Abstract
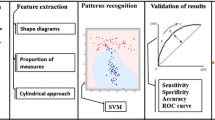
Lung cancer is the major cause of death among patients with cancer worldwide. This work is intended to develop a methodology for the diagnosis of lung nodules using images from the Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC–IDRI). The proposed methodology uses image processing and pattern recognition techniques. To differentiate the patterns of malignant and benign forms, we used a Minkowski functional, distance measures, representation of the vector of points measures, triangulation measures, and Feret diameters. Finally, we applied a genetic algorithm to select the best model and a support vector machine for classification. In the test stage, we applied the proposed methodology to 1405 (394 malignant and 1011 benign) nodules from the LIDC–IDRI database. The proposed methodology shows promising results for diagnosis of malignant and benign forms, achieving accuracy of 93.19 %, sensitivity of 92.75 %, and specificity of 93.33 %. The results are promising and demonstrate a good rate of correct detections using the shape features. Because early detection allows faster therapeutic intervention, and thus a more favorable prognosis for the patient, herein we propose a methodology that contributes to the area.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alajlan N, Kamel MS, Freeman G (2006) Multi-object image retrieval based on shape and topology. Image Commun 1(10):904–918. doi:10.1016/j.image.2006.09.002
Alajlan N, Rube IE, Kamel MS, Freeman G (2007) Shape retrieval using triangle-area representation and dynamic space warping. Pattern Recognit 1(7):1911–1920. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2006.12.005
Armato SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, Zhao B, Aberle DR, Henschke CI, Hoffman EA, Kazerooni EA, MacMahon H, Van Beeke EJR, Yankelevitz D, Biancardi AM, Bland PH, Brown MS, Engelmann RM, Laderach GE, Max D, Pais RC, Qing DPY, Roberts RY, Smith AR, Starkey A, Batrah P, Caligiuri P, Farooqi A, Gladish GW, Jude CM, Munden RF, Petkovska I, Quint LE, Schwartz LH, Sundaram B, Dodd LE, Fenimore C, Gur D, Petrick N, Freymann J, Kirby J, Hughes B, Casteele AV, Gupte S, Sallamm M, Heath MD, Kuhn MH, Dharaiya E, Burns R, Fryd DS, Salganicoff M, Anand V, Shreter U, Vastagh S, Croft BY (2011) The lung image database consortium (lidc) and image database resource initiative (idri): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans. Med Phys 1(2):915–31. http://www.biomedsearch.com/nih/Lung-Image-Database-Consortium-LIDC/21452728.html
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2013) LIBSVM—a library for support vector machines. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/
Chen W, Li Z, Bai L, Lin Y (2011) Nf-kappab in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and therapy target. Front Biosci (Landmark edition) 1:1172–1185. doi:10.2741/3782
Dandil E, Cakiroglu M, Eksi Z, Ozkan M, Kurt O, Canan A (2014) Artificial neural network-based classification system for lung nodules on computed tomography scans. In: 2014 6th International conference of soft computing and pattern recognition (SoCPaR), p 382–386. doi:10.1109/SOCPAR.2014.7008037
David L, Kien K, Marie FD (2011) Computation of minkowski measures on 2d and 3d binary images. Image Anal Stereol 1(2):83–92. http://www.ias-iss.org/ojs/IAS/article/view/811
de Carvalho Filho AO, de Sampaio WB, Silva AC, de Paiva AC, Nunes RA, Gattass M (2014) Automatic detection of solitary lung nodules using quality threshold clustering, genetic algorithm and diversity index. Artif Intell Med 1(3):165–177. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2013.11.002
de Valk J, Eijkman E (1984) Analysis of eye fixations during the diagnostic interpretation of chest radiographs. Med Biol Eng Comput 1(4):353–360. doi:10.1007/BF02442106
Duda RO, Hart PE (1973) Pattern Classif Scene Anal. Wiley-Interscience Publication, New York
El-Baz A, Nitzken M, Khalifa F, Elnakib A, Gimelfarb G, Falk R, El-Ghar M (2011) 3D shape analysis for early diagnosis of malignant lung nodules. In: Szekely G, Hahn H (eds) Information processing in medical imaging, Lecture notes in computer science, vol 6801, p 772–783. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-22092-0-63
Elizabeth D, Nehemiah H, Retmin Raj C, Kannan A (2012) Computer-aided diagnosis of lung cancer based on analysis of the significant slice of chest computed tomography image. Image Process IET 1(6):697–705. doi:10.1049/iet-ipr.2010.0521
Fujimoto J, Wistuba II (2014) Current concepts on the molecular pathology of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol 1(4):306–313. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2014.06.008 (Lung Carcinoma: Beyond The WHO Classification)
Galloway MM (1975) Texture analysis using gray level run lengths. Comput Graphics Image Process 1(2):172–179. doi:10.1016/S0146-664X(75)80008-6
Gould M, Maclean C, Kuschner W, Rydzak C, Owens D (2001) Accuracy of positron emission tomography for diagnosis of pulmonary nodules and mass lesions: a meta-analysis. JAMA 285(7):914–924. doi:10.1001/jama.285.7.914
Hadwiger H (1957) Vorlesungen über Inhalt, Oberfläche und Isoperimetrie. Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften. Springer. https://books.google.com.br/books?id=-BWoAAAAIAAJ
Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE, Tatham RL (2006) Multivariate data analysis, vol 6. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246(3):697–722. doi:10.1148/radiol.2462070712
Jabon SA, Raicu DS, Furst JD (2009) Content-based versus semantic-based retrieval: an lidc case study. Proc SPIE 7263:72,631L–72,631L–8. doi:10.1117/12.812877
