Abstract
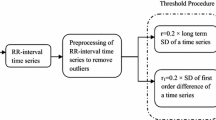
Multiscale entropy (MSE) and refined multiscale entropy (RMSE) techniques are being widely used to evaluate the complexity of a time series across multiple time scales ‘t’. Both these techniques, at certain time scales (sometimes for the entire time scales, in the case of RMSE), assign higher entropy to the HRV time series of certain pathologies than that of healthy subjects, and to their corresponding randomized surrogate time series. This incorrect assessment of signal complexity may be due to the fact that these techniques suffer from the following limitations: (1) threshold value ‘r’ is updated as a function of long-term standard deviation and hence unable to explore the short-term variability as well as substantial variability inherited in beat-to-beat fluctuations of long-term HRV time series. (2) In RMSE, entropy values assigned to different filtered scaled time series are the result of changes in variance, but do not completely reflect the real structural organization inherited in original time series. In the present work, we propose an improved RMSE (I-RMSE) technique by introducing a new procedure to set the threshold value by taking into account the period-to-period variability inherited in a signal and evaluated it on simulated and real HRV database. The proposed I-RMSE assigns higher entropy to the age-matched healthy subjects than that of patients suffering from atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, sudden cardiac death and diabetes mellitus, for the entire time scales. The results strongly support the reduction in complexity of HRV time series in female group, old-aged, patients suffering from severe cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular diseases, and in their corresponding surrogate time series.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Joseph KP, Kannathal N, Lim CM, Suri JS (2006) Heart rate variability: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput 44(12):1031–1051
Ahmed MU, Rehman N, Looney D, Rutkowaski TM, Mandic DP (2012) Dynamical complexity of human responses: a multivariate data-adaptive framework. Bull Pol Acad Sci Tech Sci 60(3):433–445
Aziz W, Schlindwein FS, Wailoo M, Biala T, Rocha FC (2011) Heart rate variability of normal and growth restricted children. Clin Auton Res 22:91–97
Bari V, Valencia JF, Vallverdu M, Girardengo G, Marchi A, Bassani T, Caminal P, Cerutti S, George AL Jr, Brink PA, Crotti L, Schwartz PJ, Porta A (2014) Multiscale complexity analysis of the cardiac control identifies asymptomatic and symptomatic patients in long QT syndrome type 1. PLoS ONE 9(4):1–10
Buchman TG (2002) The community of the self. Nature 420(6912):246–251
Chandra T, Yeates DB, Wong LB (2003) Heart rate variability analysis—current and future trends. A Report in Business Briefing: Global Healthcare, 1–5
Costa MD, Goldberger AL (2015) Generalized multiscale entropy analysis: application to quantifying the complex volatility of human heartbeat time series. Entropy 17(3):1197–1203
Costa M, Goldberger AL, Peng C-K (2005) Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Phys Rev E 71(2):021906-1–021906-17
Costa MD, Peng CK, Goldberger AL (2008) Multiscale analysis of heart rate dynamics: entropy and time irreversibility measures. Cardiovasc Eng 8(2):88–93
Escudero J, Acar E, Fernandez A, Bro R (2015) Multiscale entropy analysis of resting-state magnetoencephalogram with tensor factorisations in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Bull 119:134–10044
Esteban RG, Marques de Sa JP, Alvarez JLR, Perez OB (2008) Characterization of heart rate variability loss with aging and heart failure using sample entropy. Comput Cardiol 35:41–44
Ferrario M, Signorini MG, Magenes G, Cerutti S (2006) Comparison of entropy-based regularity estimators: application to the fetal heart rate signal for the identification of fetal distress. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(1):119–125
Fogedby HC (1992) On the phase space approach to complexity. J Stat Phys 69(1–2):411–425
Goldberger AL (1996) Non-linear dynamics for clinicians: chaos theory, fractals, and complexity at the bedside. Lancet 347:1312–1314
Goldberger JJ (1999) Sympathovagal balance: How should we measure it? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 276(4):H1273–H1280
Goldberger AL, Peng CK, Lipsitz LA (2002) What is physiological complexity and how does it change with aging and disease. Neurobiol Aging 23:23–26
Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2002) Fractal dynamics in physiology: alterations with disease and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(1):2466–2472
Grassberger P (1991) Information and complexity measures in dynamical systems. In: Atmanspacher H, Scheingraber H (eds) Information dynamics. Plenum Press, New York, pp 15–33
Hausdorff JM, Mitchell SL, Firtion R, Peng CK, Cudkowicz ME, Wei JY, Goldberger AL (1997) Altered fractal dynamics of gait: reduced stride interval correlations with aging and Huntington’s disease. J Appl Physiol 82:262–269
Hayano J, Yamasaki F, Sakata S, Okada A, Mukai S, Fujinami T (1997) Spectral characteristics of ventricular response to atrial fibrillation. Am J Physiol 273:H2811–H2816
Hornero R, Abasolo D, Escudero J, Gomez C (2009) Nonlinear analysis of electroencephalogram and magnetoencephalogram recordings in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Philos Trans R Soc A 367(1887):317–336
