Abstract
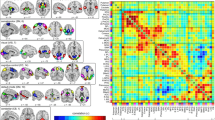
Global field synchronization (GFS) quantifies the synchronization level of brain oscillations. The GFS method has been introduced to measure functional synchronization of EEG data in the frequency domain. GFS also detects phase interactions between EEG signals acquired from all of the electrodes. If a considerable amount of local brain neurons has the same phase, these neurons appear to interact with each other. EEG data were received from 17 obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) patients and 17 healthy controls (HC). OCD effects on local and large-scale brain circuits were studied. Analysis of the GFS results showed significantly decreased values in the delta and full frequency bands. This research suggests that OCD causes synchronization disconnection in both the frontal and large-scale regions. This may be related to motivational, emotional and cognitive dysfunctions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch A, Cooperman A (2015) The cognitive neuropsychology of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a critical review. J Obsessive-Compulsive Relat Disord 5:24–36
Anderer P, Gruber G, Saletu B, Klösch G, Zeitlhofer J, Pascual-Marqui RD (2002) Non-invasive electrophysiological neuroimaging of sleep. Int Congr Ser 1232:795–800
Aydin S, Arica N, Ergul E, Tan O (2015) Classification of obsessive compulsive disorder by EEG complexity and hemispheric dependency measurements. Int J Neural Syst 25:1550010
Babiloni C, Ferri R, Binetti G, Cassarino A, Dal Forno G, Ercolani M, Ferreri F, Frisoni GB, Lanuzza B, Miniussi C (2006) Fronto-parietal coupling of brain rhythms in mild cognitive impairment: a multicentric EEG study. Brain Res Bull 69:63–73
Babiloni C, Ferri R, Binetti G, Vecchio F, Frisoni GB, Lanuzza B, Miniussi C, Nobili F, Rodriguez G, Rundo F (2009) Directionality of EEG synchronization in Alzheimer's disease subjects. Neurobiol Aging 30:93–102
Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA (1988) An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 56:893
Brown P (2007) Abnormal oscillatory synchronisation in the motor system leads to impaired movement. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:656–664
Bucci P, Mucci A, Volpe U, Merlotti E, Galderisi S, Maj M (2004) Executive hypercontrol in obsessive-compulsive disorder: electrophysiological and neuropsychological indices. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1340–1348
Buschman TJ, Miller EK (2007) Top-down versus bottom-up control of attention in the prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices. Science 315:1860–1862
Cavedini P, Ferri S, Scarone S, Bellodi L (1998) Frontal lobe dysfunction in obsessive-compulsive disorder and major depression: a clinical-neuropsychological study. Psychiatry Res 78:21–28
Cui D, Liu X, Wan Y, Li X (2010) Estimation of genuine and random synchronization in multivariate neural series. Neural Netw 23:698–704
Dierks T, Strik WK, Maurer K (1995) Electrical brain activity in schizophrenia described by equivalent dipoles of FFT-data. Schizophr Res 14:145–154
Engel AK, Moll CK, Fried I, Ojemann GA (2005) Invasive recordings from the human brain: clinical insights and beyond. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:35–47
Fries P, Reynolds JH, Rorie AE, Desimone R (2001) Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291:1560–1563
Friston KJ, Frith CD (1995) Schizophrenia: a disconnection syndrome. Clin Neurosci 3:89–97
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Delgado P, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1989) The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale: II. Validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:1012–1016
Gray C, König P, Engel A, Singer W (1989) Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature 338:334–337
Jeong J, Gore JC, Peterson BS (2001) Mutual information analysis of the EEG in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 112:827–835
Klimesch W (1997) EEG-alpha rhythms and memory processes. Int J Psychophysiol 26:319–340
Klimesch W (1999) EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: a review and analysis. Brain Res Rev 29:169–195
Knyazev GG (2007) Motivation, emotion, and their inhibitory control mirrored in brain oscillations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:377–395
Knyazev GG (2012) EEG delta oscillations as a correlate of basic homeostatic and motivational processes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:677–695
Knyazeva M, Jalili M, Brioschi A, Bourquin I, Fornari E, Hasler M, Meuli R, Maeder P, Ghika J (2010) Topography of EEG multivariate phase synchronization in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 31:1132–1144. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.07.019
Koenig T, Lehmann D, Saito N, Kuginuki T, Kinoshita T (2001) Decreased functional connectivity of EEG theta-frequency activity in first-episode, neuroleptic-naive patients with schizophrenia:preliminary results. Schizophr Res 50:55–60
Koenig T, Prichep L, Dierks T, Hubl D, Wahlund LO, John ER, Jelic V (2005) Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 26:165–171. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.03.008
Koenig T, van Swam C, Dierks T, Hubl D (2012) Is gamma band EEG synchronization reduced during auditory driving in schizophrenia patients with auditory verbal hallucinations? Schizophr Res 141:266–270. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2012.07.016
Kopp F, Schröger E, Lipka S (2006) Synchronized brain activity during rehearsal and short-term memory disruption by irrelevant speech is affected by recall mode. Int J Psychophysiol 61:188–203
Kopřivová J, Congedo M, Horáček J, Praško J, Raszka M, Brunovský M, Kohútová B, Höschl C (2011) EEG source analysis in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 122:1735–1743
