Abstract
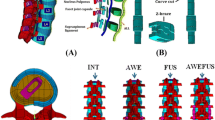
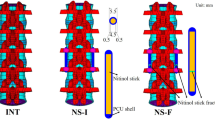
Surgeons often use spinal fixators to manage spinal instability. Dynesys (DY) is a type of dynamic fixator that is designed to restore spinal stability and to provide flexibility. The aim of this study was to design a new spinal fixator using topology optimization [the topology design (TD) system]. Here, we constructed finite element (FE) models of degenerative disc disease, DY, and the TD system. A hybrid-controlled analysis was applied to each of the three FE models. The rod structure of the topology optimization was modelled at a 39 % reduced volume compared with the rigid rod. The TD system was similar to the DY system in terms of stiffness. In contrast, the TD system reduced the cranial adjacent disc stress and facet contact force at the adjacent level. The TD system also reduced pedicle screw stresses in flexion, extension, and lateral bending.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erbulut DU, Zafarparandeh I, Ozer AF, Goel VK (2013) Biomechanics of posterior dynamic stabilization systems. Adv Orthop 2013:451956. doi:10.1155/2013/451956
Anand N, Baron E (2013) Minimally invasive approaches for the correction of adult spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 22(Suppl 2):S232–S241
Fritzel P, Hagg O, Wessberg P, Nordwall A, Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group (2001) 2001 volvo award winner in clinical studies: lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain. Spine 26(23):2521–2534
Gibson JN, Grant IC, Waddell G (1999) The Cochrane review of surgery for lumbar disc prolapse and degenerative lumbar spondylosis. Spine 24(17):1820–1832
Eck JC, Humphreys SC, Hodges SD (1999) Adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion: a review of clinical, biomechanical, and radiologic studies. Am J Orthop 28(6):336–340
Schlegel JD, Smith JA, Schleusener RL (1996) Lumbar motion segment pathology adjacent to thoracolumbar, lumbar, and lumbosacral fusions. Spine 21(8):970–981
Gardner A, Pande KC (2002) Graf ligamentoplasty: a 7-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S157–S163
Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O (2002) The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S170–S178
Rohlmann A, Burra NK, Zander T, Bergmann G (2007) Comparison of the effects of bilateral posterior dynamic and rigid fixation devices on the loads in the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Eur Spine J 16(8):1223–1231
Schaeren S, Broger I, Jeanneret B (2008) Minimum four-year follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. Spine 33(18):636–642
Würgler-Hauri CC, Kalbarczyk A, Wiesli M, Landolt H, Fandino J (2008) Dynamic neutralization of the lumbar spine after microsurgical decompression in acquired lumbar spinal stenosis and segmental instability. Spine 33(3):66–72
Kim CH, Chung CK, Jahng TA (2011) Comparisons of outcomes after single or multilevel dynamic stabilization: effects on adjacent segment. J Spinal Disord Tech 24(1):60–67
Eberlein R, Holzapfel A, Frohlich M (2004) Multi-segment FEA of the human lumbar spine including the heterogeneity of the annulus fibrosus. Comput Mech 34(2):147–163
Freudiger S, Dubios G, Lorrain M (1999) Dynamic neutralization of the lumbar spine confirmed on a new lumbar spine simulator in vitro. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 119(3–4):127–132
Niosi CA, Zhu QA, Wilson DC, Keynan O, Wilson DR, Oxland TR (2006) Biomechanical characterization of the three-dimensional kinematic behavior of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system: an in vitro study. Eur Spine J 15(6):913–922
Zander T, Rohlmann A, Burra NK, Bergmann G (2006) Effect of a posterior dynamic implant adjacent to a rigid spinal fixator. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 21(8):767–774
Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, Dipl-Ing, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2003) Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine and its effects on adjacent segments: an in vitro experiment. J Spinal Disord Tech 16(4):418–423
Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2006) Influence of a dynamic stabilization system on load bearing of a bridged disc: an in vitro study of intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J 15(8):1276–1285
Niosi CA, Wilson DC, Zhu Q, Keynan O, Wilson DR, Oxland TR (2008) The effect of dynamic posterior stabilization on facet joint contact forces. Spine 33(1):19–26
Zhong ZC, Wei SH, Wang JP, Feng CK, Chen CS, Yu CH (2006) Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys 28(1):90–98
Lin CY, Wirtz T, LaMarca F, Hollister SJ (2007) Structural and mechanical evaluations of a topology optimized titanium interbody fusion cage fabricated by selective laser melting process. J Biomed Mater Res A 83(2):272–279