Hu M, Liang H (2012) Adaptive multiscale entropy analysis of multivariate neural data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(1):12–15
Humeau A, Mahe G, Blondeau FC, Rousseau D, Abraham P (2011) Multiscale analysis of microvascular blood flow: a multiscale entropy study of laser Doppler flowmetry time series. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(10):2970–2973
Kemper KJ, Hamilton C, Atkinson M (2007) Heart rate variability: Impact of in outlier identification and management strategies on common measures in three clinical populations. Pediatr Res 62(3):337–342
Kudat H, Akkaya V, Sozen AB, Salman S, Demirel S, Ozcan M, Atilgan D, Yilmaz MT, Guven O (2006) Heart rate variability in diabetes patients. J Int Med Res 34(3):291–296
Liang SF, Kuo CE, Hu YH, Pan YH, Wang YH (2012) Automatic stage scoring of single-channel sleep EEG by using multiscale entropy and autoregressive models. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 61(6):1649–1657
Lvanov PCh, Amaral LAN, Goldberger AL, Havlin S, Rosenblum MG, Struzik Z, Stanley HE (1999) Multifractality in human heartbeat dynamics. Nature 399:461–465
Malik M (1996) Heart rate variability-standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Eur Heart J 17(3):354–381
Malik M, Camm AJ (eds) (1995) Heart rate variability. Futura, Armonk
Oppenheim AV, Schafer RW (1975) Digital signal processing. Prentice-Hall, Engle-Wood Cliffs
Peng CK, Mietus J, Hausdorff JM, Havlin S, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL (1993) Long-range anti-correlations and non-Gaussian behavior of the heartbeat. Phys Rev Lett 70:1343–1346
Peng CK, Hausdorff JM, Goldberger AL (2000) Fractal mechanisms in neural control: human heartbeat and gait dynamics in health and disease. In: Walleczek J (ed) Nonlinear dynamics, self-organization, and biomedicine. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Available at www.physionet.org/tutorials/fmnc/
Pincus SM, Goldberger AL (1994) Physiological time-series analysis: What does regularity quantify? AJP Heart Circ Physiol 266(4):H1643–H1656
Ramaekers D, Ector H, Aubert AE, Rubens A, de Werf FV (1998) Heart rate variability and heart rate in healthy volunteers; Is the female autonomic nervous system cardioprotective ? Eur Heart J 19(9):1334–1341
Rangayyan RM (2002) Biomedical signal analysis: a case study approach. IEEE Press, India, pp 317–321
Richman JS, Moorman JR (2000) Physiological time series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278(6):H2039–H2049
Sunkaria RK, Saxena SC, Kumar V, Singhal AM (2010) Wavelet based R-peak detection for HRV studies. J Med Eng Technol 34(2):108–115
Trunkvalterova Z, Javorka M, Tonhajzerova I, Javorkova J, Lazarova Z, Javorka K, Baumert M (2008) Reduced short-term complexity of heart rate and blood pressure dynamics in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1: multiscale entropy analysis. Physiol Meas 29(7):817–828
Umetani K, Singer DH, McCraty R, Atkinson M (1998) Twenty-four hour time domain heart rate variability and heart rate: relations to age and gender over nine decades. J Am Coll Cardiol 31(3):593–601
Valencia JF, Porta A, Vallverdu M, Claria F, Baranowski R, Baranowska EO, Caminal P (2009) Refined multiscale entropy: application to 24-h holter recordings of heart period variability in healthy and aortic stenosis subjects. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(9):2202–2213
Wessel N, Schirdewan A, Kurths J (2003) Intermittently decreased beat-to-beat variability in congestive heart failure. Phys Rev Lett 91(11):119801-1–119801-2
Wu SD, Wu CW, Lin SG, Wang CC, Lee KY (2013) Time series analysis using composite multiscale entropy. Entropy 15(3):1069–1084
Wu SD, Wu CW, Lin SG, Lee KY, Peng CK (2014) Analysis of complex time series using refined composite multiscale entropy. Phys Lett A 378:1369–1374
Xu Y, Zhao L (2013) Filter based multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiological time series. Phys Rev E 88(2):022716-1–022716-13
http://www.physionet.org website
Yoo CS, Yi SH (2006) On the physiological validity and the effects of detrending in the multiscale entropy analysis of heart rate variability. J Korean Phys Soc 48(4):670–676
Zeng W, Glass L (1996) Statistical properties of heart beat intervals during atrial fibrillation. Phys Rev E 54:1779–1784
Zhang YC (1991) Complexity and 1/f noise. A phase space approach. J Phys I Fr EDP Sci 1(7):971–977
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering and administration of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar (Punjab), for providing every kind of technical and administrative help for the present work carried out in its ‘Medical Imaging and Computational Modeling of Physiological Systems Research Laboratory.’ The authors also acknowledge all help provided by ‘Biomedical Signal Processing and Telemedicine Laboratory. The Authors are highly thankful to the unknown reviewers for their critical and valuable suggestions towards improvement of the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marwaha, P., Sunkaria, R.K. Exploring total cardiac variability in healthy and pathophysiological subjects using improved refined multiscale entropy. Med Biol Eng Comput 55, 191–205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1476-y