery. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 9:942–945
Rotariu O, Udrea LE, Strachan NJC, Badescu V (2005) Targeting magnetic carrier particles in tumour microvasculature—a numerical study. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 7:3209–3218
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by VEGA Grant 1/0082/08 and Magselectofection project of 6. FP of EU under the contract No.: LSHB-CT-2006-019038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babinec, P., Krafčík, A., Babincová, M. et al. Dynamics of magnetic particles in cylindrical Halbach array: implications for magnetic cell separation and drug targeting. Med Biol Eng Comput 48, 745–753 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0636-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0636-8