Kubicki S, Herrmann W, Fichte K, Freund G (1979) Reflections on the topics: EEG frequency bands and regulation of vigilance. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol 12:237–245
Lee K-H, Williams L, Haig A, Gordon E (2003) “Gamma (40 Hz) phase synchronicity” and symptom dimensions in schizophrenia. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 8:57–71
Lee SH, Park YM, Kim DW, Im CH (2010) Global synchronization index as a biological correlate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Res 66:333–339. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2009.12.004
Lehmann D, Faber PL, Gianotti LR, Kochi K, Pascual-Marqui RD (2006) Coherence and phase locking in the scalp EEG and between LORETA model sources, and microstates as putative mechanisms of brain temporo-spatial functional organization. J Physiol Paris 99:29–36
Lehmann D, Michel CM (1990) Intracerebral dipole source localization for FFT power maps. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophystol 76:271–276
Leocani L, Locatelli M, Bellodi L, Fornara C, Hénin M, Magnani G, Mennea S, Comi G (2001) Abnormal pattern of cortical activation associated with voluntary movement in obsessive-compulsive disorder: an EEG study. Am J Psychiatr 158:140–142
Leung LS, Yim CC (1993) Rhythmic delta-frequency activities in the nucleus accumbens of anesthetized and freely moving rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 71:311–320
Li Z, Ouyang G, Li D, Li X (2011) Characterization of the causality between spike trains with permutation conditional mutual information. Phys Rev E 84:021929
Liddle PF (1996) Functional imaging—schizophrenia. Br Med Bull 52:486–494
Ma CC, Liu AJ, Liu AH, Zhou XY, Zhou SN (2013) Electroencephalogram global field synchronization analysis: a new method for assessing the progress of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin EEG Neurosci 45(2):98–103
Menzies L, Chamberlain SR, Laird AR, Thelen SM, Sahakian BJ, Bullmore ET (2008) Integrating evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychological studies of obsessive-compulsive disorder: the orbitofronto-striatal model revisited. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:525–549
Merker B (2013) Cortical gamma oscillations: the functional key is activation, not cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:401–417
Millon T, Davis RO (1996) Disorders of personality: DSM-IV and beyond, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 505–510
Mormann F (2003) Synchronization phenomena in the human epileptic brain. Doctoral dissertation, PhD thesis, Dissertation in Physics, University of Bonn, Germany
Murphy M, Riedner BA, Huber R, Massimini M, Ferrarelli F, Tononi G (2009) Source modeling sleep slow waves. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:1608–1613
Nolte G, Bai O, Wheaton L, Mari Z, Vorbach S, Hallett M (2004) Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clin Neurophysiol 115:2292–2307
Olley A, Malhi G, Sachdev P (2007) Memory and executive functioning in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a selective review. J Affect Disord 104:15–23
Park JY, Lee J, Park H-J, Kim J-J, Namkoong K, Kim SJ (2012) Alpha amplitude and phase locking in obsessive-compulsive disorder during working memory. Int J Psychophysiol 83:1–7
Park YM, Che HJ, Im CH, Jung HT, Bae SM, Lee SH (2008) Decreased EEG synchronization and its correlation with symptom severity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Res 62:112–117. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2008.06.009
Pogarell O, Juckel G, Mavrogiorgou P, Mulert C, Folkerts M, Hauke W, Zaudig M, Möller H-J, Hegerl U (2006) Symptom-specific EEG power correlations in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Psychophysiol 62:87–92
Purcell R, Maruff P, Kyrios M, Pantelis C (1998) Cognitive deficits in obsessive-compulsive disorder on tests of frontal-striatal function. Biol Psychiatry 43:348–357
Sauseng P, Klimesch W (2008) What does phase information of oscillatory brain activity tell us about cognitive processes? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:1001–1013
Saxena S, Rauch SL (2000) Functional neuroimaging and the neuroanatomy of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin N Am 23:563–586
Summerfield C, Mangels JA (2005) Coherent theta-band EEG activity predicts item-context binding during encoding. NeuroImage 24:692–703
Velikova S, Locatelli M, Insacco C, Smeraldi E, Comi G, Leocani L (2010) Dysfunctional brain circuitry in obsessive-compulsive disorder: source and coherence analysis of EEG rhythms. NeuroImage 49:977–983
Von Stein A, Sarnthein J (2000) Different frequencies for different scales of cortical integration: from local gamma to long range alpha/theta synchronization. Int J Psychophysiol 38:301–313
Wackermann J (1999) Towards a quantitative characterisation of functional states of the brain: from the non-linear methodology to the global linear description. Int J Psychophysiol 34:65–80
Wen D, Bian Z, Li Q, Wang L, Lu C, Li X Resting-state EEG Coupling analysis of amnestic mild cognitive impairment with type 2 diabetes mellitus by using permutation conditional mutual information. Clin Neurophysiol. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2015.05.016
Williams JB (1988) A structured interview guide for the Hamilton Depression Rating scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:742–747
Worden MS, Foxe JJ, Wang N, Simpson GV (2000) Anticipatory biasing of visuospatial attention indexed by retinotopically specific-band electroencephalography increases over occipital cortex. J Neurosci 20:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özçoban, M.A., Tan, O., Aydin, S. et al. Decreased global field synchronization of multichannel frontal EEG measurements in obsessive-compulsive disorders. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 331–338 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1689-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1689-8