Krewer H, Geiger B, Hall L, Goldgof D, Gu Y, Tockman M, Gillies, R (2013) Effect of texture features in computer aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules in low-dose computed tomography. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC), pp 3887–3891. doi:10.1109/SMC.2013.663
Kumar S, Ramesh J, Vanathi P, Gunavathi K (2011) Robust and automated lung nodule diagnosis from ct images based on fuzzy systems. In: 2011 International conference on process automation, control and computing (PACC), pp 1–6. doi:10.1109/PACC.2011.5979050
Lederlin M, Revel MP, Khalil A, Ferretti G, Milleron B, Laurent F (2013) Management strategy of pulmonary nodule in 2013. Diagn Int Imaging 1(11):1081–1094. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2013.05.007
Leef 3rd J, Klein J (2002) The solitary pulmonary nodule. Radiol Clin N Am 1(1):123–143, ix. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp012290
Mecke K, Stoyan D (2002) Morphology of condensed matter: physics and geometry of spatially complex systems. Lecture notes in physics. Springer. https://books.google.com.br/books?id=0BeJY4ZwndsC
Mecke K, Buchert T, Wagner H (1993) Robust morphological measures for large-scale structure in the Universe. Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik Garching, München: MPA. Max-Planck-Inst. für Astrophysik. https://books.google.com.br/books?id=jLzgGwAACAAJ
Michal C, Elke T, Abhir B, David P (2008) Integral geometry descriptors for characterizing emphysema and lung fibrosis in HRCT images. First Int Workshop Pulm Image Anal 1:155–164
Miyake N, Kim H, Itai Y, Tan JK, Ishikawa S, Katsuragawa S (2009) Automatic detection of lung nodules in temporal subtraction image by use of shape and density features. In: 2009 Fourth international conference on innovative computing, information and control (ICICIC), pP 1288–1292. doi:10.1109/ICICIC.2009.118
Nascimento LB, de Paiva AC, Silva AC (2012) Lung nodules classification in ct images using shannon and simpson diversity indices and svm. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on machine learning and data mining in pattern recognition, 12. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 454–466
Orozco H, Osiris Vergara Villegas O, Maynez L, Sanchez V, De Jesus Ochoa Dominguez H (2012) Lung nodule classification in frequency domain using support vector machines. In: 2012 11th International conference on information science, signal processing and their applications (ISSPA), pp 870–875. doi:10.1109/ISSPA.2012.6310676
Parveen SS, Kavitha C (2014) Article: classification of lung cancer nodules using svm kernels. Int J Comput Appl 1(25):25–28 (full text available)
Patil SS, Godoy MC, Sorensen JI, Marom EM (2014) Lung cancer imaging. Semin Diagn Pathol 1(4):293–305. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2014.06.007 (Lung Carcinoma: Beyond The WHO Classification)
Roth K, Boike J, Vogel HJ (2005) Quantifying permafrost patterns using minkowski densities. Permafr Periglac Process 1(3):277–290. doi:10.1002/ppp.531
Santaló L (2004) Integral geometry and geometric probability. Cambridge Mathematical Library. Beijing World Publishing Corporation (BJWPC). https://books.google.com.br/books?id=xq1iiumncV4C
Schölkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with kernels: support vector machines, optimization, and beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge (Regularization)
Seemann MD, Seemann O, Luboldt W, Bonél H, Sittek H, Dienemann H, Staebler A (2000) Differentiation of malignant from benign solitary pulmonary lesions using chest radiography, spiral CT and HRCT. Lung Cancer 1(2):105–124. doi:10.1016/S0169-5002(00)00104-5
Sone S, Takashima S, Li F, Yang Z, Honda T, Maruyama Y, Hasegawa M, Yamanda T, Kubo K, Hanamura K, Asakura K (1998) Mass screening for lung cancer with mobile spiral computed tomography scanner. Lancet 351(9111):1242–1245. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)08229-9
Stewart (2014) World Cancer Report 2014. IARC Nonserial Publication, New York
Umbaugh SE, Snyder J, Fedorovskaya E (2011) Digital image processing and analysis: human and computer vision applications with cviptools, second edition. J Electron Imaging 1(3):039, 901–039, 901–903. doi:10.1117/1.3628179
van Erkel A, Pattynama P (1998) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis: basic principles and applications in radiology. Eur J Radiol 1(2):88–94
Way TW, Sahiner B, Chan HP, Hadjiiski L, Cascade PN, Chughtai A, Bogot N, Kazerooni E (2009) Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on ct scans: improvement of classification performance with nodule surface features. Med Phys 1(7):3086–3098. doi:10.1118/1.3140589
Yang X, Shen X, Long J, Chen H (2012) An improved median-based otsu image thresholding algorithm. AASRI Proc 1:468–473. doi:10.1016/j.aasri.2012.11.074 (conference on modelling, identification and control)
Ye X, Lin X, Dehmeshki J, Slabaugh G, Beddoe G (2009) Shape-based computer-aided detection of lung nodules in thoracic CT images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1(7):1810–1820. doi:10.1109/TBME.2009.2017027
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the Foundation for the Protection of Research and Scientific and Technological Development of the State of Maranhão (FAPEMA) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Carvalho Filho, A.O., Silva, A.C., de Paiva, A.C. et al. Computer-aided diagnosis system for lung nodules based on computed tomography using shape analysis, a genetic algorithm, and SVM. Med Biol Eng Comput 55, 1129–1146 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1577-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1577-7