Abstract
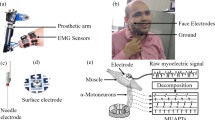
In this paper, we proposed to utilize a novel spatio-spectral filter, common spatio-spectral pattern (CSSP), to improve the classification accuracy in identifying intended motions based on low-density surface electromyography (EMG). Five able-bodied subjects and a transradial amputee participated in an experiment of eight-task wrist and hand motion recognition. Low-density (six channels) surface EMG signals were collected on forearms. Since surface EMG signals are contaminated by large amount of noises from various sources, the performance of the conventional time-domain feature extraction method is limited. The CSSP method is a classification-oriented optimal spatio-spectral filter, which is capable of separating discriminative information from noise and, thus, leads to better classification accuracy. The substantially improved classification accuracy of the CSSP method over the time-domain and other methods is observed in all five able-bodied subjects and verified via the cross-validation. The CSSP method can also achieve better classification accuracy in the amputee, which shows its potential use for functional prosthetic control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Assaf Y (2006) Surface myoelectric signal analysis: dynamic approaches for change detection and classification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(11):2248–2256
Andreasen D, Gabbert D (2006) Electromyographic switch navigation of power wheelchairs. In: Annual conference of the rehabilitation engineering and assistive technology society of North America
Arieta A, Katoh R, Yokoi H, Wenwei Y (2006) Development of a multi-DOF electromyography prosthetic system using the adaptive joint mechanism. Appl Bionics Biomech 3(2):101–112
Barry D, Gordon K, Hinton G (1990) Acoustic and surface EMG diagnosis of pediatric muscle disease. Muscle Nerve 13(4): 286–290
Bhullar H, Loudon G, Fothergill J, Jones N (1990) Selective noninvasive electrode to study myoelectric signals. Med Biol Eng Comput 28(6):581–586
Day S (2002) Important factors in surface EMG measurement. Bortec Biomedical Ltd publishers, Calgary, pp 1–17
De Luca C (2002) Surface electromyography: detection and recording. DelSys Incorporated, pp 1–10
Disselhorst-Klug C, Silny J, Rau G (1997) Improvement of spatial resolution in surface-EMG: a theoretical and experimental comparison of different spatial filters. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 44(7):567–574
Du S, Vuskovic M (2004) Temporal vs. spectral approach to feature extraction from prehensile EMG signals. In: Information reuse and integration, 2004. IRI 2004. IEEE international conference on proceedings of the 2004 , pp 344–350. IEEE
Duda R, Hart P, Stork D (2000) Pattern classification, 2nd edn, Wiley, New York
Englehart K, Hudgins B (2003) A robust, real-time control scheme for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50(7):848–854
Farina D, Cescon C (2001) Concentric-ring electrode systems for noninvasive detection of single motor unit activity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48(11):1326–1334
Farina D, Schulte E, Merletti R, Rau G, Disselhorst-Klug C (2003) Single motor unit analysis from spatially filtered surface electromyogram signals. Part I: spatial selectivity. Med Biol Eng Comput 41(3):330–337
Farquhar J, Hill J, Lal T, Schölkopf B (2006) Regularised CSP for sensor selection in BCI. In: 3rd international brain-computer interface workshop and training course, pp 14–15
Freeman W, Holmes M, Burke B, Vanhatalo S (2003) Spatial spectra of scalp EEG and EMG from awake humans. Clin Neurophysiol 114(6):1053–1068
Fukunaga K (1990) Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. Academic Press, London (1990)
Graupe D, Cline W (1975) Functional separation of EMG signals via arma identification methods for prosthesis control purposes. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 2:252–259
Hahne J, Graimann B, Muller K (2012) Spatial filtering for robust myoelectric control. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(5):1436–1443
Huang H, Zhou P, Li G, Kuiken T (2008) An analysis of EMG electrode configuration for targeted muscle reinnervation based neural machine interface. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 16(1):37–45
Huang H, Zhou P, Li G, Kuiken T (2009) Spatial filtering improves EMG classification accuracy following targeted muscle reinnervation. Ann Biomed Eng 37(9):1849–1857
Hudgins B, Parker P, Scott R (1993) A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40(1):82–94
Koles Z (1991) The quantitative extraction and topographic mapping of the abnormal components in the clinical EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 79(6):440–447
Lemm S, Blankertz B, Curio G, Muller K (2005) Spatio-spectral filters for improving the classification of single trial EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(9):1541
Peerdeman B, Boere D, Witteveen H, Veld R, Hermens H, Stramigioli S, Rietman H, Veltink P, Misra S (2011) Myoelectric forearm prostheses: State of the art from a user-centered perspective. J Rehabil Res Dev 48(6):719
Proakis J, Manolakis D (1996) Digital signal processing. Macmillan Publishing Company, New York, vol 1(99), 2
Ramoser H, Muller-Gerking J, Pfurtscheller G (2000) Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined handmovement. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 8(4):441–446
Reucher H, Rau G, Silny J (1987) Spatial filtering of noninvasive multielectrode EMG: Part I-introduction to measuring technique and applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2:98–105
Reucher H, Silny J, Rau G (1987) Spatial filtering of noninvasive multielectrode EMG: Part II-filter performance in theory and modeling. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2: 106–113
Wheeler K, Jorgensen C (2003) Gestures as input: Neuroelectric joysticks and keyboards. IEEE Pervasive Comput 2(2):56–61
Yang Y, Chevallier S, Wiart J, Bloch I (2012) Automatic selection of the number of spatial filters for motor-imagery BCI. ESANN 2012. In: 20th European symposium on artificial neural networks, computational intelligence and machine learning, pp 109–114
Zhou P, Lowery M, Englehart K, Huang H, Li G, Hargrove L, Dewald J, Kuiken T (2007) Decoding a new neural–machine interface for control of artificial limbs. J Neurophysiol 98(5): 2974–2982
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (Grant No. 2011CB013305), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 11JC1406000) and the State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Vibration (Grant No. MSVZD201204). Zhiguo Zhang is partially supported by the University of Hong Kong Seed Funding Programme for Basic Research (Grant No. 201203159009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, G., Zhang, Z., Zhang, D. et al. Spatio-spectral filters for low-density surface electromyographic signal classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 51, 547–555 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-012-1024-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-012-1024-3