Bendsoe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Suzuki K, Kikuchi N (1991) A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 93(3):291–318
Chang CL, Chen CS, Huang CH, Hsu ML (2012) Finite element analysis of the dental implant using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys 34(7):999–1008
Liao YC, Feng CK, Tsai MW, Chen CS, Cheng CK, Ou YC (2007) Shape modification of the Boston brace using a finite element method with topology optimization. Spine 32(26):3014–3019
Huang SY, Lin YH, Liu CL, Wei SH, Feng CK, Chen CS (2007) Rubber band selection for a dynamic splint for flexor tendon repair-A finite element study. J Med Biol Eng 27(3):156–160
Liu CL, Zhong ZC, Hsu HW, Shih SL, Wang ST, Hung C, Chen CS (2011) Effect of the cord pretension of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system on the biomechanics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Eur Spine J 20(11):1850–1858
Chen SH, Zhong ZC, Chen CS, Chen WJ, Hung C (2009) Biomechanical comparison between lumbar disc arthroplasty and fusion. Med Eng Phys 31(2):244–253
Zhong ZC, Chen SH, Hung CH (2009) Load- and displacement controlled finite element analyses on fusion and non-fusion spinal implants. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 223(2):143–157
Liu CL, Zhong ZC, Shih SL, Hung C, Lee YE, Chen CS (2010) Influence of Dynesys system screw profile on adjacent segment and screw. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(6):410–417
Umehara S, Tadano S, Abumi K, Katagiri K, Kaneda K, Ukai T (1996) Effects of degeneration on the elastic modulus distribution in the lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine 21(7):811–819
Kettler A, Rohlmann F, Ring C, Mack C, Wilke HJ (2011) Do early stages of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration really cause instability? Evaluation of an in vitro database. Eur Spine J 20(4):578–584
Wilke HJ, Rohlmann F, Neidlinger-Wilke C, Werner K, Claes L, Kettler A (2006) Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J 15(6):720–730
Galbusera F, Bellini CM, Anasetti F, Ciavarro C, Lovi A, Brayda-Bruno M (2011) Rigid and flexible spinal stabilization devices: a biomechanical comparison. Med Eng Phys 33(4):490–496
Zhu Q, Larson CR, Sjovold SG, Rosler DM, Keynan O, Wilson DR, Cripton PA, Oxland TR (2007) Biomechanical evaluation of the total facet arthroplasty system: 3-dimensional kinematics. Spine 32(1):55–62
Phillips FM, Tzermiadianos MN, Voronov LI, Havey RM, Carandang G, Renner SM, Rosler DM, Ochoa JA, Patwardhan AG (2009) Effect of the total facet arthroplasty system after complete laminectomy-facetectomy on the biomechanics of implanted and adjacent segments. Spine J 9(1):96–102
Goel VK, Mehta A, Jangra J, Faizan A, Kiapour A, Hoy RW, Fauth AR (2007) Anatomic facet replacement system (AFRS) restoration of lumbar segment mechanics to intact: a finite element study and in vitro cadaveric investigation. SAS J 1(1):46–54
Chiang MF, Teng JM, Huang CH, Cheng CK, Chen CS, Chang TK, Chao SH (2004) Finite element analysis of cage subsidence in cervical interbody fusion. J Med Biol Eng 24(4):201–208
Goel VK, Grauer JN, Patel TCh, Biyani A, Sairyo K, Vishnubhotla S, Matyas A, Cowgill I, Shaw M, Long R, Dick D, Panjabi MM, Serhan H (2005) Effects of charite´ artificial disc on the implanted and adjacent spinal segments mechanics using a hybrid testing protocol. Spine 30(24):2755–2764
Panjabi M, Henderson G, Abjornson C, Yue J (2007) Multidirectional testing of one- and two-level ProDisc-L versus simulated fusions. Spine 32(12):1311–1319
Yamamoto I, Panjabi MM, Crisco T, Oxland T (1989) Three-dimension movement of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine 14(11):1256–1260
Kiapour A, Ambati D, Hoy RW, Goel VK (2012) Effect of graded facetectomy on biomechanics of Dynesys dynamic stabilization system. Spine 37(10):E581–E589
Vaga S, Brayda-Bruno M, Perona F, Fornari M, Raimondi MT, Petruzzi M, Grava G, Costa F, Caiani EG, Lamartina C (2009) Molecular MR imaging for the evaluation of the effect of dynamic stabilization on lumbar intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J 18(Suppl 1):40–48
Kim H, Lim DH, Oh HJ, Lee KY, Lee SJ (2011) Effects of nonlinearity in the materials used for the semi-rigid pedicle screw systems on biomechanical behaviors of the lumbar spine after surgery. Biomed Mater 6(5):055005
Park WM, Kim K, Kim YH (2013) Effects of degenerated intervertebral discs on intersegmental rotations, intradiscal pressures, and facet joint forces of the whole lumbar spine. Comput Biol Med 43(9):1234–1240
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant (NSC 101-2314-B-075-001-MY3) from the National Science Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HM., Liu, CL., Pan, YN. et al. Biomechanical analysis and design of a dynamic spinal fixator using topology optimization: a finite element analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 52, 499–508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1154-x